This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Pham Thi Yen - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Endometrial hyperplasia is a common obstetric and gynecological disease in women, especially in pre- and post-menopausal age. Although the disease can be benign, there are still a large number of endometrial hyperplasia that progress to cancer. Endometrial hyperplasia is also a factor affecting female fertility. So what is endometrial hyperplasia and how is it treated?
1. What is endometrial hyperplasia?
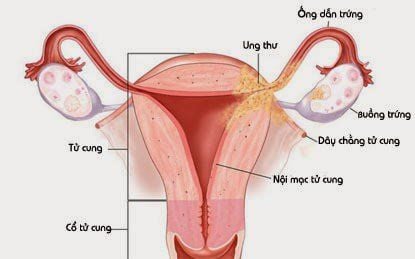
The endometrium is a structural layer of the uterus. From the outside to the inside, the uterus has three layers: the peritoneal layer, the muscular layer, and the endometrium. The endometrium is a glandular epithelium consisting of two layers: a thin basal layer that changes little with the menstrual cycle, a superficial layer that changes with the menstrual cycle, and sheds during menstruation.
Endometrial hyperplasia (also called endometrial hyperplasia) is the proliferation of glands of irregular size and shape, accompanied by an increased gland/stromal ratio. In simpler terms, endometrial hyperplasia is a condition in which the endometrium or lining of the uterus increases the production of cells leading to excess, causing the endometrium to become too thick.
2. What is the mechanism of endometrial hyperplasia?
Normally, the lining of the uterus has the ability to change during the menstrual cycle according to hormonal changes. At the beginning of the cycle, the hormone estrogen (secreted by the ovaries) helps the endometrial lining to grow and thicken. Next to the middle of the cycle, an egg is released from the ovary causing ovulation, at which time the hormone progesterone begins to develop, preparing for the endometrium to receive and nourish the fertilized egg. If the egg is not fertilized, estrogen and progesterone levels gradually decrease. When the level of the hormone progesterone begins to decrease, it will cause a menstrual period, also known as mucosal shedding.
Thus, endometrial hyperplasia occurs due to an excessive amount of estrogen but a lack of progesterone. The hormone progesterone is not produced, so the endometrium does not shed, but continues to increase in response to estrogen. The cells of the endothelium can accumulate together and become abnormal. Endometrial hyperplasia is benign or can progress to cancer.
3. What are the symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia?
Bleeding when your period is heavier or lasts longer than usual; Menstrual cycle shorter than 21 days. Bleeding after menopause. Classification of endometrial hyperplasia The World Health Organization divides endometrial hyperplasia into 4 large categories, in which:
Typical hyperplasia (no atypical cells means no nucleated cells). malformation or abnormal division) has 2 types: Simple hyperplasia; Complex hyperplasia (structural changes)
Atypical hyperplasia h (with atypical cells) has 2 types: Simple atypical hyperplasia; Complex hyperplasia atypical (with atypical structure and cytology)
Risk of endometrial hyperplasia turning into endometrial cancer:
Simple hyperplasia: 1% Complex hyperplasia: 3% Atypical simple hyperplasia: 8% Atypical complex hyperplasia: 30%
4. Diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia
In fact, there are many causes of abnormal uterine bleeding. In the case of abnormal bleeding in women over 35 years of age or women under 35 years of age with bleeding that does not go away with medication, your doctor may now order you to perform diagnostic tests for endometrial hyperplasia and Cancers include:
Transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus to measure the thickness of the endometrium. Endometrial biopsy to remove tissue from the endometrium and examine under the microscope, detect endometrial cancer (if any).
5. Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia
Treatment options for endometrial hyperplasia will vary depending on your age and the type of hyperplasia you have.
In many cases of typical hyperplasia, the patient is treated medically with a progestin. Progestin can be taken orally, intramuscularly, intrauterine device, or vaginal cream. Particularly for premenopausal and postmenopausal people with complex hyperplasia (typical type), hysterectomy may be considered. Progestin treatment can cause vaginal bleeding that resembles a menstrual period.
If the patient has atypical endometrial hyperplasia, especially complicated atypical hyperplasia, the risk of cancer is increased (30%). If the patient has had enough children and does not want to have more children, the doctor will remove the uterus because this is the best treatment option. But if the woman is young, has not had children or wants to have more children, at this time, she will try to treat with drugs, if the condition does not improve, the uterus will be removed. When endometrial hyperplasia is too much of a risk, hysterectomy becomes a life-or-death option. At this time, patients should consider choosing a very experienced doctor because if there is a complication, it will be very serious.
Laparoscopic appendectomy at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital is an optimal choice to solve pathological appendages, with a fast recovery time compared to laparotomy and minimal use of antibiotics. born according to the antibiotic prophylaxis regimen in surgery.
Vinmec Hai Phong has the most modern equipment in Vietnam, anesthesia machine in the operating room, clean operating room system, always applying the most advanced treatment techniques in the world, a team of experienced specialists. including:
Doctor of CKII Pham Thi Tuyet Mai: Over 30 years of experience in examination and treatment in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Doctor CKII Tran Thi Mai Huong: Has 25 years of experience in examination and treatment in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology, lower tract surgery, laparoscopic surgery. Doctor CKI Pham Thi Yen: Has 11 years of experience in examination and treatment in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Doctor CCII Bui Thi Thu : Has 25 years of experience in examination and treatment in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology Dr. Tran Thi Thanh Huyen . Thanks to the most modern equipment in Vietnam such as anesthesia machine in the operating room. The procedures are carried out seriously (before surgery must be fully timed out before surgery...), people are regularly urged to check, and always update the latest regulatory procedures in the world. ... Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital is the address for the treatment of gynecological diseases in general, chosen by a large number of customers.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.