This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Le Van Linh - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital and Master, Doctor Tran Lam Khoa - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec International General Hospital Central Park .Placental edema is a serious, life-threatening condition in which the fetus has an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the tissues around the heart, lungs, abdomen, or under the skin.
1. What is placental edema?
Placental edema is a condition in which the fetus has fluid accumulation in 2 or more body cavities or 1 cavity with skin edema, which can be caused by abnormalities such as: abnormalities of the heart, digestive tract, thoracic cavity, fetal blood transfusion. fetus in twins...Placental edema has a relatively low incidence, occurring in 1/1000 births. If you're pregnant and your baby is diagnosed with placental edema, your doctor may order early labor. However, even with treatment, more than half of infants with placental edema die shortly before or after birth.
2. Classification of placental edema
There are two types of placental edema: immune and non-immune. They depend on the cause of the placental edema.Non-immune placental edema is the most common type. Example:
Severe anemia, including thalassemia Fetal bleeding Fetal bleeding with heart or lung defects Genetic and metabolic disorders, including Turner syndrome and Gaucher disease Viral and bacterial infections such as Parvovirus B19, Cytomegalovirus (CMV), toxoplasmosis, syphilis, and herpes Vascular malformations Tumors Immune placental edema usually occurs when the blood types of the mother and fetus are incompatible, also known as Rh factor incompatibility. . If you are Rh negative and have an Rh positive baby, your immune system will attack the baby's red blood cells. This causes anemia. This type of placental edema is uncommon today because Rh-negative women are often treated with Rh immunoglobulin to prevent this problem.
3. Symptoms of placental edema
A pregnant woman may experience the following symptoms if the fetus has placental edema:Polyhydramnios Thick placenta The fetus may also have an abnormally large spleen, heart or liver and can be observed fluid surrounds the heart or lungs on ultrasound.
A baby born with placental edema may have the following symptoms:
Pale skin Bruising Swelling (edema), especially in the abdomen Abnormally enlarged liver and spleen Difficulty breathing Severe jaundice
4. Diagnosis of placental edema
Diagnosis of placental edema is usually made during fetal ultrasound. Your doctor may notice that your baby has placental edema during routine ultrasound scans. Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to take pictures directly inside the body. You may also have an ultrasound during your pregnancy if you notice your baby moving less often or you experience other pregnancy complications, such as high blood pressure.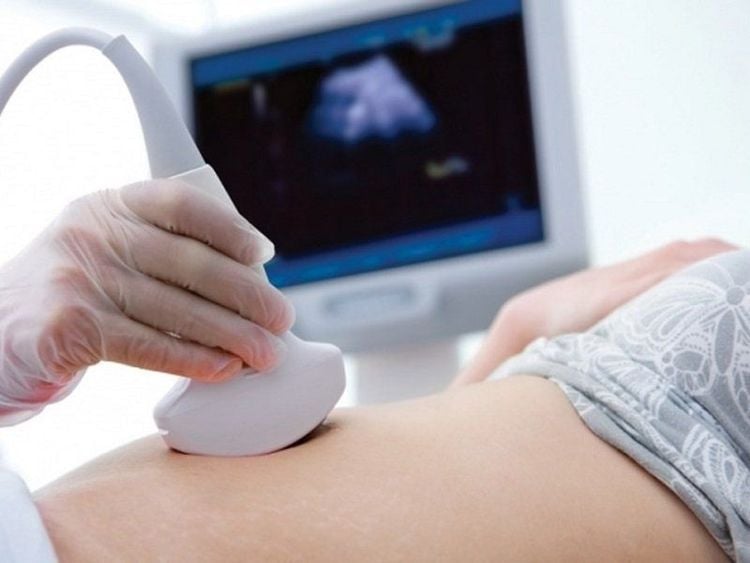
Siêu âm thai: Chẩn đoán tốt nhất bệnh phù nhau thai
Fetal blood test Amniocentesis Amniocentesis Fetal echocardiography to check for structural defects of the heart.
5. Is placenta edema dangerous?
When diagnosed with placental edema, the pregnant woman will be asked to terminate the pregnancy, because she cannot continue to nourish the fetus. Otherwise, the fetus may still die in the womb after a while. In case the baby is born, the baby often cannot live because of premature birth or comorbidities, besides the mother is prone to bleeding, hypertension, preeclampsia, eclampsia because the uterus is too large and must contain the placenta with the edematous fetus.Therefore, in cases where the fetus is diagnosed with placental edema, the mother must go to a medical facility with adequate emergency equipment to prevent dangerous complications that may occur.
6. Treatment of placental edema
Placental edema usually cannot be treated during pregnancy. In some cases, your doctor may give your baby a blood transfusion (intrauterine fetal blood transfusion) to help increase the chances that the baby will survive until birth.In most cases, the doctor will induce labor early to give the baby the best chance of survival. This is done with medication that induces early labor or an emergency cesarean section.
Once the baby is born, treatment can be used such as:
Using a needle to remove excess fluid from the space around the lungs, heart, or abdomen (thoracic cavity) Assisted breathing with a ventilator breathing Use medication to control heart failure
Sử dụng thuốc đối với bé để kiểm soát suy tim
The risk of death is higher for fetuses diagnosed with placental edema very early (less than 24 weeks of age) or those with structural abnormalities, such as structural heart defects.
To prevent placental edema, pregnant women should not smoke, drink alcohol and get vaccinated before pregnancy such as flu, measles and rubella vaccine, .. Go to the doctor and monitor the pregnancy regularly period at prestigious and highly specialized medical facilities.
Placental edema is a disease that can be detected early in routine ultrasounds. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is implementing a package Maternity service, helping pregnant women to feel secure in monitoring, periodic examination, early detection of fetal abnormalities (if any) and Careful care during labor and delivery. With a team of doctors with rich expertise, experience wholeheartedly for the health benefits of patients will bring satisfaction to you!
Master, Doctor Tran Lam Khoa is trained and used to specialize in fetal medicine and prenatal diagnosis at Necker Hospital - Prenatal diagnosis center - Fetal intervention and treatment center France's largest. This is also the place where difficult and complicated diseases are concentrated with the world's leading professors of fetal medicine and fetal intervention. Currently, Doctor Khoa is working at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital, he will directly diagnose, treat, and intervene in fetuses to bring healthy babies and bring happiness to parents. future mother.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com