This is an automatically translated article.
CSF is the fluid around the brain and spinal cord, has an important role in taking necessary supplies from the blood and removing waste products from brain cells, protecting brain cells.1. What is cerebrospinal fluid?
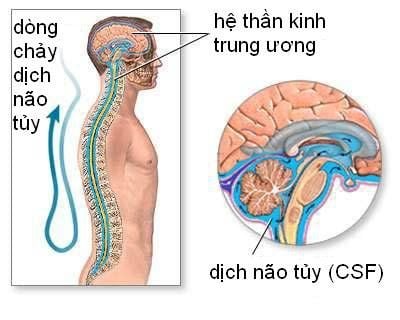
The cerebrospinal fluid is a special, colorless extracellular fluid that travels around the brain and spinal cord and protects the brain and spinal cord. Normally, in adults, the amount of cerebrospinal fluid is about 140ml and the cerebrospinal fluid renews 3 to 4 times in 24 hours. The function of cerebrospinal fluid is mainly to protect the brain and spinal cord against mechanical trauma and participate in the nutritional and metabolic tasks of the central nervous system.2. Origin of cerebrospinal fluid
The cerebrospinal fluid is produced from the choroidal plexus filled in the lateral ventricles, through the foramen of Monro into the third ventricle, through the foramen of Luschka into the subarachnoid space of the brain, and through the foramen of Magendie to the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord. CSF is constantly renewed, every 2 hours about 20ml of CSF is produced and reabsorbed back into the vein. The biological components of the cerebrospinal fluid are regularly regulated by the interconnected regions of the blood-brain, blood-CSF and CSF-blood barrier systems.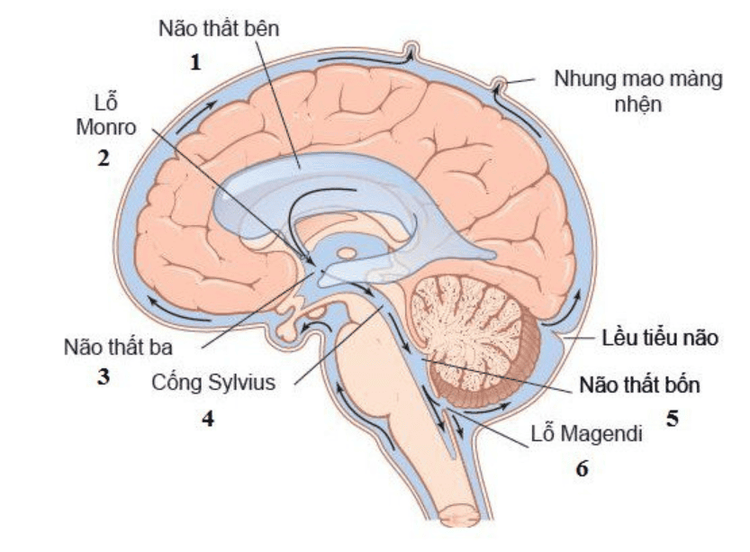
Hệ thống dịch não tủy
3. Function of cerebrospinal fluid
3.1 Nutritional and metabolic functions Cerebrospinal fluid provides necessary nutrients, metabolizes the nervous system, and at the same time removes wastes generated in the process of metabolism, performing secondary metabolism with the organization. central nervous function. Specifically:
In the early fetal stage: CSF is responsible for nourishing the fetus, but this function will gradually disappear as the fetus grows. CSF has the ability to smooth and buffer between the brain and spinal cord with the dura mater and outer hard bones (cranium, spine) 3.2 Protective function CSF has the function of protecting the central nervous system before peripheral trauma through 2 mechanisms:
CSF smooths and acts as a buffer between the brain and spinal cord with hard outer bone, protecting the brain and spinal cord from being damaged by mechanical trauma . In addition, this fluid helps prevent toxins from entering the nervous system. In terms of immunity against harmful agents such as viruses, bacteria, parasites... 3.3 Transport function Cerebrospinal fluid is responsible for transporting certain substances necessary for the brain and body.
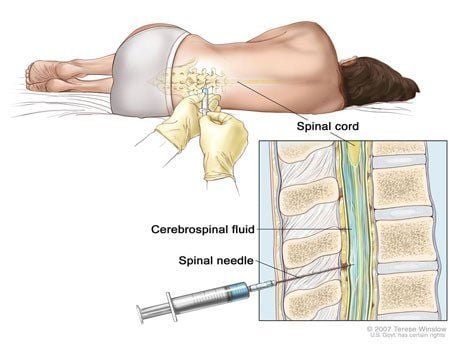
4. Cerebrospinal fluid test helps diagnose disease
When the central nervous system is damaged, there is disease in the brain and meninges, the cerebrospinal fluid will also have corresponding changes. Therefore, the examination of cerebrospinal fluid will most clearly reflect the condition of the brain and meninges thanks to their close relationship. Cerebrospinal fluid test is a test performed with the purpose of checking the status of cerebrospinal fluid, the components in the cerebrospinal fluid, and measuring the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid. From there, helping doctors make an accurate diagnosis of brain diseases, treatment and prognosis of diseases related to the central nervous system such as myelitis, meningitis, brain cancer, etc. Changes in the properties and composition of the cerebrospinal fluid can diagnose some diseases of the brain and meninges. Therefore, the test of cerebrospinal fluid helps diagnose diseases such as purulent meningitis, viral meningitis, cerebral hemorrhage, tuberculous meningitis, ...

Xét nghiệm dịch não tủy cần được thực hiện tại cơ sở y tế uy tín
5. When is the cerebrospinal fluid test done?
5.1 Purpose If a person has high levels of a substance called immunoglobulin, which the body uses to fight disease or other things involving nerve cells, this could be a symptom of multiple sclerosis hard. If your doctor suspects you think you have Alzheimer's disease or another type of dementia, certain proteins associated with the disease may be present in the cerebrospinal fluid. In cases where the cerebrospinal fluid is discolored, it is more likely to be a sign of hemorrhagic disease (bleeding in the brain) or stroke. 5.2 Indications Suspected brain injury such as cerebral hemorrhage, meningitis,... Aspiration to measure cerebrospinal fluid pressure, cerebrospinal fluid circulation; Cerebrospinal fluid test (biochemistry, cells, microorganisms, pH, quantification of enzymes, neurotransmitters....) when brain or spinal cord injury is suspected. Indications for therapeutic purposes: Delivering the drug into the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord; Local anesthetics for surgical purposes; Antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, corticosteroids... to treat diseases of the central nervous system or radiculopathy.
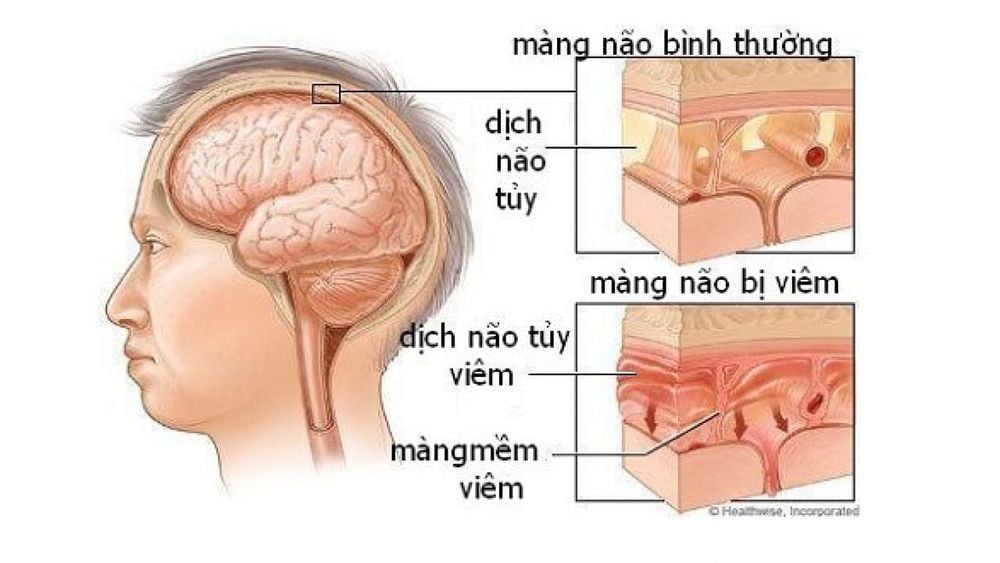
Bệnh nhân viêm màng não
5.3 Contraindications Increased pressure in the skull Brain tumor Severe brain edema Neck spinal cord injury Infection in the needle puncture area Blood clotting disorder Customers can directly go to Vinmec health system nationwide for examination or Contact the hotline here for support.
SEE ALSO:
Find out the cerebrospinal fluid test to find the cause of the headache Spinal puncture diagnose meningitis Is lumbar puncture painful and harmful?