This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II, Senior Doctor Doan Du Dat - General Internal Medicine - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International General HospitalIn the human body, platelets are a cell that plays an important role in hemostasis, forming blood clots to protect the integrity of blood vessels.
1. About platelet cells in human blood
Platelets (English name: Platelets or Thrombocytes) are a type of cell in human blood. Platelets are cells without a nucleus, in fact they are a cell fragment of a platelet (megakaryocyte), a type of white blood cell produced in the bone marrow.Platelets are the smallest of all blood cells, when viewed under a microscope, platelets are dark purple spots only 20% the diameter of red blood cells. Platelets are round or oval with biconvex (lens-like) surfaces approximately 2μm in diameter (ranged from 1.2–2.3 μm) with a maximum diameter of up to 3 μm.
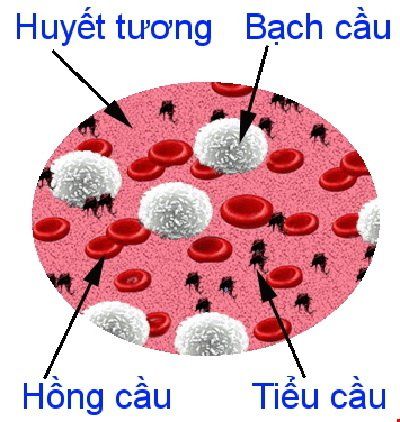
Tế bào tiểu cầu
Therefore, in many cases in which a patient has a complete blood count showing severe thrombocytopenia, a splenectomy may be indicated to reduce platelet destruction.
Xét nghiệm công thức máu để biết số lượng tiểu cầu trong một thể tích máu
2. Normal platelet count in the body
PLT (Platelet Count) – The number of platelets in a volume of blood.The normal number of platelets in the blood is usually about 150,000 to 400,000 platelets/μl of blood (1 μl = 1 mm3), with an average of 200,000 platelets/μl of blood. Each liter of blood contains about 150-400 billion platelets.
Normal platelet count values in the CBC will vary from person to person and will vary depending on the patient's psychological state, gender, age, race and special Therefore, in order to determine that the body is always healthy, we should regularly check blood count tests and general health checks, in order to prevent possible signs of disease. may occur, so that timely treatment can be taken.
A platelet count that is too low can cause bleeding. And the number of platelets is too high, it will form blood clots, obstructing blood vessels that can cause stroke, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, blood vessel blockage,...
Some possible causes leading to an increase/decrease in platelets in the body:
Increase: bone marrow proliferative disorders, idiopathic thrombocytosis, bone marrow fibrosis, after bleeding, after splenectomy, inflammatory diseases. Reduce: bone marrow suppression or replacement, chemotherapy agents, splenic enlargement, disseminated intravascular coagulation, platelet antibodies, post-transfusion purpura, allogeneic thrombocytopenia Infant...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.