This is an automatically translated article.
Calcium is important in maintaining the normal functioning of nerve cells, muscles and bones. If the amount of calcium in the blood is deficient, the body will automatically take calcium from the bone system, leading to weak bones.1. Calcium salt
Calcium salts are easily recognized in the hematoxylin and eosin fractions by their homogenous basophilia. Various forms of calcium salts are widely used as primary therapy to bind phosphorus in the diet and maintain normal calcium levels in children.
The most effective calcium salt is as a phosphate binder if taken immediately before, during or immediately after a meal. The prescribed dose of calcium salt is to ensure that it is proportional to the estimated phosphorus intake at each meal. Because of its better solubility than calcium carbonate, calcium acetate has been shown to associate a larger proportion of dietary phosphorus with the same amount of calcium absorbed.
According to the Food and Nutrition Board, the acceptable limit for oral calcium in children 1 to 19 years of age is about 2500 mg per day. Therefore, the safety margin between the desired effects and the maximum limit is relatively narrow. An upper limit of dietary calcium in infants has not been established. Studies have shown that about 1g of elemental calcium can reduce serum phonemic concentrations by 48% when used appropriately.
Dosages of calcium vary widely and are adjusted according to serum calcium and phosphorus concentrations and depending on the age of the patient. Complications associated with the use of calcium salts include hypercalcemia and soft tissue calcification and the frequency of these problems increases with concomitant use of vitamin D.

Muối canxi
2. Types of calcium salts
2.1 Calcium glucoheptonate Calcium gluceptate supplements are intended for people who do not get enough calcium in their regular diet or who have more calcium needs. They are used to prevent or treat certain conditions that can cause hypocalcemia (not enough calcium in the blood). The body needs calcium to make strong bones. Calcium is also needed for the heart, muscles, and nervous system to function properly.
2.2 Calcium glubionate (or calcium glubionate) This is a mineral supplement to prevent or treat low blood calcium levels in people who are not getting enough calcium from their diet.
2.3 Calcium gluconate Calcium gluconate is used as a mineral supplement and medicine when there is not enough calcium in the diet. This supplement may be taken to treat or prevent osteoporosis or rickets, a consequence of hypocalcemia. It is recommended by injection into a muscle, and can also be taken orally.
Calcium Gluconate Injection is a sterile, supersaturated solution of calcium gluconate for intravenous administration only. Each mL contains: Calcium gluconate 94 mg; calcium saccharate (tetrahydrate) 4.5 mg; water for injection q.s. Hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may have been added to adjust the pH (6.0 to 8.2). Calcium saccharate provides 6% of total calcium and stabilizes a supersaturated calcium gluconate solution. Each 10ml injection provides 93 mg of elemental calcium (Ca++) equivalent to 1 g of calcium gluconate.
Canxi Gluconate tiêm
2.4 Calcium Citrate Calcium citrate is a salt commonly used as a source of calcium in many over-the-counter supplements.
2.5 Calcium Phosphate It is often seen as an over-the-counter supplement, antacid, or as an added ingredient in some toothpastes.
2.6 Calcium lactate Calcium lactate is a salt consisting of two lactate anions for each calcium cation (Ca2+). It is prepared commercially by neutralizing lactic acid with calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide.
Approved by the FDA as a safe food, calcium lactate is used as a firming agent, flavoring agent, leavening agent, stabilizer, and thickener. Calcium lactate is also found in calcium daily dietary supplements. It is also available in various hydrate forms, with calcium pentahydrate being the most common.
2.7 Calcium levulinate Calcium levuline is relatively new and is made from the direct reaction between L- or levulinic acid levulose and calcium hydroxide 3. Calcium levuline formulation is used as a calcium supplement, with high calcium content being used as a calcium supplement. was observed to be 14.8% higher than the content commonly found in calcium lactate 3. This formulation is considered a low molecular weight organic calcium ion, easily absorbed through the intestinal wall 3.
This new application of calcium is used as a food fortifier, to fortify foods such as sauces, condiments, beer, beverages, soft drinks, milk and dairy products, soy milk Soy and soy products may use calcium, or with calcium lactate, calcium chloride, and other compounds, for tablets, capsules, or injections 3.
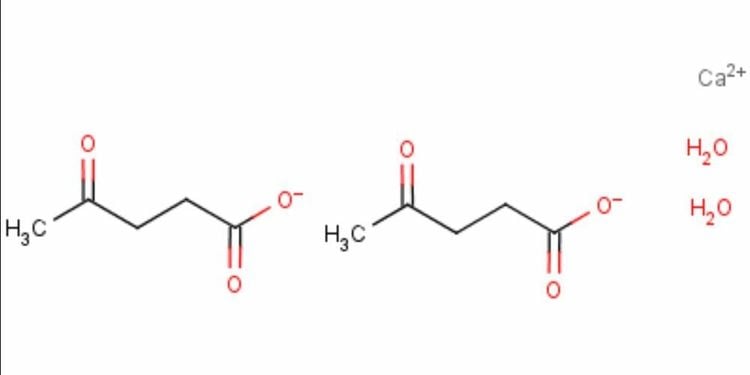
Công thức canxi levuline
2.8 Calcium chloride Calcium chloride is an ionic compound of calcium and chlorine. It is highly soluble in water and very perishable. It is a solid salt at room temperature, and it behaves like a typical ionic halide. It has several common applications such as brine for refrigeration plants, ice and dust control on roads and in cement. It can be produced directly from limestone, but large amounts are also produced as a by-product of the Solvay process. Due to its hygroscopic nature, it must be kept in sealed containers.
2.9 Calcium carbonate Calcium carbonate is an inorganic salt used as an antacid. It is a basic compound that works by neutralizing hydrochloric acid in gastric secretions. A subsequent increase in pH may inhibit pepsin activity. An increase in bicarbonate and prostaglandin ions may also confer a cytoprotective effect. Calcium carbonate can also be used as a nutritional supplement or to treat hypocalcem.
Calcium plays an important role in the anatomy, physiology and biochemistry of organisms and cells, especially in signal transduction. The skeleton acts as a primary storage site for the element and releases Ca2+ ions into the bloodstream under controlled conditions.

Calcium carbonate
Circulating calcium is either free, ionized, or bound to blood proteins such as serum albumin. Although calcium flow to and from bone is neutral, about 5 mmol is passed a day. Bones serve as an important storage point for calcium, as it contains 99% of the body's total calcium. Low calcium intake may also be a risk factor in the development of osteoporosis. The best absorbed form of calcium is tablets of calcium salts such as carbonate or phosphate. Calcium gluconate and calcium lactate are well absorbed by pregnant women. Seniors absorb calcium lactate, gluconate and citrate better unless they supplement their calcium with a full breakfast.
Articles refer to the source: drugbank.ca, sciencedirect.com
MORE:
Hypocalcemia: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment What to do when hypocalcaemia? Relationship between hypoparathyroidism and hypocalcemia