This is an automatically translated article.
Susceptibility is when the body's immune system is stimulated to produce antibodies against pathogens. So what is hypersensitivity disease, including what types of hypersensitivity?
1. What is hypersensitivity?
When pathogens enter the body, the immune system will be stimulated to produce antibodies against the pathogen, which is the body's specific defense measure, called sensitization. Depending on the pathogenesis and location of the pathogen, the immune system will have an appropriate sensitization method.2. Methods of sensitization
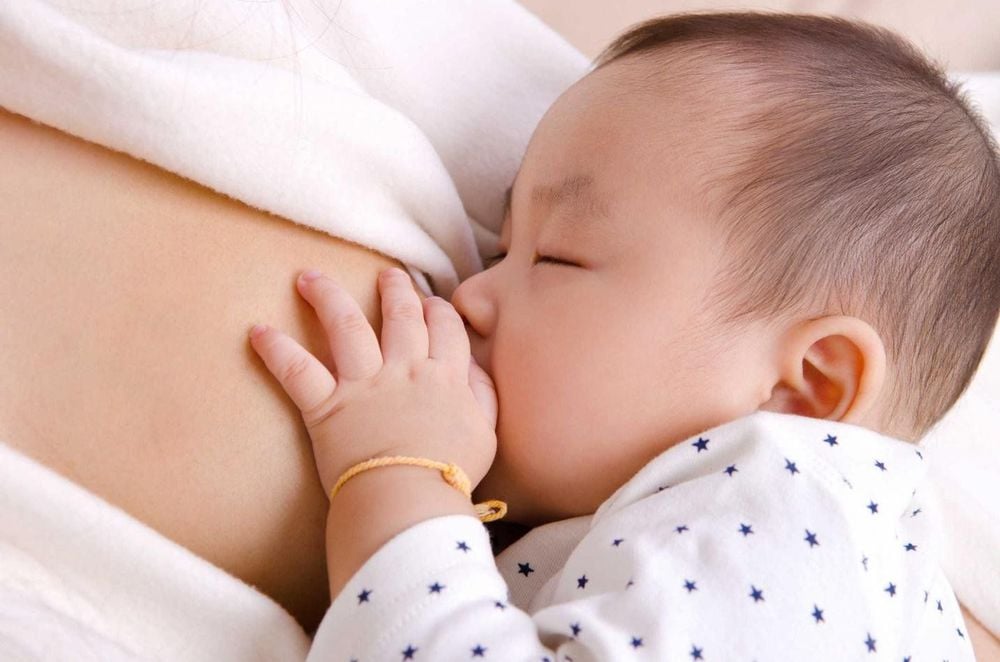

Miễn dịch thụ động tự nhiên được truyền từ mẹ cho thai nhi thông qua sữa non
Specific immune mechanisms of the body are formed by active sensitization or passive sensitization. Both types of sensitization occur naturally or artificially.
2.1 Passive sensitization
Passive sensitization is the body's immunity that is acquired but does not require exposure to antigens.
Passive immunity is obtained by transferring serum (or gamma globulin) from an immune person to a non-immune person. Or use sensitized individuals to create immune cells and transfer those cells to non-immune people. Natural Passive Immunity: Immunity transmitted from mother to fetus through the placenta (IgG) or through colostrum (IgA). Artificial Passive Immunity: The transmission of antibodies from an already immune person or animal to a person who is not immune. This sensitization measure is usually applied in situations of acute prophylactic treatment of certain diseases such as measles, tetanus, diphtheria, rabies, or poisoning by insects, meat foods, .. Both antibodies from Both humans and animals are effective and help to provide immediate immunity, but heterologous antibodies often cause anaphylaxis and pathological complications, and the duration of effect is short. Meanwhile, allogeneic antibodies carry the risk of transmitting diseases such as HIV, hepatitis, ....

Mẫn cảm là hệ miễn dịch của cơ thể được kích thích để tạo ra kháng thể chống lại tác nhân gây bệnh
2.2 Active sensitization
Active sensitization is the body's immunity that is formed after exposure to an antigen.
Natural Active Immunity: The body produces antibodies in an immune response to protect and fight the pathogen after being exposed to a pathogen that causes an infection but has not yet shown symptoms, or shows signs of infection. show clinical symptoms. Artificial Active Immunity: The body produces antibodies in an immune response to protect and fight a pathogen after exposure to a dead, or living pathogen or its components. . This active sensitization measure is vaccination including live attenuated vaccines, inactivated vaccines, subunit vaccines, and toxoid vaccines. Vaccination can confer lifelong protective immunity against some diseases such as tuberculosis, measles, mumps, rubella, chickenpox,. .. or it can also last for several months. In addition, another method of increasing the immune response is the injection of antigens that have been weakened by the addition of adjuvants, which are chemical and biological agents.
3. Vaccines used for artificial active sensitization
Vắc-xin sống giảm độc lực có thể làm tăng nguy cơ gây bệnh đối với người bị suy giảm miễn dịch
3.1 Live attenuated vaccines
Live attenuated vaccines contain live bacteria, viruses, and pathogens that have been attenuated to produce immunity, including humoral immunity. and cell-mediated immunity.
However, sensitization using live attenuated vaccines may increase the risk of disease in immunocompromised individuals.
Live attenuated vaccines prevent viral infections such as tuberculosis, measles, chickenpox, mumps, rubella, hepatitis A, yellow fever, ...
3.2 Inactivated vaccines
Vaccines Inactivated bead contains dead virus, which is inactivated by heat, chemicals or ultraviolet light. Inactivated vaccines prevent diseases such as polio, influenza, rabies, cholera, typhoid, whooping cough, plague, ....
3.3 Antitoxin vaccine
Virus subunit vaccine Reduces the toxicity of viral toxins and antigens required for immunity. This sensitization measure is less effective than live attenuated vaccines. Subunit vaccines prevent diseases such as diphtheria , tetanus , ...
4. Effects of artificial active sensitization
Tiêm vắc-xin để phòng ngừa tác nhân gây bệnh
Most active artificial sensitization measures are used for prophylaxis, i.e. vaccination to prevent pathogens. However, in some cases, such as rabies, a vaccine can be used to treat it after the body is attacked by the virus that causes the disease. Depending on the following conditions, this sensitization method will have different efficacy:
Pathogenicity mechanism Incubation time Rate of pathogen replication
5. Side effects of artificial active sensitization
Artificial active hypersensitivity by vaccination can cause some side effects such as:
Fever Fatigue Irritability. Joint pain, arthritis (rubella) Convulsions, death (whooping cough) Neurological disorders (flu). Sensitization is the body's way of creating an immune response to protect against pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, ...
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you must You can contact the Vinmec Health System Hotline nationwide, or register for an online examination HERE.