This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by MSc, Dr. Trinh Thi Thanh Huyen - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalIf a pregnant woman is infected with HIV, the possibility of transmitting the virus to the fetus is very high. However, if a pregnant woman is found to have HIV, being given medication and taking other steps can significantly reduce the risk of HIV transmission to her unborn baby.
1. What is HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)?
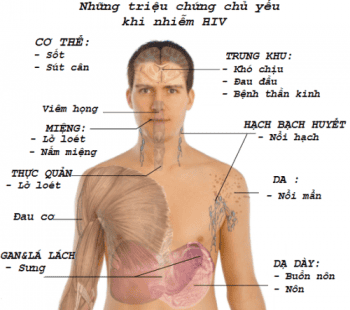
HIV is a virus that attacks the cells of the immune system and causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in humans. AIDS is Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, the final stage of HIV infection.
HIV is transmitted through sex, blood and from mother to child (during pregnancy, childbirth and lactation). The majority of children infected with HIV are transmitted by HIV-infected pregnant mothers to the baby before, during and after birth. If a pregnant mother is infected with HIV without any preventive interventions, the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV will be about 25-40% in developing countries and about 16-20% in Europe. Europe and North America.
2. How is HIV transmitted from mother to child?
There are many risk factors for HIV transmission from mother to child. Among them, the most important risk factor affecting HIV transmission from mother to child is the viral load in the mother's blood. A high HIV load can be attributed to two main reasons: the mother is newly infected with HIV or the mother has an advanced HIV/AIDS infection.
The amount of HIV in a pregnant woman's blood is directly proportional to the rate of HIV transmission from mother to child in both ART-treated women and in ART-naive women.
The more severe the AIDS clinical stage of a pregnant woman, the higher the rate of mother-to-child HIV transmission. Pregnant women in the early stages of HIV infection have a high rate of mother-to-child HIV transmission because of the very high HIV sera. HIV-infected pregnant women with sexually transmitted infections are at increased risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV because of the increased amount of HIV in reproductive tract fluids and lesions of the reproductive tract. Drug use, smoking, and unprotected sex with multiple partners during pregnancy are associated with increased rates of mother-to-child HIV transmission.

Một phụ nữ mang thai nhiễm HIV thì khả năng truyền virus cho thai nhi là rất cao
Premature babies have a higher risk of acquiring HIV from their mothers than full-term babies. The risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV increases with the length of time between rupture of membranes and delivery. This risk increases by about 2% for each hour after the water breaks. Interventions such as fetal monitoring, fetal scalp electrode placement, episiotomy, and colectomy can all increase fetal exposure to HIV in the mother's blood and vaginal fluids and increase the risk of transmission. HIV from mother to child.
Newborn-related factors such as an immature immune system, especially premature babies, can increase the risk of mother-to-child HIV transmission. Babies with gastrointestinal lesions who are breastfed are at higher risk than other children.
Breastfeeding increases the rate of HIV transmission from mother to child. This rate is highest among those who both breastfeed and feed their babies a substitute, followed by those who exclusively breastfeed.
3. Mechanism of HIV transmission from mother to child
Mother-to-child transmission of HIV occurs through 3 stages: HIV transmission in utero and during pregnancy, during labor and transmission after birth and through breast milk.
HIV transmission in utero and during pregnancy can occur from the first trimester to term because HIV is transmitted directly from mother to fetus through the placenta.
Uterine contractions during labor can damage small blood vessels and cause bleeding into the vagina. Bleeding will increase the amount of HIV present in the vagina, leading to an increased risk of HIV infection for the fetus when passing through the mother's vagina. If the delivery involves interventions such as episiotomy, fetoplasty or suction, the epithelium and large blood vessels may be damaged, bleeding may increase the risk of HIV infection for the fetus. When passing through the vagina to come out, the fetus can swallow vaginal fluids containing HIV into the digestive tract.
If the mother is HIV-positive, if possible, she should feed her baby with food that completely replaces breast milk to cut off the source of transmission because HIV from breast milk can penetrate into the lining of the baby's digestive tract or the breast of the mother. Mothers can scratch and infect the nursing baby directly.
4. Why is HIV testing necessary for pregnant women?
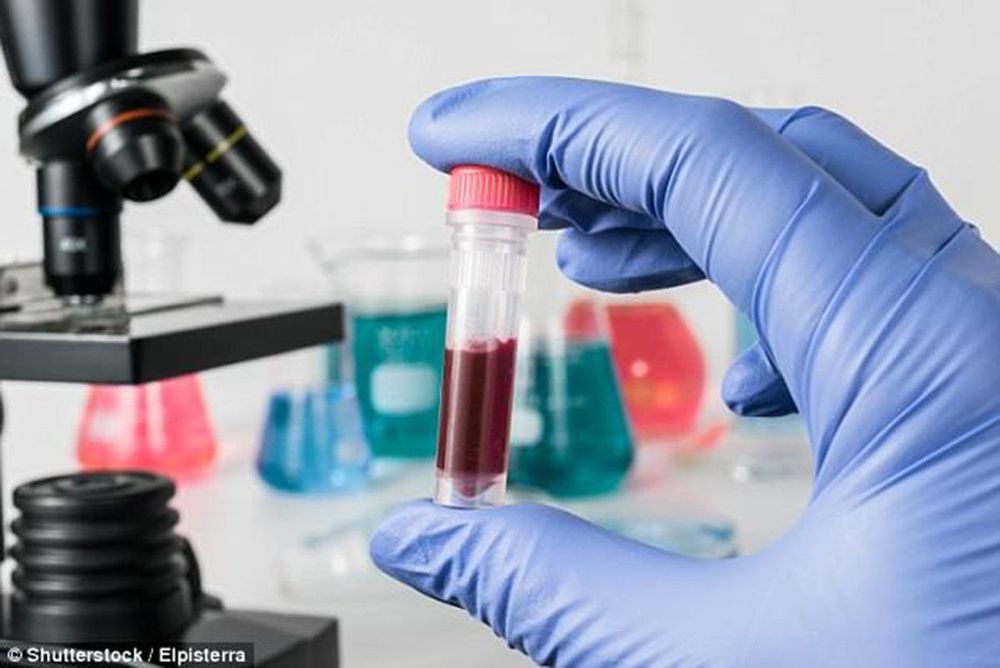
Xét nghiệm HIV cho tất cả phụ nữ mang thai là một trong những can thiệp của chương trình dự phòng lây nhiễm HIV từ mẹ sang con
HIV testing for all pregnant women is one of the interventions of the program to prevent mother-to-child HIV transmission. Currently, prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission is still mainly focused on pregnant women and women already infected with HIV. For a program to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV to be effective, there is a need to focus on diagnosing HIV status for all pregnant women. Early detection of HIV status in pregnant women will have the following effects:
Helping pregnant women with HIV make their own decisions about childbirth, taking measures to prevent HIV transmission from their mothers to the child. Helping pregnant women without HIV know about HIV, about HIV testing during pregnancy, about prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV... Help pregnant women practice safe behaviors to reduce the risk of transmission transmit HIV to themselves and their children... Supporting pregnant women living with HIV emotionally and psychologically in many aspects such as:
Identify and express affection and support, help pregnant women stabilize their spirits spirit, build internal strength to overcome all crises Access to service facilities when in need, especially in health Overcoming stigma and alienation from the community Self-determination and confidence in life ... In addition, early detection of HIV infection in pregnant women in order to apply interventions to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV including: ARV prophylaxis, use of substitute milk and Introduce postpartum care and treatment services. Pregnant women infected with HIV should be consulted with HIV/AIDS care and treatment facilities to consider ARV treatment or treatment to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
Vinmec International General Hospital offers a Package of Examination and Screening for social diseases to help customers detect diseases early and have effective treatment and prevent dangerous complications. The screening package for social diseases at Vinmec is for all ages, both men and women.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: acog.org