This is an automatically translated article.
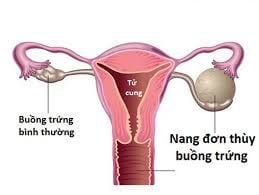
Ovarian cysts are sacs that form on the surface of a woman's ovaries during or after ovulation to hold a mature egg. Most of these ovarian cysts are harmless and cause no symptoms, and usually go away without treatment. But if the ovarian cyst is large, it can cause twisting, rupture or bleeding, causing pain for the patient.1. Causes of ovarian functional cysts
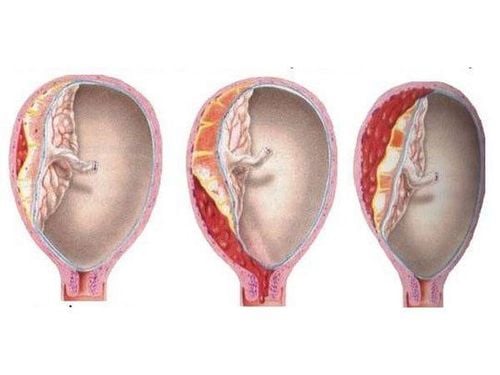
Ovarian cysts or functional ovarian cysts usually disappear after ovulation, but if the egg is not released or the sac closes after the egg is released, the sac may swell to contain fluid.Ovarian cysts are caused by one or more small changes in the way the ovaries produce or release eggs. During the menstrual cycle, ovarian cysts can develop due to:
When the follicle in the ovary fails to release an egg and bulges with fluid inside the ovary or on the surface of the follicle. Cysts occur when the corpus luteum does not go away but continues to swell with fluid inside. This is the most common type of ovarian cyst. The development of functional ovarian cysts is also common during treatment with clomiphene (such as Clomid or Serophene) in infertility cases. These cysts should go away after treatment ends, although it may take several months. They pose no danger to pregnancy. Some functional ovarian cysts may be a benign cyst or be related to endometriosis or cancer.
2. Symptoms of ovarian functional cyst

Đi tiểu thường xuyên, nếu một u nang lớn đang ép vào bàng quang
If the ovarian cyst is larger, then symptoms will begin such as:
Frequent urination, if a large cyst is pressing on the bladder. Stomachache. Menstrual changes. Weight gain. More serious symptoms may develop if the cyst twists, bleeds, or ruptures. See your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms of pain, shock or bleeding:
Sudden severe abdominal or pelvic pain Nausea and vomiting Sudden feeling dizzy, weak Vaginal bleeding or symptoms of shock due to heavy bleeding. There are many other causes of signs or symptoms of ovarian cysts, which is why it's important to get checked out early if you have any unusual pelvic symptoms.
3. Who is at risk for ovarian cysts?
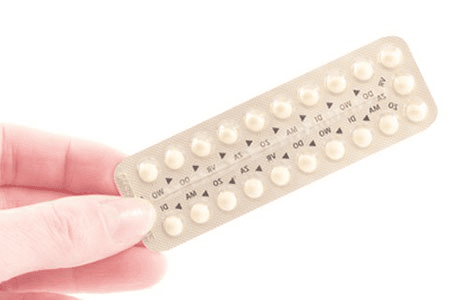
Factors that may increase the risk of developing ovarian cysts include:Previous history of ovarian cysts. Recent use of clomiphene, such as Clomid or Serophene. Use low-dose progestin-only birth control (such as some implants, pills, and devices).
Sử dụng biện pháp tránh thai chỉ có progestin liều thấp có thể là yếu tố nguy cơ phát triển u nang cơ năng buồng trứng
4. Diagnostic test for ovarian functional cyst
If an ultrasound shows you have a cyst with a fluid-filled ovary without severe pain, your doctor may suggest waiting and watching for a while. The patient can then check the cyst 1 to 2 months later to see if the size has changed. Most cysts will go away in 1 to 2 months without treatment or after 1 or 2 menstrual periods.Your doctor will recommend further testing or treatment if:
The initial ultrasound does not show which type of cyst or both ovaries are affected. The patient has moderate to severe pain or vaginal bleeding. Ovarian cyst does not get smaller or go away as expected. You have risk factors for ovarian cancer, such as a family history of cancer or genetic changes. The higher the risk of ovarian cancer, the more tests you need to do to find the cause of the ovarian cyst. Laparoscopy allows the doctor to look at the ovaries through a lighted instrument and take a sample of the cyst for biopsy. After examining the sample, your doctor may decide to surgically remove the cyst or the entire ovary with laparoscopy. CA-125 (cancer antigen) testing is only recommended for women who are at very high risk for ovarian cancer. These are patients with a large family history of cancer.

Xét nghiệm CA-125 (kháng nguyên ung thư) chỉ được khuyến nghị cho những phụ nữ có nguy cơ mắc ung thư buồng trứng rất cao
5. Treatment of ovarian cysts
Most cysts are harmless, cause no symptoms, and go away without treatment. When treatment is needed, the goals of treatment include:Relieve painful symptoms or relieve pressure on the pelvis. Prevents multiple cysts from growing by preventing ovulation. Treatment with oral contraceptives to prevent ovulation. 5.1 Initial treatment Because cysts often go away without treatment, your doctor may recommend a period of observation without treatment to see if cysts go away on their own. are not. The doctor will make an appointment to see the patient again after 1 to 2 months.
If the cyst does not go away, your doctor will do more tests to make sure your symptoms are not caused by another type of ovarian cyst. Patients can use pain relievers at home to help relieve uncomfortable symptoms during this time.
5.2 Continuity of Treatment If the ovarian cyst does not go away, appear abnormal on ultrasound, or cause symptoms, the patient may need medical or surgical treatment.
Your doctor may suggest that you try birth control pills for a few months to prevent more cysts from forming.
Laparoscopic cystectomy may be necessary if an ovarian cyst is painful and does not go away despite medical treatment. If the cyst looks abnormal on ultrasound or if you have other risk factors for ovarian cancer, your doctor may recommend laparotomy instead of using a laparoscopy.
Performing laparoscopic surgery and other types of surgery should generally be carried out in reputable hospitals to minimize the possibility of possible complications. Vinmec International General Hospital gathers a team of qualified and skilled medical doctors from all over the country and abroad; The equipment system is focused on investment, meeting international standards, thus ensuring the best possible surgery.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.