This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Master, Doctor Bui Minh Duc - Department of General Internal Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
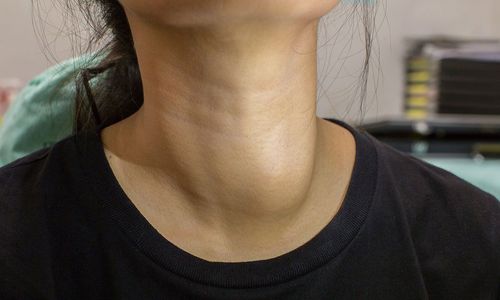
Thyroid nodules are solid or fluid-filled nodules that form in the thyroid gland, a small gland located at the base of your neck, just above your breastbone. Most thyroid nodules are not dangerous and cause no symptoms. Only a small percentage of thyroid nodules are cancerous.
1. Circumstances of detecting a thyroid nodule
Circumstances of detecting thyroid nodules can occur in many cases, the patient has no symptoms, the doctor discovers the thyroid nodule during a routine medical examination or the doctor can detect the thyroid nodule. thyroid during the scan performed for other health reasons. However, some thyroid nodules can become large enough to be seen or cause difficulty swallowing or breathing.
Treatment options depend on the type of thyroid nodule in the patient.
Trắc nghiệm: Loại bỏ tin đồn và tìm hiểu sự thật về bệnh suy giáp
Suy giáp là một hội chứng chứ không phải căn bệnh riêng biệt. Tuy nhiên, vẫn còn rất nhiều thông tin gây tranh cãi về bệnh suy giáp. Hãy cùng trả lời 8 câu hỏi sau để phá vỡ một số nghi ngờ về bệnh lý này nhé!
Nguồn tham khảo: webmd.com
2. Symptoms of thyroid nodules
Most thyroid nodules have no signs or symptoms, but with larger nodules they can:Make the patient feel a thyroid nodule See a thyroid nodule, usually on the front of your neck Compression of the trachea or esophagus, causing difficulty breathing or swallowing
In some cases, the thyroid nodules overproduce thyroxine - a hormone secreted by the thyroid gland. Too much thyroxine can cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as:
Unexplained weight loss Increased sweating Hand tremors Anxiety Fast or irregular heartbeat
Only a small number of thyroid nodules are cancerous, but determining which nodules are cancerous cannot be done by assessing the patient's symptoms. Most thyroid cancer nodules grow slowly and are small when doctors find them. Rarely, invasive thyroid cancer with nodules may be large, firm, fixed, and rapidly growing.
3. When to see a doctor?
Although most thyroid nodules heal and cause no problems, ask your doctor to evaluate any abnormalities in your neck, especially if breathing or swallowing is difficult. It is important to assess the possibility that a thyroid nodule is cancerous.
Seek medical attention if you develop signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as:
Sudden weight loss despite eating normally or increasing your intake of palpitations palpitations Difficulty sleeping Muscle weakness Anxiety or irritability respect

Also see a doctor if you have signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism, including:
Fear of cold Feeling tired easily Dry skin Memory problems Depression Constipation
4. Causes of thyroid nodules
There are several causes of nodules to develop in the thyroid gland, including:
An overgrowth of normal thyroid tissue, called a thyroid nodule. It is not clear exactly why thyroid tissue develops, but it is not cancerous and does not cause serious consequences unless the size of the nodule is too large, causing compression. Some thyroid nodules cause hyperthyroidism. A thyroid cyst, which is a fluid-filled cavity (cyst) in the thyroid gland is most commonly caused by a degenerative thyroid nodule. Usually, the solid components mix with the fluid in a thyroid cyst. Cysts are not usually cancerous, but sometimes they contain solid tissue that can be cancerous. Chronic thyroiditis: Hashimoto's disease, a thyroid disorder, can cause thyroid inflammation and the formation of large nodules. Often accompanied by hypothyroidism.
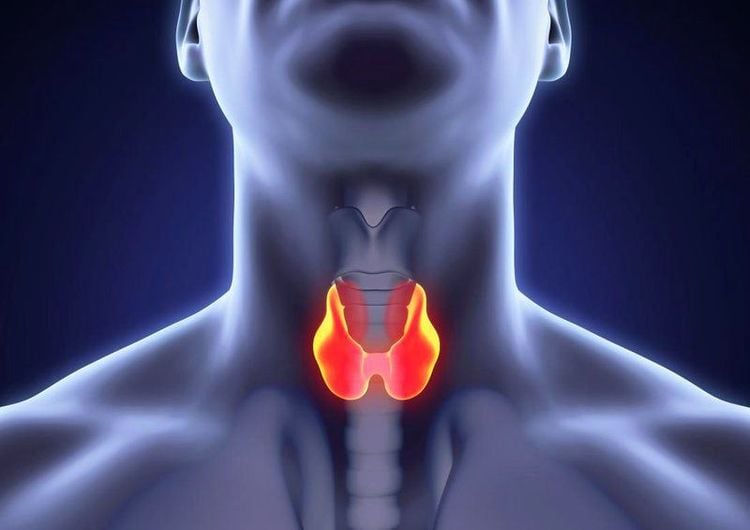
Multinodular goiter: The term goiter is used to describe an increase in the size of the thyroid gland, which can be caused by iodine deficiency or another disorder of the thyroid gland. Multinodular goiter consists of many distinct masses of the thyroid gland, but its etiology is unknown. Thyroid cancer: A thyroid nodule has a low risk of being cancerous. However, a nodule that is large and hard or causes pain or discomfort is more of a concern and should be checked by a doctor. Certain factors increase the risk of thyroid cancer, such as a family history of thyroid cancer or other endocrine disease and a history of radiation exposure from medical therapy or from radioactive fallout core. Iodine deficiency: Lack of iodine in your diet can sometimes cause your thyroid gland to grow into a thyroid nodule. But iodine deficiency is not common in many countries, where iodine is frequently added to table salt and other foods.
5. Complications of thyroid nodules
Complications associated with a thyroid nodule include:
Difficulty swallowing or breathing: Large nodules or multinodular goiter can interfere with swallowing or breathing. Hyperthyroidism: Occurs when a thyroid nodule or thyroid gland produces thyroid hormone, leading to hyperthyroidism, causing weight loss, muscle weakness, fear of heat and anxiety, agitation. Potential complications of hyperthyroidism include cardiac arrhythmias, an episode of acute thyrotoxicosis, a rare but potentially life-threatening complication that requires immediate medical attention. In relation to thyroid nodule surgery: If your doctor recommends surgery to remove a thyroid nodule, you may need lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.

6. Diagnosis of thyroid nodules
When evaluating a thyroid nodule, one of the primary goals of the doctor is to rule out the possibility of cancer. But your doctor will also evaluate your thyroid function with tests including:
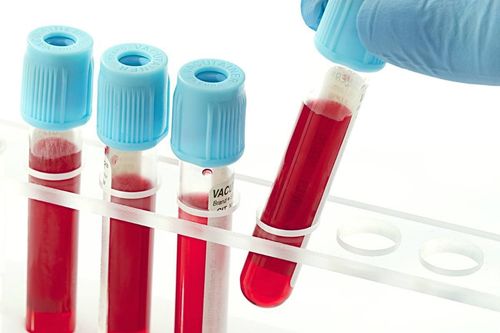
Physical exam: Your doctor may ask you to swallow during a thyroid test to assess thyroid mobility. Your doctor will also look for signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as tremors, increased reflexes, and a fast or irregular heartbeat. Your doctor will also check for signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as slow heart rate, dry skin, and facial swelling. Thyroid function tests: Tests that measure blood levels of TSH and thyroid hormone can show whether you have hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Ultrasound: This imaging technique uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of your thyroid gland. Thyroid ultrasound provides the best information about the shape and structure of thyroid nodules. Doctors can use it to distinguish cysts from solid nodules or to determine if multiple nodules are present. Doctors may also use it as a guide in performing fine-needle aspiration aspiration.
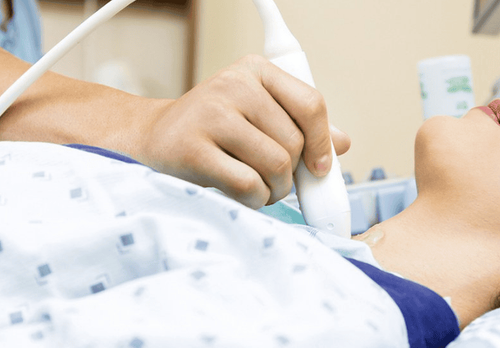
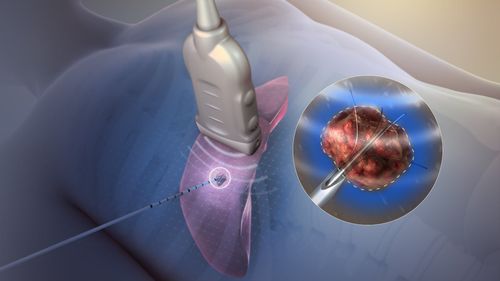
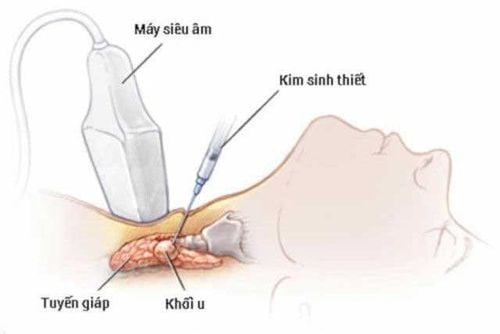
Needle aspiration of thyroid nodules: Thyroid nodules are usually cytologically done to make sure no cancer is present. During the procedure, your doctor will insert a very thin needle into the nodule and remove a sample of cells. The procedure is usually done in the operating room, takes about 20 minutes, and has few risks. Usually, your doctor will use ultrasound to help guide the position of the needle. Your doctor then sends the samples to a lab to analyze them under a microscope. Thyroid scan: Your doctor may perform a thyroid scan to help evaluate thyroid nodules. In this test, an isotope of radioactive iodine is introduced into the patient's body. The patient then lies on a table while a special camera creates an image of his or her thyroid gland on a computer screen. Thyroid hormone-secreting nodules - called hot nodules - appear on scans because they occupy more isotopes than normal thyroid tissue. Hot nuclei are almost always noncancerous. In some cases, nuclei capture few isotopes - known as cold nuclei. Cancerous nodules are usually cold. However, thyroid scans cannot distinguish between cold nodules that are cancerous and those that are not.
7. Treatment of thyroid nodules
Treatment depends on the type of thyroid tumor the patient has.
7.1 Treating benign nodules
If a thyroid nodule is not cancerous, treatment options include:
Routine follow-up: If cytology shows the patient has a noncancerous thyroid nodule , your doctor may recommend just monitoring. This monitoring includes a physical exam and regular thyroid function tests, which may also include ultrasound. The patient is also likely to have to undergo nuclear cytology again if the nucleus grows larger. If a benign thyroid nodule does not change, the person may never need treatment. Thyroid hormone treatment: If your thyroid function tests show that your thyroid isn't producing enough thyroid hormone, your doctor may recommend thyroid hormone treatment. Surgery: A noncancerous thyroid nodule can sometimes require surgery if it's so large it's hard to breathe or swallow. Doctors may also consider surgery for people with large multinodular goiter, especially when the tumor is pressing on the airways, esophagus, or blood vessels. Nodules diagnosed as unidentified or suspicious on cytology also require surgical resection and they may be biopsied to check for signs of cancer.
7.2 Treating Causes of Hyperthyroidism
If a thyroid nodule is overproducing thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism), your doctor may recommend treatment for hyperthyroidism. This treatment may include:
Radioactive iodine: Using radioactive iodine to treat hyperthyroidism. Taken as a capsule or in liquid form, radioactive iodine is absorbed by your thyroid gland. This treatment reduces the size of the thyroid nodules and the signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism subside, usually within two to three months. Synthetic antithyroid drugs: In some cases, your doctor may prescribe an antithyroid medication such as methimazole (Tapazole) to relieve symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Treatment is generally long-term and can have side effects such as elevated liver enzymes and agranulocytosis, so it's important to discuss the risks and benefits of treatment with your doctor. Surgery: If radioactive iodine or antithyroid drugs are not indicated, surgery can be performed to remove the overactive thyroid nodules. You will likely discuss the risks of surgery with your doctor.

7.3 Treatment of cancerous nodules
Treatment for a cancerous thyroid nodule is surgery.
Close monitoring: Very small cancers have a low risk of growing, so your doctor may be able to closely monitor nodules before treating them. This decision is usually made by a thyroid specialist. Close monitoring includes ultrasound monitoring and performing blood tests. Surgery: A common treatment for cancerous nodules is surgical removal. In the past, the standard treatment was to remove most of the thyroid tissue — called quasi-total thyroidectomy. Today, however, it is possible to have more limited surgery to partially remove the thyroid gland for some cancerous nodules. Indications for subtotal thyroidectomy may be used depending on the extent of the disease. Risks of thyroid surgery include damage to the recurrent nerve that controls the vocal cords and damage to the parathyroid glands (four small glands located behind the thyroid gland that regulate calcium metabolism). After a total thyroidectomy, you will need lifelong treatment with levothyroxine to supply your body with thyroid hormone. A thyroid specialist will help determine the exact amount to take because it may require more than hormone replacement to control cancer risk. Alcohol injection: Another option for controlling small cancerous nodules is alcohol injection. This technique injects absolute alcohol into the cancerous thyroid nodule to destroy it. Multiple courses of treatment are usually required.

The package of screening and screening for thyroid diseases of Vinmec International General Hospital helps: Check thyroid function. Screening & early detection of common thyroid diseases such as simple goiter, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, thyroid nodules, thyroid cancer, etc. appropriate and timely treatment.
For advice and to register for an appointment, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec hospital and clinic system HERE.
SEE MORE
Common pathologies in the thyroid gland Where is the thyroid gland located and what is its function? There are 10 signs, immediately think of thyroid disease