This is an automatically translated article.
Antibiotics have many active ingredients, belonging to many different groups. Antibiotics are prepared in many forms such as powder for injection, solution for injection, tablets, capsules... However, in fact, not all antibiotics have the form of ointment for skin application. So what are the precautions when using antibiotic ointment?
1. By what mechanism do skin ointments work?
Ointment for the skin is the most important and popular form of topical medicine today. The main excipients of topical ointments are lipids (vaseline, lanolin).
Topical ointments increase the absorption of the skin, so the active ingredients will penetrate deeper than other topical forms of medicine. Although the ointment has the ability to soften the skin, it interferes with the secretion of the skin, causing skin congestion, limiting sweating, and causing congestion. In addition, topical ointments can affect skin circulation, causing vasodilation or vasoconstriction. Depending on the excipients, the ointment will penetrate more or less into the skin, shallowly or deeply.
2.Indication of antibiotic ointment applied to the skin
Currently, although there are hundreds of different antibiotic active ingredients have been prepared and put into clinical treatment. However, there are very few antibiotic active ingredients that can be used topically and are formulated into antibiotic ointments.
Antibacterial ointments with active ingredients are antibiotics Erythromycin and Clindamycin are the 2 most commonly used ointments in the treatment of pustular acne and folliculitis. Antibiotic ointments with active ingredients are mupirocin, polymyxin, bacitracin and neomycin are topical ointments commonly used in the treatment of skin infections such as impetigo... In which, Bacitracin is a common antibiotic to treat In infections, the drug helps kill bacteria or bacteriostatic by inhibiting the synthesis of cell envelope, thereby damaging the bacterial plasma membrane. Previously, the drug was used for injection, but it was highly toxic to the kidneys, so now it is only used topically. In addition, antibiotic ointment has a very good effect in preventing infections in skin wounds, treating some eye diseases such as: chalazion, acute and chronic conjunctivitis (pink eye) , corneal ulcer, keratitis, lacrimal sac...
To cure inflammatory skin diseases, apply antibiotic ointment to the infected surface 1-5 times/day as directed by your doctor. To treat eye infections, apply a thin strip (about 1cm) of antibiotic eye ointment to the conjunctiva, as often as prescribed by your doctor.
MORE: Learn about Tetracycline Ointment
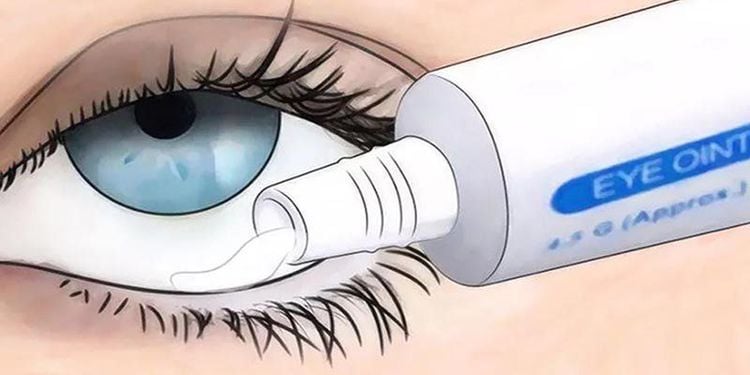
Thuốc mỡ Tetracyclin điều trị một số bệnh về mắt
3.Side effects of topical antibiotic ointment
Contact dermatitis is a common side effect of topical antibiotic ointments containing the active ingredients polymyxin, bacitracin and neomycin. Therefore, it is best to avoid long-term use of these drugs if there is an alternative medicine. that is more appropriate.
Some cases of severe allergic reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Lyell's syndrome that can be attributed to topical antibiotic ointments have been reported.
4.Note when using topical antibiotic ointment
To avoid side effects, patients using topical antibiotic ointment must be suitable for the pathology, stage and severity of the disease, the affected skin area, sometimes it is also necessary to consider age and gender. . Do not arbitrarily use antibiotic ointment without a doctor's prescription.
Not only effects on the skin, topical ointments can also be absorbed through the skin into the bloodstream and have systemic effects. Thus, topical ointments still have both local and systemic effects, the drug should be used with extreme caution, especially when applied to children or applied to a large area of skin.
Besides, patients also do not use ointment form on the skin on open lesions that are in the acute stage or are bleeding. Topical ointments are commonly used for chronic stage lesions. When applied to the skin with open wounds need to be very careful, because the antibiotic active ingredients in antibacterial ointments can be absorbed through the open wound and cause side effects.
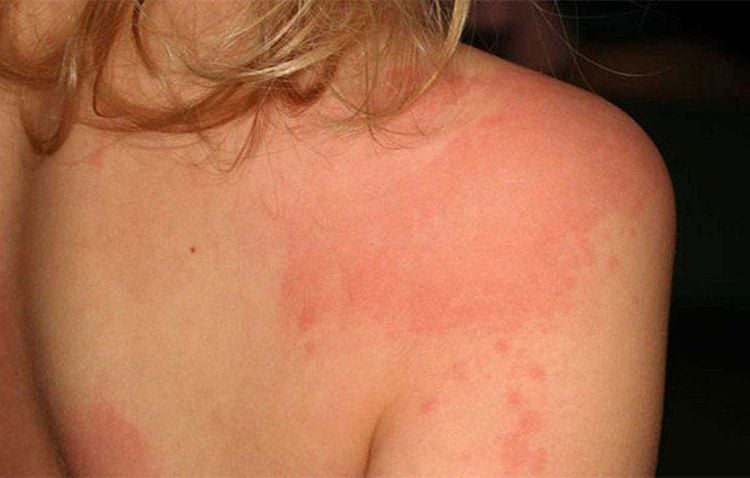
Người bệnh cũng không nên tự ý sử dụng thuốc mỡ kháng sinh vì có một số thuốc có thể gây phát ban da
Pregnant women should be clearly advised by their doctor about the benefits and risks before using topical antibiotic ointments. Because some drugs can cause skin rashes or slow allergic reactions. Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in the drug may result in a shock-like state after topical application of the drug in patients.
In addition, patients also do not arbitrarily use antibiotic ointment too often than indicated, use it for a longer time or use it on a larger area of skin. Usually, a course of medication lasts from about 10-15 days, patients need to adhere to the medication instructions and monitor their disease status, periodically re-examine their health or schedule a doctor's appointment for assessment and treatment. Adjust medication if necessary.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.