This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by MSc Vu Van Quan - Department of General Surgery & Anesthesia - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
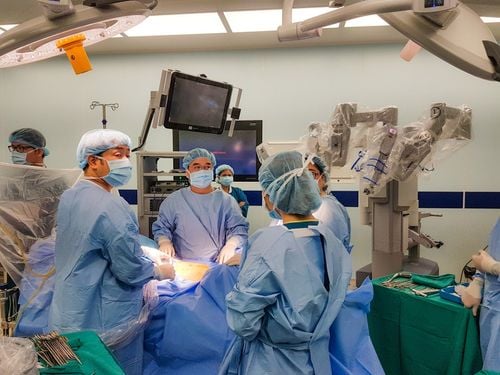
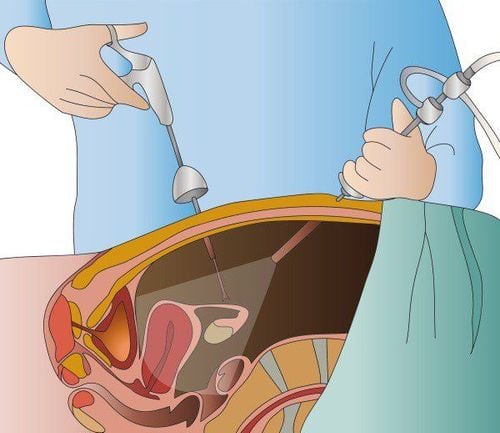
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique that minimizes pain for the patient, has a fast recovery time, and shortens the number of days in the hospital. This is a technique used to diagnose and treat diseases inside the abdomen.
1. What is laparoscopic surgery?
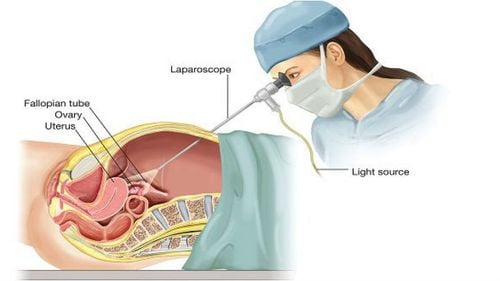
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique that can visualize the organs inside the abdomen. In some cases, X-ray or ultrasound cannot determine the exact cause, condition, and location of the lesion, forcing direct observation through laparoscopy. The doctor uses a metal tube with a camera and a light inserted into the patient's body through a small incision, so that all parts of the abdomen can be viewed to make a diagnosis and measure. specific treatment.
Compared with traditional methods, laparoscopic surgery has many outstanding advantages such as:
Less pain for the patient; Quick recovery time; The hospital stay is shortened; Accurate analysis, less surgical trauma; Observation of all adjacent organs and abdominal cavity; Quick recovery of bowel movements; Minimizing complications of intestinal adhesions and postoperative wound infection; Does not leave large scars, ensuring aesthetics; Reduce immune disorders and affect respiratory function...
2. When is laparoscopic surgery performed?
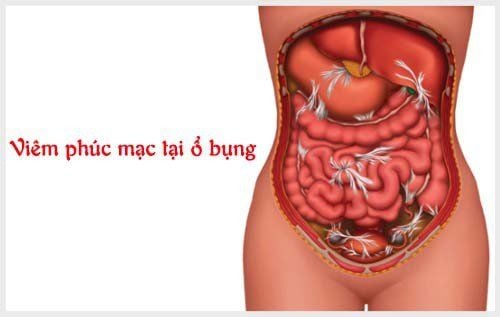
Phẫu thuật nội soi ổ bụng có thể được thực hiện khi bị viêm phúc mạc do thủng cơ quan nội tạng
Laparoscopic surgery is indicated in the following cases:
Liver and biliary surgery (cholecystectomy, surgery to remove gallstones and common bile ducts, liver resection, biliary-enteric bypass surgery) ) through laparoscopic or open surgery. Resection of the appendix. Perforation of gastric or duodenal ulcer. Gastroesophageal reflux, diaphragmatic hernia. Gastric surgery (partial gastrectomy or total gastrectomy for benign or malignant tumors, gastric bypass surgery, gastrojejunostomy). Surgery to treat obesity (also called bariatric surgery) such as gastric bypass, gastric banding, or gastric bypass. Surgical treatment of small bowel or colon obstruction. Abdominal trauma such as damage to the liver, spleen or intestines. Peritonitis due to perforation of internal organs. Pancreatic and splenic surgeries such as pancreaticoduodenectomy, splenectomy and pancreatic tail body, and pancreaticojejunostomy (mostly through open surgery). Colon and rectal surgery. Laparoscopic surgery to remove part or all of the colon. Surgery for inguinal and other abdominal wall hernias with mesh placement through open or laparoscopic surgery. Rectal surgeries (hemorrhoids, anal fistula, anal fissure, posterior sacral hair follicle abscess, ...) with new means such as Longo surgery, suspension and hemorrhoidal vasectomy (HAL/ Doppler RAR).
3. The procedure of laparoscopic surgery through the abdomen
Before laparoscopic surgery, the patient is under general anesthesia, completely losing sensation during surgery.
The doctor makes a small incision less than 1.5 inches above the navel to insert the endoscope into the body. During surgery, carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide gas will be injected into the abdomen through a needle to help see the abdominal organs and organs in the most clear way.
To create a path for the endoscope to enter the body, the doctor uses a trocar tube to poke through the incision first. The endoscope is attached with an observation device and a specialized lighting device, the image obtained through the camera is transmitted to an external screen. Based on that image, the doctor can assess the condition, location of the injury, and the extent of the damage to come up with the most appropriate treatment plan.
4. Common manifestations after laparoscopic surgery
Sau quá trình phẫu thuật nội soi ổ bụng, người bệnh có thể gặp một số triệu chứng như: mệt mỏi, choáng váng, chóng mặt
4.1 Normal manifestations after surgery After laparoscopic surgery, patients may experience some symptoms such as: fatigue, dizziness, dizziness, pain at the incision, back pain, shoulder pain. .. These are common symptoms after surgery due to the effects of anesthetics and gases used during endoscopy and will disappear after 1-2 days.
For the fastest recovery, the patient should get up and walk gently to avoid intestinal adhesions and quickly pass stools. Eat liquid food, dilute porridge before going to the toilet.
4.2 Abnormal manifestations after surgery Complications after laparoscopic surgery rarely occur, however, patients and family members need to monitor their health, quickly take the patient to the hospital when there are symptoms. following:
Bleeding in the abdominal cavity; Bleeding or hernia in the incision areas; Internal bleeding; Surgical site infection; Inflammation of the abdominal wall; Blood clots entering the lungs, pelvis, leg blood vessels, heart, or brain; Complications of Anesthesia... Complications after laparoscopic surgery may not appear immediately. When there are abnormal signs of health, it is necessary to quickly go to the hospital for timely examination and treatment.
Performing laparoscopic surgery and other types of surgery should generally be carried out in reputable hospitals to minimize the possibility of possible complications.