This is an automatically translated article.
For babies, there are birth defects that no one wants, among which is hirschsprung disease. So what is hirschsprung disease, is it dangerous and how is it treated?
1. What is Hirschsprung's disease?
Hirschsprung's disease is a birth defect in which nerve cells are missing at the end of a child's intestines. Normally, the gut contains many nerve cells along its length that control how the intestines function. When the intestines are deprived of neurons, it no longer functions well. This damage causes a blockage in the intestine because stool does not move through the intestines normally.
Usually, the areas that lack neurons are the rectum and sigmoid colon. However, some children are missing the nerve cells for the entire colon or part of the small intestine.
In short-segment Hirschsprung disease, nerve cells are missing from the last part of the large intestine.
In long-segment Hirschsprung disease, nerve cells are missing from most or all of the large intestine and sometimes the last part of the small intestine. Rarely, neurons are missing in the entire large and small intestine.
In children with Hirschsprung's disease, stool moves through the intestines until it reaches the part where the nerve cells are missing. At that point, the stool movement slows down or stops.
2. What causes Hirschsprung's disease?
During the baby's early development in the womb, nerve cells stop growing towards the end of the baby's intestines causing Hirschsprung's disease. Scientists believe that genetic defects can increase the risk of Hirschsprung disease in children. However, there is no test that can screen for a baby's hirschsprung disease while the mother is pregnant. Scientists are studying whether a mother's health or lifestyle history during pregnancy increases the chances of her baby developing Hirschsprung's disease.
Hirschsprung's disease occurs in about one out of every 5,000 newborns. Children with Down syndrome and other medical problems, such as congenital heart defects, are at much higher risk. For example, about one in 100 children with Down syndrome also has Hirschsprung disease.
Hirschsprung disease is congenital, or is present at birth. However, the symptoms may or may not be obvious. If you have a child with Hirschsprung disease, you are more likely to have children with Hirschsprung disease than people who do not have children with Hirschsprung disease. Also, if one parent has Hirschsprung disease, there is a higher chance that their child will have Hirschsprung disease.
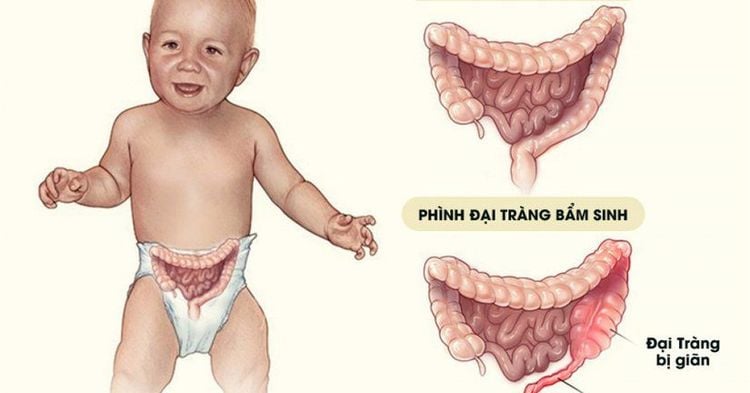
Hirschsprung là một bệnh lý bẩm sinh gặp ở trẻ sơ sinh
3. What are the signs and symptoms of Hirschsprung's disease?
The main signs and symptoms of Hirschsprung's disease are constipation or bowel obstruction, which usually appears soon after birth. Many otherwise healthy infants and children also show signs of having trouble passing stools. However, unlike healthy children and infants, children with Hirschsprung's disease usually do not respond to constipation medications that are given by mouth. Usually, an infant or child with Hirschsprung disease will have other symptoms, including
Slower growth Stiffness, bloating, Unexplained fever Vomiting Symptoms can vary from child to child, but the This change was independent of the number of missing intestinal neurons. Regardless of where in the intestines is missing nerve cells, once stool reaches this area, a blockage will form and the child will develop symptoms.
Symptoms in infants. An initial symptom in some infants is the absence of the first bowel movement within 48 hours of birth. Other symptoms may include:
Green or brown vomit Diarrhea, often bloody Symptoms of Hirschsprung disease in toddlers and older children may include: inability to pass stools no enema or suppository, abdominal swelling, diarrhea, often bloody, slow growth.
4. How do I know if my child has Hirschsprung disease?
Usually, the doctor will know if your baby has Hirschsprung disease based on: your baby's physical examination, family medical history, symptoms, test results...
If your doctor suspects If they suspect Hirschsprung disease, they may refer your child to a pediatric gastroenterologist for further evaluation. Some commonly used medical tests are:
Rectal biopsy A rectal biopsy is a procedure that involves taking a small sample of tissue from the rectum for microscopic examination. Rectal biopsy is the best test to diagnose or rule out Hirschsprung disease.
Abdominal X-ray An X-ray is an image created using radiation and recorded on film or on a computer. Your child will lie on a table or stand while an abdominal X-ray is taken so that a bowel obstruction can be seen.
Anorectal pressure Anorectal manometry is a test that uses a pressure transducer to measure how well a child's rectum is functioning. During surgery, your doctor will inflate a small balloon inside your child's rectum. Normally, a child's rectal muscles relax. Otherwise, your doctor may suspect Hirschsprung disease.
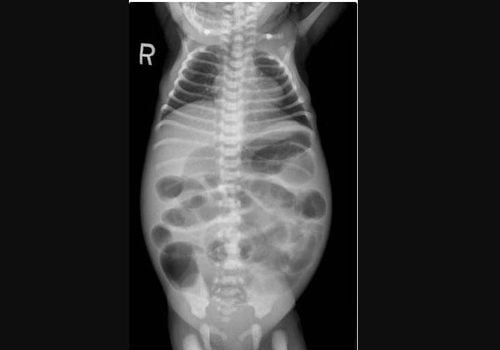
X quang bụng trẻ bị bệnh Hirschsprung
5. How is Hirschsprung's disease treated?
Hirschsprung's disease is a life-threatening disease and the current treatment is applied mainly surgical repair by bringing the intestine with normal nerve ganglia to the anus with preservation of the anal sphincter . Children who have surgery for Hirschsprung's disease will often feel better and grow better physically.
However, some children may experience complications or problems after surgery such as: anal stenosis, constipation, diarrhea, fecal leakage from the anus, enteritis. Usually, these problems will improve over time with your doctor's guidance.
6. Nutrition and precautions with Hirschsprung disease
If the surgeon removes the child's colon, the child will need to drink more fluids to compensate for the loss of water and prevent dehydration. They also need twice as much salt as a healthy child. The doctor can measure the sodium in the child's urine and adjust the child's diet to make sure enough salt is replaced.
Some babies may need a tube feeding for a while. A feeding tube is a passageway for a baby to receive formula or liquid food directly into the baby's stomach or small intestine. In this case, the doctor will insert a feeding tube through the nose.
For your child's health, always consult reputable doctors and medical facilities to properly understand hirschsprung disease as well as accompany your child.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.