This is an automatically translated article.
Labor does not always start spontaneously, but through the intervention of a doctor. This procedure is called labor induction.
1. What is labor induction?
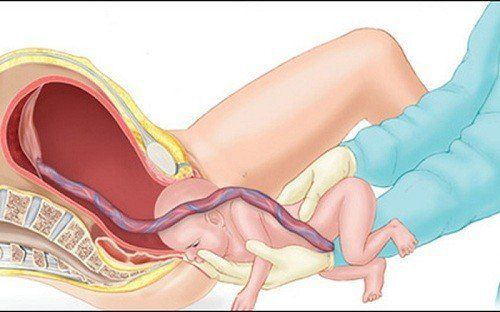
Labor is a progressive process of many phenomena, the most important of which is uterine contractions that make the cervix clear, resulting in the expulsion of the fetus and placenta.
Induction of labor is a process by which the doctor will stimulate uterine contractions to help a woman give birth vaginally. The mother's pregnancy usually ends at 38-40 weeks, at this time, the mother will have uterine contractions, signaling the beginning of labor and the baby is about to be born. However, in the case of women who do not have labor pain even after the due date has passed. Doctors are required to perform labor induction procedure, induce labor to end the pregnancy.
Certain medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, heart or lung problems in the mother can also cause the doctor to perform the induction of labor. If there are any signs of fetal distress or stillbirth, as well as if you live too far from the hospital or have a history of rapid labor, your doctor may also recommend this method. These are just a few of the common reasons a doctor might need to induce labor.
The success of labor induction for vaginal delivery will depend on many factors, one of which is the dilation and clearance of the cervix. If a woman's cervix has a greater dilation and clearance, the more likely it is to have a vaginal birth. Your doctor may prescribe medication to ripen the cervix before induction of labor.
This procedure is usually done in the hospital's Delivery Room to help the doctor monitor the fetus before the induction of labor to make sure the baby's condition is stable.
Induction of labor fails when the mother's uterus is unresponsive to stimulation or when the uterus has an abnormality that endangers the woman or the cervix is not dilated.

2. Why induction of labor?
Normally, labor is a process where uterine contractions occur, causing the cervix to gradually dilate, resulting in the pregnancy and placenta being expelled. By what mechanism this labor occurs, is not yet understood exactly, so it is impossible to predict with accuracy, but in labor related to the hormonal system is stimulated, changes in neurology, endocrinology, and other local mechanical factors that induce labor, manifests spontaneous uterine contractions, causes maternal pain, and regular contractions increasing day by day.
In cases where it is necessary to terminate the pregnancy to ensure the safety of both the fetus and the mother, if the fetus continues to be maintained in the mother's womb, the mother's and the fetus's life will be threatened as The old and degenerated placenta cannot guarantee the role of providing nutrition to the fetus. The cause of the fetus causes serious illness for the mother. The fetus cannot be maintained in the mother's womb due to severe illness or severe birth defects.
Induction of labor is recommended when the health of the mother and fetus is at risk. In special cases the induction of labor is done for no medical reason, such as the woman who lives far from the hospital. This situation is called elective induction of labor. Selective induction of labor is not performed before 39 weeks of pregnancy.
Trắc nghiệm: Đặc điểm cơn đau đẻ và diễn biến cuộc chuyển dạ
Cơn đau đẻ là dấu hiệu thông báo sự chào đời của em bé. Cùng thử sức với bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp các bà mẹ mang thai nhận biết cơn đau đẻ và diễn biến cuộc chuyển dạ để chuẩn bị trước tâm lý những gì sắp xảy ra đối với mình.The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Tạ Quốc Bản , Sản phụ khoa , Khoa Sản phụ khoa - Bệnh viện Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Phú Quốc
3. Measures to induce labor
This depends largely on the state of the mother's cervix at that time. If your cervix hasn't started to soften or dilate (open) yet, your body isn't ready for labor.
In that case, the doctor will use medical or "mechanical" methods to ripen the cervix before inducing labor.
Here are labor induction methods that can be flexible for each specific case.
3.1. Amniocentesis Amniocentesis is considered to be one of the most natural methods of labor induction (actively acting to induce uterine contractions when spontaneous labor is not possible).
This method is to stimulate the production of prostaglandins - hormones that help contractions occur. The technician inserts a gloved finger into the cervix, moves the finger in a circular motion, and separates the thin membrane that connects the amniotic sac to the uterine wall.
Amniotomy is a simple method of inducing true labor. This method is even indicated not for any special medical reasons, but simply because the due date is so close. However, this method of intervention still contains certain risks.
3.2. Amniocentesis The method of amniocentesis can only be performed when the cervix is dilated, by using a long needle or a Kocher stick to puncture the amniotic membrane, then using a finger to widen the amniotic membrane. Amniocentesis can be performed alone or in combination with oxytocin infusion.
Assess the amount and color of amniotic fluid, if the amniotic fluid is clear, continue to monitor the mother for normal delivery, and if the amniotic fluid is green with meconium, it is necessary to have a cesarean section immediately.
Need to monitor the fetal heart rate before and immediately after performing amniocentesis, if the fetal heart rate is normal, continue monitoring, and if the fetal heart rate fails (too fast or too slow), the doctor needs to have an immediate treatment plan. to avoid asphyxia.
3.3. Foley Ball This is a method of inserting a Foley catheter through the opening in the cervix. Inject 10 ml of 0.9% saline serum to inflate the rubber balloon to apply pressure to help the cervix clear and open. When the cervix is dilated to 3 cm, the catheter will slide out on its own and labor is initiated. May be combined with intravenous oxytocin if necessary.
This method used to be used to terminate large pregnancies, but is rarely used now due to the introduction of more superior drugs to help pregnant women go into labor more easily.
3.4. Prostaglandins This is a method of using local medicine to induce labor by having the woman put this medicine in the vagina or under the tongue. Prostaglandin works to help the cervix ripen and soften, making labor faster and easier. The drug commonly used today is misoprostol.
Insert into the posterior vaginal bag at a dose of 50 mcg every 3 hours, up to a maximum of 6 doses or 25 mcg every 3 hours, up to 8 doses or orally 50 mcg every 4 hours.
Currently, the drug is recommended to use Prostaglandin only in cases of stillbirth or severe birth defects. Should not be used in cases of pregnancy beyond the date, severe intrauterine growth retardation. Uterine contractions should be monitored on obstetric monitoring.
3.5. Amniocentesis combined with oxytocin infusion Oxytocin will be prescribed to be mixed into an infusion bottle and given slowly intravenously to the mother to stimulate uterine contractions. Next, when the cervix is dilated enough, the doctor will press the amniotic fluid, tearing the amniotic membrane wide.
Monitor and adjust the number of infusion rates as ordered to achieve the right number of contractions as labor progresses.
In addition, depending on the situation of the delivery, if the contractions are quick, give oxytocin slow flow or it can be combined with tocolytic drugs that have a softening effect on the cervix.
A leader delivery is considered successful when contractions are regular, fetal heart rate is good, position is fully dilated and cervix is fully dilated, it is possible to deliver a vaginal delivery and remove a healthy fetus.
3.6. Nipple stimulation Nipple stimulation stimulates the pituitary gland to release oxytocin. This method is effective if the cervix is already convenient.
Can be done by stimulating the areola on each side for about 5-30 seconds, about 2-3 minutes, stopping stimulation when there is a uterine contraction.
4. Risks associated with induction of labor
With some methods, a pregnant woman's uterus can be overstimulated, causing uterine contractions to become too frequent. Too many contractions can lead to changes in the baby's heart rate, umbilical cord problems, and other problems. Other risks of cervical ripening and induction of labor may include the following complications:
Infection in mother and baby Uterine rupture Increased risk of cesarean section Fetal death. Certain medical conditions discovered before pregnancy or occurring during pregnancy can also contribute to the occurrence of these complications.
All methods of labor induction have strict indications and contraindications. In addition, when performing these methods, they must be performed in medical facilities capable of surgery. Because induction of labor does not always make it possible for a pregnant woman to have a normal delivery, when it fails or has a variable pregnancy, the woman must be transferred to a cesarean section immediately to ensure the life of the pregnant woman and the fetus.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a package maternity service as a solution to help pregnant women feel secure because of the companionship of the medical team throughout the pregnancy. When choosing Maternity Package, pregnant women can:
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of qualified doctors Regular check-up, early detection of abnormalities Maternity package helps to facilitate the process. birthing process Newborns get comprehensive care
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.