This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Nguyen Thai Ngoc Chau - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology, Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital. Uncle has 9 years of experience in the field of Pediatrics - Neonatology, former Deputy Head of Pediatrics Department of Phuong Chau International Hospital (Can Tho). His strength is examination and treatment of children's nutrition problems, pediatric emergency resuscitation, pediatric pathology treatment.If a pregnant woman is infected with rubella, the virus can cross the placenta and be transmitted to the fetus, causing congenital rubella syndrome. In case the mother has the disease at a young age, the baby has a higher rate of congenital rubella.
1. Overview of rubella disease
Rubella, also known as German Measles, is an infectious disease caused by the rubella RNA virus, family Togaviridae. According to epidemiology, the disease occurs all over the world, peaking in winter or spring, but can also appear sporadically throughout the year.The disease is transmitted from an infected person carrying the virus to a healthy person through the respiratory tract or from mother to fetus, during the period before and 1 week after the rash. Humans are the sole reservoir of the pathogen and those who are not immune can contract rubella. On the contrary, people after contracting the disease will have sustainable immunity.
Common manifestations of rubella disease include fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, ... but still about 20 - 50% of people infected with the virus have no symptoms. Although the disease usually has a benign course, there is still a risk of some complications such as encephalitis and/or meningoencephalitis, thrombocytopenia bleeding...
2. Rubella in pregnant women

Pregnant women infected with rubella also have similar clinical manifestations to normal people infected with this disease. For pregnant women infected with rubella , the most concerned thing is the birth defects of the fetus in the womb due to congenital rubella infection .
2.1. Rate of congenital rubella infection The risk of transmission from the mother infected with rubella to the fetus is very high, especially in the first months of pregnancy. The rate of babies with congenital rubella by time of pregnancy is as follows:
First month: From 81 - 90%; Second month: From 60 - 70%; Third month: From 35 - 50%; Pregnancy at 13 - 16 weeks: 17%; Pregnancy at 17 - 20 weeks: 5%; After the 20th week of pregnancy, the rate gradually decreased to 0 - 5%. Thus, it can be seen that rubella infection in women during the first 3 months of pregnancy leads to a very high risk of congenital rubella in the baby. Statistics also show that up to 25% of babies have birth defects as a result of congenital rubella syndrome.
2.2. Management of rubella in pregnancy Rubella vaccine cannot be given to pregnant women. Therefore, if not vaccinated before pregnancy, the diagnosis of rubella infection in pregnant women plays a very important role. Steps for examination and follow-up are related to the decision to terminate or keep the pregnancy, specifically:
Pregnant women in the first 3 months with rubella: Counseling for termination of pregnancy when a confirmed diagnosis is made. When pregnant from 13 to 18 weeks of rubella infection: Counseling on the risk of congenital rubella in the baby, combined with amniocentesis to confirm the diagnosis. If rubella is found in the amniotic fluid, counseling for termination of pregnancy; otherwise, negative cases will continue to be monitored. Pregnant women over 18 weeks with rubella: There is little risk of having a baby with congenital rubella, but close pregnancy monitoring is still needed. In particular, women infected with rubella in the first 18 weeks of pregnancy are also very susceptible to miscarriage, stillbirth or premature birth. If the pregnancy is continued for a long time, the child will also not be able to develop healthily, often underweight, slow in growth, or sick with illness and poor intelligence. Therefore, pregnant women need to go to reputable medical facilities or specialized hospitals to do all the necessary tests to ensure the safety of both mother and child.
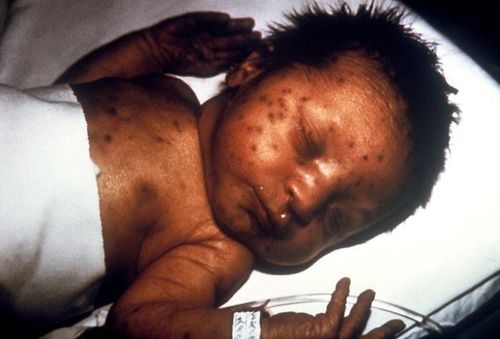
3. Congenital rubella syndrome
3.1. Definition Congenital rubella syndrome is diagnosed in a newborn:
Has a rash at birth or appears within 48 hours of birth; The patient has hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, and jaundice...; Exploitation of mothers with a history of rubella infection during pregnancy; Cord blood antibody testing found both IgG and IgM positive for rubella. Based on fetal malformations, congenital rubella syndrome is also classified into 2 groups A and B. Currently, there is no specific treatment method, so babies with congenital rubella are only focused on managing complications. symptoms of the disease. Congenital rubella syndrome can transmit the virus for a year or longer.
3.2. Prevention of risk Pregnant mothers who have not been vaccinated against rubella and exposure to infected people are the main risk factors for the baby to have congenital rubella syndrome. Moreover, the rate of babies born with congenital rubella has also decreased significantly since vaccination. Some developed countries have almost eliminated rubella through vaccination programs for children and women of reproductive age (15-40 years old).
Therefore, vaccinating those who are not immune to the virus is a simple but effective way to prevent rubella and congenital rubella syndrome. It should be noted that at least 3 months after the prenatal vaccination, women should become pregnant.
In addition, maternal immunity can protect the baby for 6 to 9 months after birth. Therefore, it is necessary to vaccinate children with rubella from 12 months of age or earlier when there is an epidemic.
As a key area of Vinmec Health system, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of top doctors and nurses in Pediatrics : consists of leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All doctors are well-trained, professional, conscientious, knowledgeable about young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.