This is an automatically translated article.
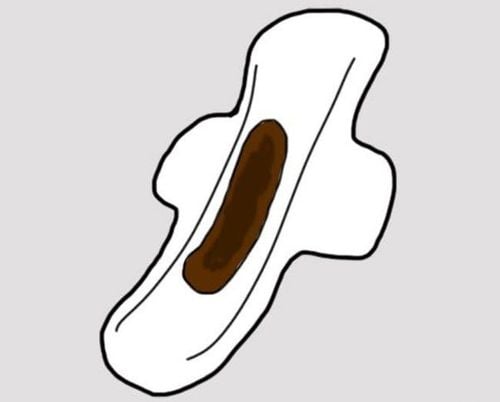
Menopause is the loss of menstrual periods in a woman for 1 year with an average age of about 51 years. In particular, bleeding after menopause is one of the unusual signs for a woman's health. Vaginal bleeding after menopause may signal benign endometrial hyperplasia, more dangerously, endometrial cancer.1. What is postmenopausal blood?
Menopause is the period in which a woman permanently stops menstruating with the definite sign of amenorrhea that persists within 12 months of the last menstrual period. The mean age of menopause was 51 years and the cut-off was between 45 and 55 years.
During this period of menopause and after menopause, a woman's body undergoes changes in both exocrine and endocrine dysfunction. Specifically, for the decline in exocrine function, the woman will have atrophy of the follicle leading to a decrease in ovarian follicle reserve. As for the endocrine function, the lack of estrogen during this period will lead to the symptoms of menopause.
The consequences of menopause are complex, including vasomotor disorders, mood disorders, urogenital atrophy, skin atrophy, osteoporosis, cardiovascular problems, and body metabolism disorders. ..
Among the above disorders, bleeding after menopause is a dangerous sign that any woman should pay attention and not ignore. A sign of this condition is abnormal vaginal bleeding during post-menopause that a woman may think of as cases such as the return of menstrual periods after menopause, menopause but then return. or some patients get their period again 2 years after menopause. But all of the above are defined as postmenopausal bleeding and it is a postmenopausal disease that a woman should be diagnosed and treated properly.
2. Causes of bleeding after menopause
Some causes of postmenopausal bleeding include:2.1. Uterine polyps
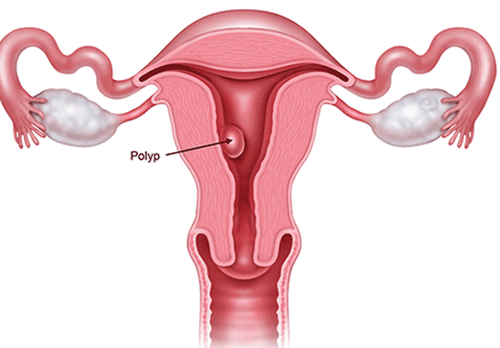
Polyp tử cung là lành tính nhưng cũng rất nguy hiểm
These are tumors located in the uterus, cervix, and uterine tubes but are not gynecological cancers. Uterine polyps are benign but also very dangerous, requiring surgical removal to prevent bleeding in a postmenopausal woman.
2.2. Endometrial atrophy or thinning of the endometrium is caused by a decrease in estrogen levels, so the tissue lining the inside of the uterus becomes thinner and leads to vaginal bleeding. This condition is usually treated with medication and hormone pills.
2.3. Endometrial thickening: Menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, hair loss, and vaginal dryness can, after treatment, lead to thickening of the endometrium or endometrial hyperplasia, causing bleeding after menopause and it can be treated with hormone-regulating drugs.
2.4. Gynecological cancer Gynecological cancer here is endometrial cancer along with the malignant growth of cells in the lining of the uterus, this is also the cause of vaginal bleeding in the later period. Menopause.
3. Diagnosing post-menopausal bleeding
Postmenopausal bleeding is diagnosed based on bleeding symptoms, personal and family history and some paraclinical techniques such as:
Endometrial biopsy with thin tube to take a small amount tissue in the lining of the uterus for examination; Transvaginal ultrasound to see the organs in the pelvis; Ultrasound injects uterine water through the catheter to see the image of the uterus; Hysteroscopy with a laparoscope inserted into the vagina and cervix can see the inside of the uterus; Dilation and curettage of the uterus to remove tissue from the cervical lining and have it examined.
4. Treatment of bleeding after menopause
In order to treat postmenopausal bleeding, the cause of the vaginal bleeding needs to be diagnosed. As noted above, if the cause is polyps causing blood after menopause, then surgical removal of these polyps can be performed. If it is due to endometrial atrophy, it will be treated with the use of drugs. Endometrial hyperplasia will be prescribed by doctors to apply progestin therapy to remove the endometrium and remove these plaques by laparoscopic or dilation and curettage of the uterus.
Importantly, women who have been diagnosed with endometrial hyperplasia are at very high risk of developing endometrial cancer - a malignant form of gynecological cancer. This case should be screened for cancer with periodic endometrial biopsies, to detect or be sure that endometrial proliferation has stabilized and has not recurred.
If a woman has been diagnosed with endometrial cancer, the most common treatment is a hysterectomy and a curettage of nearby lymph nodes.
Postmenopausal bleeding is a rather dangerous phenomenon that many women experience during menopause. Therefore, when there are any signs of abnormal vaginal bleeding, it is necessary to go to a medical facility for early diagnosis as well as timely treatment and intervention, in order to avoid excessive blood loss and affect the functioning of the patient. movements of the sex organs.
Khám tử cung tại bệnh viện Vinmec
Women experiencing post-menopausal abnormalities such as vaginal bleeding can go to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and treatment. Vinmec has a team of specialized gynecologists with rich expertise and experience in medical examination and treatment as well as surgical surgery for benign gynecological diseases, emergency diseases and diseases related to reproductive endocrinology. . Vinmec is capable of synchronously and effectively deploying the most advanced diagnostic and treatment methods, with the support of a system of modern technical equipment according to international standards.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.