This is an automatically translated article.
Psoriasis is a fairly common dermatological disease. Patients with psoriasis often experience itching, burning pain, discomfort, redness, and peeling of the skin. Psoriasis, if repeated many times, can cause skin infections, arthritis, pustular psoriasis, body redness,...1. Common types of psoriasis
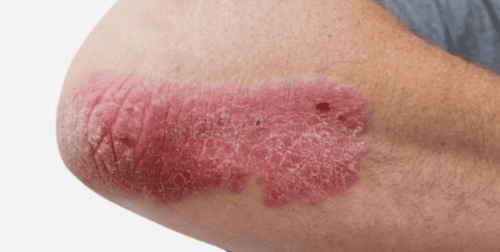
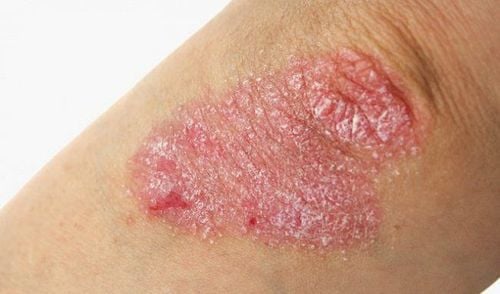
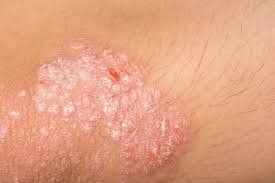
1.1 Plaque psoriasis
This form of psoriasis produces red, inflamed areas of skin; covered with silvery-white scales or plaques. Areas of skin showing this condition are usually found on the knees, elbows, and scalp.
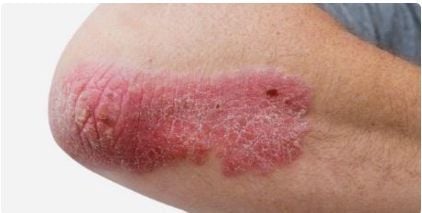
Vẩy nến thể mảng thường xuất hiện ở khuỷu tay
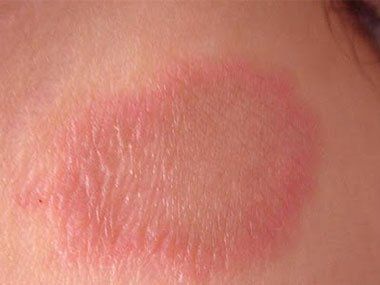
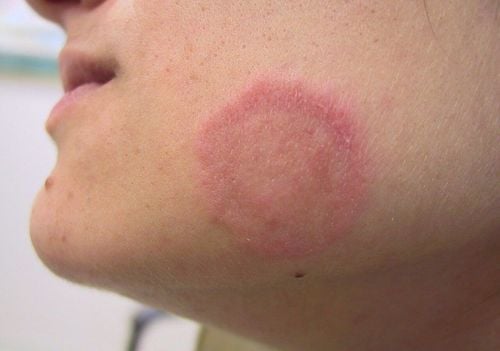
1.2 Droplet psoriasis
Droplet psoriasis causes small pink skin spots. The most common sites for these symptoms are in points like the trunk, arms, and legs. These skin spots are rarely as thick or raised above the surface of the skin as in plaque psoriasis.
1.3 Pustular psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis usually occurs in adults. It causes the skin to become inflamed and white pus-filled blisters appear. This form of psoriasis is usually limited to smaller areas of the skin, like the hands or feet, but can still spread.
1.4 Reversible psoriasis
This form of psoriasis causes inflamed areas of skin that have a bright red iridescent color. These skin areas develop in areas such as the armpits, breasts, groin, or around the folds of the genitals.
1.5 Psoriasis erythrodermic body
This form of psoriasis makes the patient's skin look like it has been sunburned. The scaly areas often peel off in large patches. In patients with erythrodermic psoriasis, fever and severe illness are common. It can be life-threatening, see your doctor right away if you start to notice symptoms.
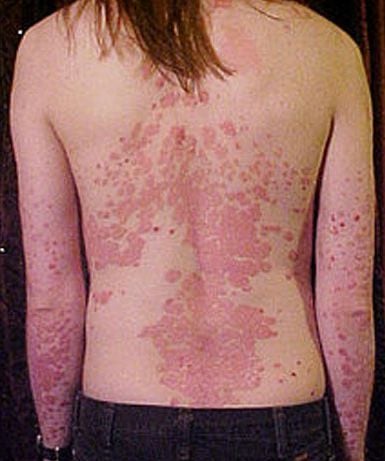
Vảy nến thể đỏ da toàn thân gây nguy hiểm đến tính mạng
2. Is psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis is a skin disease, so it cannot be passed from person to person. Touching a part of a psoriasis lesion on a person's body will not make the person sick.
3. Causes of psoriasis?
3.1 Immune system
Autoimmune diseases result when the body attacks itself. In the case of psoriasis, a type of white blood cell called a T-lymphocyte mistakenly attacks skin cells.
In a normal person's body, white blood cells are deployed to attack and destroy invading bacteria and to antagonize infection.
In the case of psoriasis, these cells mistakenly cause an overproduction of skin cells. This causes new layers of skin cells to grow too quickly, to be pushed to the surface of the skin and to begin to pile up with other skin cells. The effects on skin cells also cause red inflamed areas to develop.

Tế bào lympho T tấn công nhầm vào các tế bào da gây ra bệnh vẩy nến
3.2 Genetic factors
If someone in your family has psoriasis, your chances of getting it are higher. Approximately 2 to 3% of people have hereditary psoriasis, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF).
4. Psoriasis Triggers
The most common psoriasis triggers are:4.1 Alcoholic beverages
Alcohol with strong alcohol content can cause psoriasis flare-ups. If you are using alcohol excessively, psoriasis flares will occur more often.
4.2 Drugs
Some medications are thought to trigger psoriasis. These drugs include:
Lithium Antimalarials Blood pressure medications

Một số loại thuốc được cho rằng là gây kích hoạt bệnh vảy nến
4.3 Infections
If you are sick or fighting an infection, your immune system will go into overdrive fighting the infection. This will make an outbreak more likely. Strep throat is also often a trigger for psoriasis.
5. Diagnosis of Psoriasis
There are 2 tests or tests needed to diagnose psoriasis.
5.1 Clinical examination
During this physical exam, show the doctor all the problem areas. Also, let your doctor know if anyone in your family has psoriasis.
5.2 Biopsy test
If the symptoms are still unclear or the doctor wants to confirm their diagnosis, they may take a small sample of the patient's skin for biopsy.

Xét nghiệm sinh thiết chẩn đoán bệnh vảy nến
6. Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Psoriasis has no cure. Treatments often aim to reduce inflammation and scab formation, slow skin cell growth, and remove scaly patches. The forms of psoriasis treatment are usually divided into 3 types:
6.1 Topical drug treatment
Topical creams and ointments that are applied directly to the affected area of the skin can be very helpful in alleviating the severity of mild to moderate psoriasis.
Topical medications used to treat psoriasis are:
Topical corticosteroids Topical retinoids Anthralins Vitamin D and the like Active ingredients salicylic acid Moisturizers

Kem dưỡng ẩm giúp điều trị bệnh
6.2 Immunosuppressive drugs
These drugs include:
Methotrexate Immunosuppressants sandimmune Biologics Retinoids
6.3 Phototherapy
This psoriasis treatment uses ultraviolet (UV) or natural light. Sunlight helps destroy overactive white blood cells that are damaging skin cells and causing skin cell growth too quickly. Both UVA and UVB rays can be helpful in reducing symptoms of mild to moderate psoriasis.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as if you need to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.