This is an automatically translated article.
Scarring burns can result from exposure to certain chemicals, UV rays, or fire accidents. While some burn scars go away on their own, others take a long time to heal and may even become a permanent part of the skin. Therefore, it is necessary to know how to treat burns to prevent scarring as well as the immediate steps to take after a burn to avoid having unsightly damage later on.1. Why do scars form after burns?
Burns that leave scars are evidence of damaged and dead cells, then the skin produces a fibrous protein to repair itself. This fiber is called collagen. As the skin heals, the damaged area will leave behind discolored patches of skin, often thick, and known as scars. Depending on the depth of the burn, these scars can be temporary and sometimes permanent.2. Types of burn scars
The formation of burn scars depends on the types of burns:First degree burns - First degree burns usually involve damaged epidermis located on the surface of the skin. You may also notice some local redness, pain, and inflammation.
Second degree burns - Second degree burns injure both first layers of skin. This causes the skin to become red and inflamed. At the same time, the patient can also be very painful.
Third degree burns - Third degree burns are more severe types of burns. Not only does it damage all layers of the skin, post-burn wounds can also penetrate the skin to reach the underlying tissues and muscle structures. Once healed, the burn scars of these burns can also limit joint movement.
The following are the types of scars that burns can leave:
Hypertrophic scars - These scars are usually red or purple in color. They tend to rise to the surface of the skin and cause itching. Traction Scars – These scars often stretch the skin and muscles. Sometimes a contracture scar located near the joint makes it difficult for the patient to move. Keloids - These types of scars form glossy, hairless bumps on the skin.
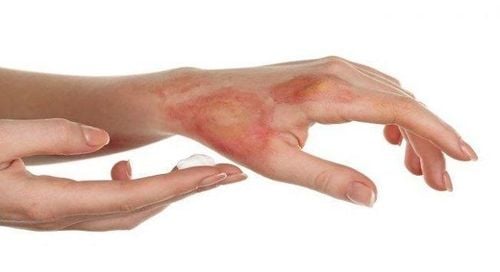
Sẻo bỏng có 3 loại: Sẹo phì đại, sẹo co kéo và sẹo lồi
3. How to treat a burn?
The ideal burn scar treatment depends on the severity and extent of the burn.For first degree burns, antibiotic cream should be applied to the burned area. This will help the wound heal faster and will also reduce inflammation and discomfort. At the same time, it is necessary to use a gauze to cover the burn to prevent infection or dirt from outside.
For second or third degree burns, wearing compression clothing can help the skin heal faster. These are often tight clothing that can be worn for months until the burn heals. Some severe cases may even require a skin graft. This technique involves using skin from another area of the body to cover the burned area.
4. Ways to help improve burn scars
Here are some other burn therapies or treatments that focus on preventing future scarring:Laser Therapy Laser light therapy uses UV light to target blood vessels in the scar tissue redundant. This can help reduce the swelling and redness associated with burn scars.
The use of laser therapy is carried out by doctors experienced in scar removal treatments using the same methods.
Steroid injections Corticosteroid injections can be used to fade scars. The mechanism of action of these drugs is anti-inflammatory, which helps reduce the appearance of some hypertrophic scars and keloids.
Cryotherapy This technique uses liquid nitrogen to freeze growing scars. The role of cryotherapy that can be used on keloid scars is to help soften these proliferative structures before they fully emerge to the skin's surface causing unsightly appearance.
Surgery Surgery can be used to treat burn scars if the scar is very prominent in the skin or to deal with cases of shrinkage scarring, helping to improve range of motion.
However, compared to the above interventions, surgery is highly invasive and may not be suitable for everyone. Based on the doctor's recommendation, the patient can choose whether or not to undergo surgery.
Physical therapy Physical therapy can help improve range of motion in areas of post-burn traction. At the same time, encouraging movement early after a burn has healed can help prevent the formation of stretch marks.
Silicone gel These substances help soften scars effectively. Silicone gel can be used on scars that are healing but not open wounds. This is an effective way to prevent burn scars and has become a popular method in recent times.
Moisturizer Moisturizer may not help with scarring. However, with nutrients provided to the skin, moisturizers can soften the appearance of scar structure, thereby indirectly preventing burn scars.
Accordingly, moisturizer needs to be used continuously for three months with application about 12 hours a day. You should consult a dermatologist about choosing the right cream for your skin characteristics as well as your scars.
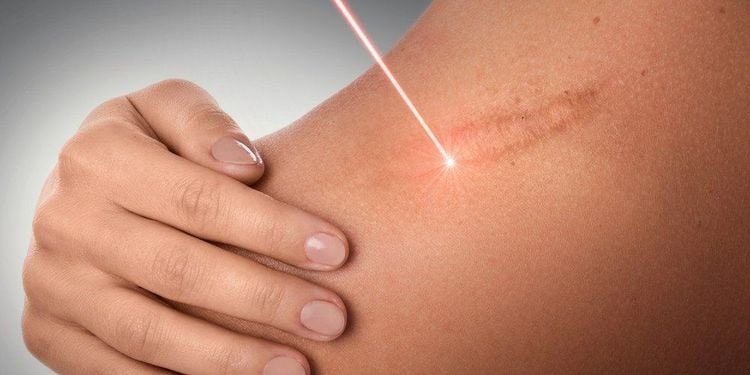
Liệu pháp laser là phương pháp thường được sử dụng để cải thiện sẹo bỏng
5. How to treat burns to prevent scars from forming?
Immediately after a burn occurs, the following steps should be taken promptly to help reduce the risk of permanent burn scarring:Rinse with cool water and allow to dry Apply antibiotic ointment Cover the area Use a non-stick bandage and a clean gauze pad Gently stretch the affected area every day so that the young skin doesn't stick together Sun protection for several months to prevent further damage. sunlight Also, see your doctor regularly until the burn heals completely. If the burn appears red, blisters, pustules or discharges, blood, pus and shows no signs of healing, see your doctor as soon as possible.
6. Complications related to burns
Infection A burn is an open wound that allows bacteria and other germs to easily enter the body if not treated properly. This can lead to a mild or severe infection. Even a skin infection at the burn can lead to sepsis if these bacteria get into the bloodstream and can also be life-threatening.Dehydration When the skin burns, the body's barrier loses its integrity so it is easy to lose large amounts of fluid. If left untreated, burns can also cause dehydration.
Traction and limited mobility This condition is usually the result of a third degree burn and then a stretch mark burn scar.
If traction scarring occurs over a large area of skin, it can cause the skin to stretch. Complications that limit mobility occur when the scar pulls close to the joints.
Muscle and Tissue Damage Severe burns can sometimes damage the underlying muscle structure and, if severe, can lead to partial body defects, loss of motor function.
Psychological damage The appearance of burn scars or any other complications not only affects the physical health but also greatly affects the psychology - psyche of the victim.
At this point, the help of psychologists if the burn scars are affecting your quality of life or mental state is essential.
In a nutshell, burn management to prevent scarring includes treating the burn according to its classification and treating the scars that form afterward. However, with proper treatment of burn wounds, complications of burns including spasticity, infection, emotional health problems, muscle damage and dehydration can be avoided. Scars will also become simpler, especially with the development of today's cosmetic skin interventions.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the national health system, please book an appointment on the website (vinmec.com) for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.