This is an automatically translated article.
Carpal rotator cuff tendinitis is a painful inflammation of the tendons in the wrist and thumb. This condition, if left untreated, can make it difficult to use your hands and fingers and limit your wrist's range of motion.1. What is rotator cuff tendinitis?
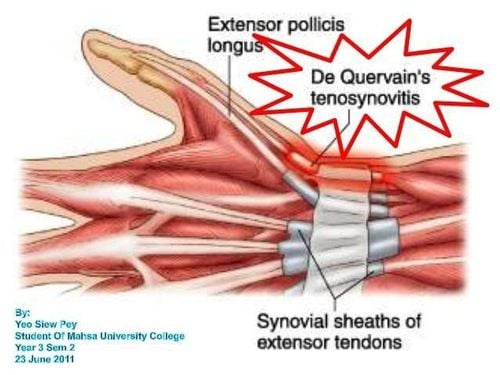
Carpal rotator cuff tendinitis, also known as de Quervain's syndrome, is a painful condition that affects the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist. If you have de Quervain's tenosynovitis, you may experience wrist pain when turning or grasping anything.Although the exact cause of rotator cuff tendinitis is unknown, any activity that relies on repetitive hand or wrist movements - such as working in gardening, playing golf or playing a racquet sport or lifting heavy objects - can all make it worse.
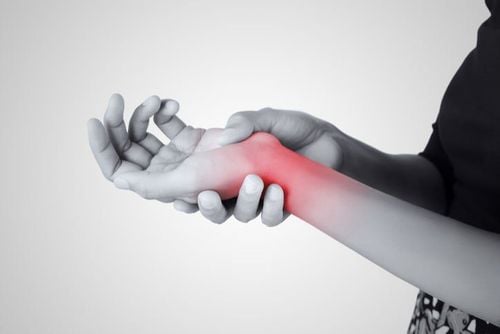
Có thể sẽ bị đau cổ tay khi xoay hoặc nắm bất cứ thứ gì
2. Symptoms of rotator cuff tendinitis
Some symptoms help identify rotator cuff tendonitis:Pain, swelling near the base of the thumb Difficulty moving the thumb and wrist when you are doing something related to grip Pain along the face behind the thumb, directly over the two tendons. This condition can come on gradually or start suddenly. In either case, the pain may radiate to your thumb or up your forearm. You may find it difficult and painful to move your thumb, especially when you try to pinch or grasp objects. The pain may get worse when you move your thumb or wrist.
Cơn đau có thể trở nên tồi tệ hơn khi bạn cử động ngón tay cái hoặc cổ tay.
3. Causes of tendonitis in the rotator cuff region
Excessive wrist movement is thought to be associated with de Quervain's tendon sheath disease.Tendons are rope-like structures that attach muscle to bone. When you grip, grip, pinch, or twist anything in your hand, the two tendons in your wrist and lower thumb slide in a tunnel covered by a tendon sheath. Repeating the same movement often can irritate the sheath around the two tendons, thickening and swelling that limit the tendon's range of motion.
Other causes of de Quervain's tendinitis include:
Direct trauma to the wrist or tendon; Scar tissue can limit movement of the tendon Arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
4. Risk factors for rotator cuff tendinitis
Age: If you are between the ages of 30 and 50, you have a higher risk of developing rotator cuff tendonitis than other age groups, including children Gender: this condition is more common in women Pregnancy: This condition may be related to pregnancy Child care: constant thumb-force use of the baby can be a factor in the development of rotator cuff tendinitis Jobs or hobbies that involve repetitive hand and wrist movements: these activities can contribute to de Quervain's tenosynovitis.5. Diagnosis of tendonitis in the rotator cuff region
To diagnose rotator cuff tendinitis, your doctor will examine your hand to see if you feel pain when you press on the thumb side of your wrist.Your doctor will also perform the Finkelstein maneuver, where you will be asked to fold your thumb into the palm of your hand and fold your fingers over your thumb. Then bend your wrist towards your little finger. If this causes pain in the long and short extensor tendons of the thumb or at the base of the thumb, you may have de Quervain's tenosynovitis.
Bác sĩ sẽ kiểm tra bàn tay để xem bạn có cảm thấy đau khi bị ấn lên cổ tay hay không.
6. Treatment of tendonitis in the rotator cuff region
The goals of treatment are to reduce inflammation, maintain motion in the thumb, and prevent recurrence. If you start treatment early, your symptoms should improve within four to six weeks. If tendinitis begins during pregnancy, symptoms may end around the end of pregnancy or during breastfeeding.Some current treatments include:
Medication: To reduce pain and swelling, your doctor may prescribe an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as ibuprofen , naproxen. Your doctor may also recommend an injection of corticosteroid medication into the tendon sheath to reduce swelling. If treatment is started within the first six months of symptoms, most people make a full recovery from a corticosteroid injection, usually after just one injection. Splints and physical therapy: Your doctor will likely use a splint to keep your thumb and wrist in place. You will wear it 24 hours a day for 4 to 6 weeks. Surgery: If the above treatments don't work, your doctor may recommend surgery to release the tendon sheath so your tendon can move smoothly. This is an outpatient procedure, which means you will go home soon after. After surgery, you'll need to see a physical therapist to do exercises to strengthen your thumb and wrist. Home remedies and lifestyle changes: see your doctor if you think you have de Quervain tendonitis. But try these home remedies to feel better and keep your thumb healthy: Ice the painful swollen area to reduce inflammation. Stop doing anything that makes the condition worse. Avoid repetitive movements and twisting and pinching movements with the wrist and thumb. If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the national health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.