This is an automatically translated article.
Written by Doctor of Medicine & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
The upper respiratory system includes, nose, pharynx, pharynx, sinuses, larynx, which is responsible for taking air outside the body, heating and filtering the air before it is put into the lungs. Meanwhile, the trachea, bronchial tree, alveoli, pleura, and lungs of the lower respiratory system are responsible for air filtration and gas exchange. Therefore, each part has certain functions.
1. Respiratory function testing methods
The lungs have the function of absorbing O2 and excreting CO2, that exchange process depends on the capacity of air and the exchange status in the pulmonary vessels. Between the lungs and the heart is closely related to the heart, distributing O2 to the body and bringing CO2 to the lungs, so changes in ventilation and gas exchange both affect the heart. The respiratory function test has 3 main purposes:
Assess gas exchange, ventilation. Hemodynamic status of the precirculation. The methods used are all aimed at achieving those purposes. 1.1 Evaluation of Ventilation 1.1.1 Inspiratory Volume Measurement Inspiratory spirometer, represented by a sinusoidal line, the graph is proportional to the volume of air inhaled. The results, depending on age, sex, stature, the average numbers of respiration are recorded on a comparison table. Here are the averages for adults, average range:
Circulating air 0.500l Inhale 1,500l Forced exhalation 1,500l Vital capacity 3,500l Residual air = 20 – 25% Lung Volume To Assess ventilation capacity on large strokes, people based on vital capacity People with little breathing exercise. In all cases, reduced respiratory amplitude due to chest wall damage or pathological changes impairing lung ventilation. For example: alveolar dilatation, pleural adhesions, pleural effusion, severe pulmonary tuberculosis, pulmonary fibrosis, it is called a state of limited ventilation.
Vital capacity is increased in people who exercise heavily or in patients with well-established previous lung injury who are being monitored for breathing exercises. The vital capacity method only shows the maximum volume of air that can be circulated, but want to know how quickly the circulation is done, how elastic the lungs are, the distribution of air in the body. How are the alveoli, it is necessary to do some other investigations.
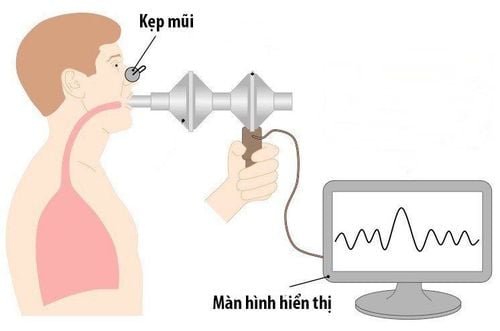
Đo thể tích hô hấp giúp đánh giá khả năng thông khí
1.1.2 Tiffeneau Maneuver The main purpose of the test is to find the maximum volume of air exhaled in one second after a forced inhalation. The symbol for that volume VEMS (Volume expiratoire maximum (seconde)
Let the recording shaft rotate quickly, then exhale forcefully. When the exhaled air volume in one second the higher the exhaled volume curve, VEMS The lower it is, the more difficult it is to exhale, eg in asthma, pulmonary fibrosis
In some bronchospasm, inhalation of acetylcholine may reduce VEMS, in contrast, with aldrin bronchial dilation, VEMS increased markedly
1.1.3 Maximum Breathing capacity This is a combined test to find vital capacity and VEMS. merge for 10-20 seconds Then calculate the maximum expiratory flow in one minute
Result: v=Vt x f (Where, v is the volume of inhalation in one minute. Vt is the volume of one respiratory rate, f is the respiratory rate) Normal V= approximately 80% of the body weight x f In the average person: V= 130l/min
1.1.4 Find the volume of residual air Residual air is the fraction the air left in the lungs, after exhaling strength. The large residual volume in alveolar dilatation indicates a low rate of lung volume respiration. On the contrary, in case the residual air volume is too small, if the lung patient has to be anesthetized for surgery, due to the lack of air buffer in the lungs, it is more susceptible to anesthetic poisoning than the normal person.
Measurement of residual air volume, an indirect method is used, measuring the solubility of a gas that does not participate in respiratory exchange, for example the inert gas Helium or Pit.
1.1.5 – Pulmonary mixing Through the residual air volume test, we can evaluate the rate of air distribution in the alveoli. If the distribution is fast N2 is quickly moved by O2 (if N2) is used but if the air is obstructed, the replacement is done very slowly, after a long time the meter reading the volume of N2 shows only the maximum number does not change.
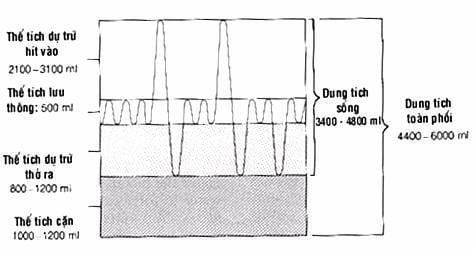
Các thể tích và dung tích tĩnh của phổi
2. Value of Ventilation Tests The above tests show the lung's ability to carry air. To confirm the test results, it is necessary to perform the same test many times and combine several types. In addition, attention must be paid to factors such as age, gender, strength, stature, exercise habits, as well as weather conditions when conducting surveys.
Air exploration is just the beginning. An important factor is the assessment of the outcome of that ventilation: the exchange of O2 and CO2 in the lungs.
2.1 Gas exchange probe Find the ratio between the circulating air volume and 02 consumed in one minute.
Perform inspiratory volume in one minute of ventilation (V then let the patient breathe O2 for one minute, then record the volume of O2 absorbed (VO2) The result V/VO2 increases, as activity increases Early and rapid increase indicates respiratory failure because the patient has to breathe a lot. But relatively little O2 is reabsorbed
The cause is usually poor distribution of inhaled air Or asymmetry between ventilation and gas exchange Due to damage to the alveolar wall, the air can enter the alveolar gas, but it cannot exchange O2 and CO2 through the capillary wall.Currently, to find this phenomenon, people use the method of calculating the exhaled CO2 volume. in one minute by infrared, based on the infrared absorption of CO2. If the exchange of O2 and CO2 is poor, less CO2 is eliminated through the lungs, the infrared solutions of CO2 will be less.
Circulatory failure due to heart failure, O2 supply to the body is less, the patient must breathe more to compensate for the lack of oxygen. h for each lung disease using separate catheters for the two bronchi. This method allows us to assess the respiration in each lung and is useful in the indications for lung surgery.
2.2 Quantification of O2 and CO2 in the blood O2 and CO2 in the blood reflect the results of respiration. In respiratory failure, heart failure O2 decreases and CO2 increases in blood. Arterial blood is taken to determine.
Normal results when, O2: 20-25 volume / 100ml of blood. Saturation rate: 98%. PaO2 = 100mmHg (pressure in the arteries).
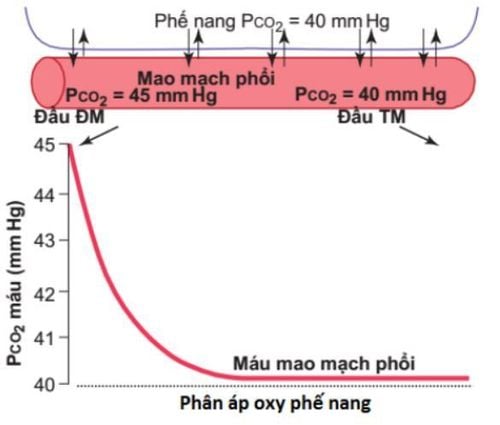
CO2: 56 volume per 100ml of blood. PaCO2 = 40mm Hg (intra-arterial pressure) for Ph = 7.4.
Based on the above results, we can calculate the circulating air volume in the alveoli, that is, the amount of air that has been taken into the alveoli, not useless air, because in the dead space, does not participate in gas exchange in the upper respiratory tract, trachea, large bronchi.
VCO2 x 6863 VA = PaCO2 VA = 2.5 x 31/min VA: volume of air through alveoli in 1 minute (ventilation alveolaire).
VCO2: volume of CO2 exhaled in 1 minute, 0.863 is a constant.
The value of gas exchange exploration. Combined with ventilation exploration, the assessment of gaseous exchange during thought and activity can help detect ventilation disorders with pathological changes in CO2 and O2 in the blood. Ventilation disorder but not accompanied by changes in CO2 and O2 in the blood at rest.
Sự vận chuyển O2 và CO2 trong máu
3. Normal ventilation but with pathological changes of blood gases 3.1 Study of hemodynamic changes Changes in respiratory pathology directly affect O2 absorption and CO2 excretion in the lungs . O2 deficiency leads to increased diastolic pressure and increased activity of the right heart, resulting in right ventricular hypertrophy and failure.
It can be detected by right heart catheterization. Cardiopulmonary and circulatory imaging of the pulmonary artery with contrast, we can also see changes due to respiratory damage, affecting the heart.
We have many types of respiratory function tests, but they all aim to assess ventilation. The result of ventilation or changes in O2 and CO2 affects the cardiovascular system, which is closely related to respiration. It is necessary to coordinate and select exploratory tests for each disease so that when determining the results as well as deciding on the appropriate treatment direction.
Vinmec International General Hospital now stands out with the functions of examination and treatment of common respiratory syndromes and diseases such as pneumonia, bronchitis, asthma, pleural effusion and many other diseases. other. The hospital also performed endoscopic diagnosis and treatment with modern medical methods for respiratory diseases, which not only brought high efficiency but also minimized complications of recurrent disease.
With modern equipment combined with the quality of the team of doctors, highly qualified medical staff has brought success in curing and treating diseases for many cases. Therefore, customers can completely trust when choosing Vinmec hospital for their health visits.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.