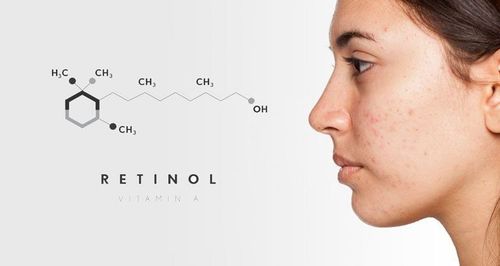
AHA, BHA, and Tretinoin are three very important ingredients found in many skincare products. Although they share several similarities, Tretinoin, AHA, and BHA each have distinct differences. Understanding the characteristics and usage of these ingredients helps you care for your skin correctly and effectively.
1. What are AHA and BHA?
Hydroxy Acids – a group of fruit-derived acids – are among the most widely used acids in skincare treatments. They are known for their diverse benefits, such as minimizing wrinkles, boosting skin elasticity, and fighting aging. Of these, Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHA) and Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHA) are two main subgroups of Hydroxy Acids.
AHA: A group of water-soluble natural acids found in foods, especially fruits. AHA works on the principle of breaking down the bonds between skin cells on the epidermis, thus encouraging cell turnover.
BHA: Has a molecular structure close to AHA, but it can dissolve in oil and therefore act within the pores. The most commonly used BHA in beauty products is Salicylic Acid. However, in certain countries, the use of Salicylic Acid in cosmetics is subject to strict regulations. Consequently, other derivatives of this substance (e.g., Salicylate, Betaine Salicylate, and Sodium Salicylate) are utilized as substitutes.
AHA and BHA are favored due to their significant skin benefits, such as:
- Improving skin texture, making it smoother and more even in color;
- Helping fade mild wrinkles and age spots;
- Preventing and treating acne by cleansing the skin’s surface (AHA) and the pores (BHA);
- Acting as antioxidants, neutralizing free radicals, and fighting skin aging;
- With high concentrations, AHA and BHA are used to treat acne, scars, melasma, and hyperpigmentation;
- Stimulating collagen synthesis, thickening the dermal layer.
By regulation, in at-home products, the concentration of AHA does not exceed 10%, while BHA is only about 1–2%. In specialized treatments, AHA or BHA concentrations may go up to 20–30% but must be prescribed by a dermatologist. In addition, because AHA and BHA thin out the skin’s stratum corneum, skin becomes more sensitive to sunlight. Therefore, when using AHA/BHA frequently or at high concentrations, you must use sunscreen and shield your skin carefully from the sun.
[SEE MORE: Tretinoin for Acne: How to Use, Benefits, Effectiveness, and Side Effects]
2. What is Tretinoin?
Tretinoin, also known as Retinoic Acid, is a widely used ingredient for treating skin aging. It can address nearly every skin concern, such as:
- Helping treat and prevent acne by accelerating cell turnover and regulating sebum;
- Fading wrinkles and preventing the formation of new wrinkles;
- Acting as an antioxidant, preventing aging by neutralizing free radicals and inhibiting the activity of Matrix Metallopeptidase enzymes (these break down collagen);
- Stimulating collagen production in the skin, thickening the dermis;
- Enhancing subcutaneous blood circulation, giving the skin a healthier pinkish tone;
- Improving skin damaged or aged by excessive UV exposure;
- Improving surface texture, smoothing the skin;
- Lightening pigmented spots due to actinic keratosis or pigment disorders;
- Used in the treatment of psoriasis.
Because it combines most of the skin-improving benefits, Tretinoin can easily irritate the skin. Therefore, when using this ingredient, you need sufficient knowledge to handle it appropriately.
3. What Is the Difference Between Tretinoin & AHA/BHA?
Both AHA/BHA and Tretinoin share the function of making it easier to shed dead skin cells. However, here are some differences:
- AHA/BHA: Works as a chemical exfoliant, mainly on the outer surface of the skin, without acting at the cellular level. They loosen and weaken the bonds between dead skin cells so that those cells can be removed more easily.
- Tretinoin: Works at the cellular level, primarily in the lower layers of the skin. This means Tretinoin influences cells to make them healthier, better eliminating dead cells. Additionally, it improves the function of tiny blood vessels, affecting both the lower and the outer layers of the skin.

4. Using Tretinoin, AHA, and BHA Correctly
4.1 Combining AHA and BHA
It is possible to combine AHA and BHA since both are in the Hydroxy Acids family. However, dermatologists generally advise caution when combining two products containing these ingredients, as it may lead to excessive exfoliation, weakening the skin’s protective barrier, and causing irritation or damage from external environmental factors.
You can find products containing both AHA and BHA in one formula (often, manufacturers adjust ingredient concentrations to be suitable). If you use separate products containing AHA or BHA as the main ingredient, apply them on alternate days. If signs of over-exfoliation appear, reduce the frequency and add skin-repairing products.
4.2 Combining AHA/BHA and Tretinoin
In theory, AHA/BHA can be used in tandem with Tretinoin (topically applied Retinoic Acid) to help address aging skin with numerous wrinkles or pigmentation spots. In practice, some clinical studies have shown favorable results using AHA/BHA combined with Tretinoin in treating acne or sun-damaged skin.
Because Tretinoin can remove dead skin cells and stimulate cell turnover, do not use it simultaneously with many peeling or exfoliating products unless directed by a doctor. You can apply Tretinoin and AHA/BHA at different times to avoid overloading the skin.
4.3 Some Notes
Although you can combine AHA/BHA with Tretinoin, to ensure safety when using skincare products, you need to be aware of potential side effects, product combination rules, and caution with active ingredients. Key principles when using products containing AHA/BHA and Tretinoin:
Use sunscreen. Most special treatments containing AHA, BHA, and Tretinoin thin out the stratum corneum of the skin, making it more sensitive and requiring extra protection. So, make it a habit to use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 and reapply every 2–3 hours.
Use moisturizers and barrier-repair products to protect skin health.
Know the possible side effects: AHA may cause tingling or a slight burning sensation; BHA can push acne to the surface; Tretinoin may cause peeling and dryness. If you are a first-time user, start with the lowest concentration and frequency, then gradually increase. Do not combine multiple strong actives at once if you are a beginner, to avoid irritation. If your skin becomes irritated, use products with skin-repairing ingredients, do not combine multiple potent products in one application (use them separately in your skincare routine), and continue using sunscreen. If your skin does not tolerate one ingredient, you can switch to more appropriate alternatives.
This article helps readers understand the similarities and differences between Tretinoin, AHA, and BHA. You should use these skincare actives correctly to achieve the beautiful skin you desire.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.