This is an automatically translated article.
Post by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Cigarette smoking and exposure to certain chemicals are among the highest causes of lung cancer. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 90% of all lung cancer cases are caused by smoking.
1. What is lung cancer?
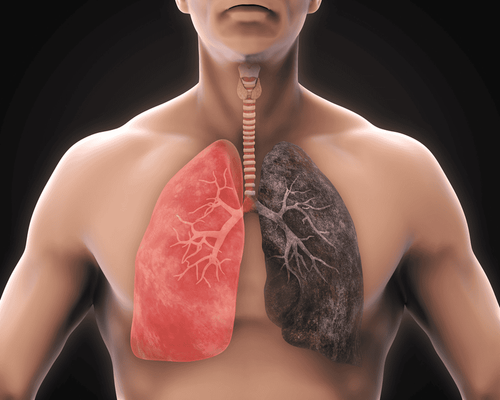
Lung cancer is cancer that starts in the lungs. There are 2 most common types of lung cancer spectrum, namely non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer.
Lung cancer stages indicate how far the cancer has spread, so that appropriate treatment can be given.
The chance of successful treatment or cure is higher when lung cancer is diagnosed and treated at an early stage, before it has metastasized. Because lung cancer does not cause obvious symptoms in its early stages, diagnosis often occurs after it has spread.
Non-small cell lung cancer has the following four main stages:
Stage 1: The cancer is in the lung and has not spread outside. Stage 2: Cancer in the lung and nearby lymph nodes. Stage 3: Cancer is in the lung and the lymph nodes between the chest. Stage 3A: Cancer occurs in the lymph nodes, but only on the same side of the chest where the cancer first started. Stage 3B: Cancer has spread to lymph nodes in the chest opposite or above the collarbone. Stage 4: Cancer has spread to both lungs, to the area around the lung, or to distant organs. Small cell lung cancer has two main stages. In limited stage, cancer is found in only one lung or nearby lymph nodes on the same side of the chest.
Extensive stage means the cancer has spread:
Throughout one lung To the opposite lung To the lymph nodes on the opposite side Fluid around the lung To the bone marrow To distant organs At the time of diagnosis 2 out of 3 people with small cell lung cancer are already in the advanced stage.
2. What causes lung cancer? Cigarette smoking and exposure to certain chemicals are among the top causes of lung cancer. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 90% of all lung cancer cases are caused by smoking.
Lung cancer can also occur due to mutations in the patient's DNA. As cells reproduce, they divide and multiply, thereby forming identical cells. This way, your body is constantly renewing itself.
Besides, inhalation of harmful substances or carcinogens is also a cause of lung cancer. Examples of substances that cause lung cancer include:
Tobacco smoke Asbestos Radon In the beginning, your body can repair itself. However, with repeated exposure, your cells will become increasingly damaged. Over time, cells will begin to function abnormally and grow uncontrollably. This is how cancer grows in your body.
Some precancerous changes must occur before the cancer actually manifests. The accumulation of extra cells causes tumors, benign or malignant. Malignant cancerous lung tumors can be life-threatening. They can spread and even recur once they've been removed.
Read on to learn about individual and environmental factors that can cause lung cancer.
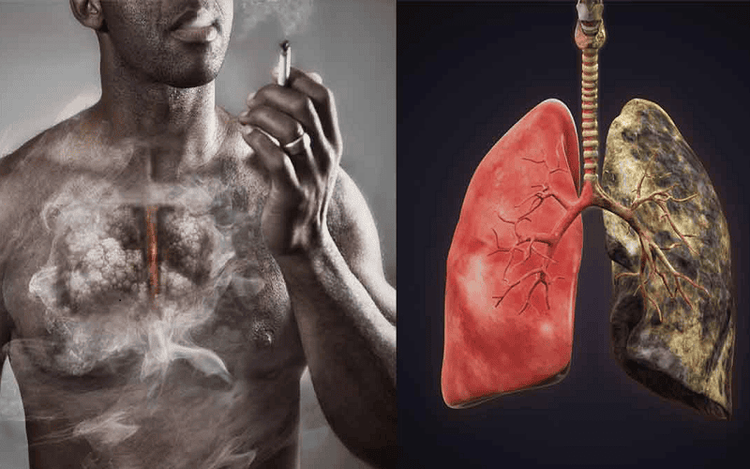
Hút thuốc lá là một trong những nguyên nhân ung thư phổi cao nhất.
This increased risk is true even if you don't smoke. It's not clear whether genetics cause lung cancer or merely increase your susceptibility to it.
Age According to the American Cancer Society, lung cancer mainly occurs in older people. Two out of three people diagnosed with lung cancer are 65 or older. The average age at the time of diagnosis is about 70. The older you are, the longer your exposure to toxic chemicals. Longer exposure increases the risk of cancer.
Past lung disease Past lung diseases can cause inflammation and scarring in the lungs. Examples of these diseases include tuberculosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. You may be at greater risk of developing lung cancer if you have a history of chronic diseases that affect your lungs.
Radiation therapy to the chest Radiation therapy used to treat other cancers such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma and breast cancer may increase the risk of lung cancer. This risk is higher if you smoke.
Secondhand smoke Even if you don't smoke, exposure to secondhand smoke can increase your risk of lung cancer. According to the US CDC, each year about 3,000 people in the United States who have never smoked die from lung cancer from breathing secondhand smoke.
Smoking Smoking is the number one risk factor for lung cancer, accounting for nearly 90% of all cases, according to the CDC. Tobacco and tobacco smoke contain more than 7,000 chemicals, many of which cause cancer. The more often and the longer you smoke, the greater your chances of getting lung cancer.
Diet A healthy and balanced diet will provide your body with the vitamins and minerals it needs to stay healthy. Not eating a varied mix of healthy foods, including fruits and vegetables, can increase your risk of lung cancer.
Environmental factor Radon is a gas that occurs naturally with the breakdown of uranium in rocks and soil. This gas can seep into building foundations and into living and working spaces.
Asbestos is an industrial material used in construction for insulation and as a fire retardant. When the material is disturbed, the tiny fibers become airborne and can be inhaled. You have a higher risk of developing lung cancer if you are regularly exposed to asbestos.
Exposure to other chemicals that can increase the risk of lung cancer such as arsenic, beryllium, cadmium, vinyl chloride, nickel compounds, coal product chromium compounds, mustard gas, chloromethyl ether diesel exhaust.
In summary, there are many causes and risk factors for lung cancer, such as smoking, exposure to certain harmful chemicals, unhealthy diet,... Therefore, cancer screening Lung cancer is the most effective measure for you to timely detect and treat lung cancer, protect your health and life. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has a Lung Cancer Screening Package with many outstanding advantages such as:
A team of highly qualified and experienced doctors. Comprehensive professional cooperation with domestic and international hospitals: Singapore, Japan, USA, .. Comprehensive treatment and care, multi-specialty coordination towards individualizing each patient. Having a full range of specialized facilities to diagnose the disease and stage it before treatment: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, histopathological diagnosis, gene-cell testing, .. Full range of main cancer treatment methods: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant... When registering for the Lung Cancer Screening Package at Vinmec, customers will receive:
Examination respiratory specialist Low-dose computed tomography lung tumor screening.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:Key statistics for lung cancer? (2016, May 16) cancer.org/cancer/lungcancer-non-smallcell/detailedguide/non-small-cell-lung-cancer-key-statistics Mayo Clinic Staff. (2015, September 25). Lung cancer mayoclinic.com/health/lung-cancer/DS00038 What are the risk factors for lung cancer? (2016, July 20) cdc.gov/cancer/lung/basic_info/risk_factors.htm What causes non-small cell lung cancer? (2016, May 16)