This is an automatically translated article.
Vaginal discharge is usually a normal and frequent phenomenon. However, there are certain types of discharge that can be a sign of an infection. Abnormal discharge may be yellow or green, thick, or foul-smelling. This article helps to provide all the information about vaginal discharge that you have.
1. What is vaginal discharge?
Vaginal discharge is usually a normal and frequent phenomenon. However, there are certain types of discharge that can be a sign of an infection. Abnormal discharge may be yellow or green, thick, or foul-smelling.
Yeast or bacterial infections often cause abnormal discharge. If you notice any discharge that looks unusual or has a bad smell, see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
2. Types of vaginal discharge
There are several different types of vaginal discharge. These types are classified based on their color and consistency. Some types of discharge are normal. Others may indicate an underlying condition that needs to be treated.
2.1. White
A slight white discharge, especially at the beginning or end of the menstrual cycle, is normal. However, if the discharge is accompanied by itching and is thick or cheese-like, it is not normal and needs to be treated. This type of discharge could be a sign of a yeast infection.
2.2. Clear and dilute
Clear and thin discharge is completely normal. It can happen at any time of the month. It can be especially heavy after exercise.
2.3. Clear and solid
When the discharge is clear but thick and is more like mucus than water, it means you are likely ovulating. This is a normal discharge pattern.

Các loại dịch âm đạo được phân loại dựa trên màu sắc và tính nhất quán của chúng
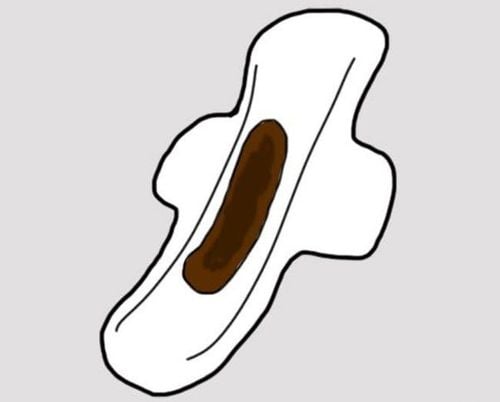
2.4. Brown or blood
Brown or bloody discharge is usually normal, especially when it occurs during or right after your menstrual cycle. Late discharge at the end of your period may be brown instead of red. You may also experience some bleeding between periods. This is called spotting.
If spotting occurs during the normal period of your period and you have recently had unprotected sex, this could be a sign of pregnancy. Bleeding in the early stages of pregnancy can be a sign of miscarriage, so you should discuss it with your gynecologist.
In rare cases, brown or bloody discharge can be a sign of endometrial or cervical cancer. It could be other problems like fibroids or other abnormal tumors. This is why it is important to have an annual pelvic exam and cervical cytology test. Your gynecologist will check for abnormalities in the cervix during these procedures.
2.5. Yellow or green
A discharge that is yellow or green, especially when it is thick, chewy or accompanied by an unpleasant odor is not normal. This type of discharge could be a sign of a trichomoniasis infection. It is usually spread through sexual contact.
3. Causes of vaginal discharge
Normal vaginal discharge is a healthy bodily function. It's your body's way of cleaning and protecting your vagina. Example: It is normal for discharge to increase with sexual stimulation and ovulation. Exercise, oral contraceptive use, and emotional stress can also lead to discharge.
However, abnormal vaginal discharge is usually due to an infection.
3.1. Bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is a fairly common bacterial infection. It causes increased vaginal discharge with a strong, foul-smelling, and sometimes fishy odor, although it causes no symptoms in some cases. Women who have oral sex or have multiple sex partners are at a higher risk of contracting this infection.
3.2. Trichomonas
Trichomonas is another type of infection. It is caused by a single-celled organism or a single-celled organism. The infection is usually spread through sexual contact, but it can also be acquired by sharing towels or bathing suits. It results in a yellow or green discharge with a foul odor. Pain, inflammation, and itching are also common symptoms, although some people do not experience any symptoms.
3.3. Fungal infections
Yeast infection is a fungal infection that produces a white, cheese-like discharge, along with an itching and burning sensation. The presence of yeast in the vagina is normal, but its growth can multiply out of control in certain cases. The following can increase the chance of a yeast infection:
Stress Diabetes Use of birth control pills Pregnancy Antibiotics, especially prolonged use for more than 10 days
Bệnh tiểu đường có thể làm tăng khả năng nhiễm trùng nấm men
3.4. Gonorrhea and Chlamydia
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can cause abnormal discharge. It is usually yellow, green, or opaque.
3.5. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection that is usually spread during sex. It occurs when bacteria spreads up the vagina and into other reproductive organs. It can produce a heavy, foul-smelling discharge.
3.6. HPV or cervical cancer
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is spread through sexual contact. It can lead to cervical cancer. Although there may be no symptoms, this type of cancer can produce bloody, brown, or watery discharge with an unpleasant odor. Cervical cancer can be easily screened with an annual Pap smear and an HPV test
4. When to seek medical help
If you have unusual discharge along with some other symptoms, see your doctor as soon as possible. Symptoms to look out for include:
Fever Abdominal pain Unexplained weight loss Fatigue Increased urination If you have any concerns about whether discharge is normal, make an appointment with your doctor.
5. What will the doctor examine for you?
When you visit your doctor for abnormal vaginal discharge, you will receive a general physical exam, including a pelvic exam. Your doctor will also ask you some questions about your symptoms, menstrual cycle, and sexual activity. In many cases, an infection can be detected by a physical or pelvic exam.
If your doctor cannot diagnose the problem right away, they may order some tests. Your doctor may want to take a curettage from your cervix to check for HPV or cervical cancer. Your discharge may also be examined under a microscope to identify an infectious agent. After your doctor can tell you the cause of the discharge, you will be presented with treatment options.
Xét nghiệm HPV là một trong những phương thức chẩn đoán bệnh
6. Vaginal discharge care at home
To prevent infection, practice good hygiene and wear breathable cotton underwear. Do not douche as they can make discharge worse by removing helpful bacteria. Also, practice safe sex and use protection to avoid STIs.
To reduce the chance of a yeast infection when taking antibiotics, eat yogurt that contains live and active bacteria. If you know you have a yeast infection, you can also treat it with an over-the-counter yeast infection topical or cream.
Currently, Vinmec has deployed the Basic Gynecological Examination and Screening Package. This examination package can detect inflammatory diseases early, making treatment easy and inexpensive. When registering for the Basic Gynecological Examination and Screening Package, customers will receive:
Gynecological examination. Transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries. Bilateral breast ultrasound. Tests such as: Treponema pallidum rapid test, Chlamydia rapid test, taking samples for cervical-vaginal cytology, bacterioscopic staining (female vaginal fluid), HPV genotype PCR automated system, total analysis Automated urine collection.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com