This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Lam Thi Kim Chi - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.Cystography on the pubic bone is now a highly appreciated and commonly used method in medicine because this technique avoids many complications due to infection as well as leaves much less complications than other methods.
1. What is a suprapubic cystography?
If the retrograde cystogram requires injecting the contrast agent through the catheter into the urethra, there is a possibility of infection, then the suprapubic cystography technique can limit this disadvantage. .
Accordingly, this method examines the bladder by taking X-rays, using water-soluble iodinated contrast agents, but the drug is used after inserting a needle directly into the bladder through the skin, on the pubic area.
2. Indications and contraindications for suprapubic cystography
The suprapubic cystography is indicated and contraindicated in the following cases:
Indicated for the following cases:
The suprapubic cystography technique is used to diagnose imaging abnormalities bladder and urethra. Investigate abnormalities of bladder and urethral urinary function. This technique helps to avoid the complications of urethritis compared with retrograde urethrography in men. Contraindicated in the following cases:
If the patient is suffering from a urinary tract infection, it should not be performed. If an infection is suspected, a urinalysis should be performed immediately. Patients with coagulopathy should also not perform this technique.
Chụp bàng quang trên xương mu chống chỉ định với khách bị rối loạn đông máu
3. What should the patient prepare before performing a suprapubic cystogram?
The patient will be given a mild sedative by the doctor 1 hour before the time of the test. Make sure the bladder is full, the main and most important condition. It is possible to give diuretics to stimulate the bladder to fill quickly (using the method of intravenous injection of 01 Lasilix tube with a dose of 20mg). Basic test performance sheets.
4. Steps to perform suprapubic cystography
Steps to perform a cystogram on the pubic bone are as follows:
Insert the needle into the bladder
Adjust the patient's position to lie on his back, then proceed to disinfect the skin, spread a sterile towel Insert the needle into the point on the midline from the pubic joint 2 knuckles, track on the light up screen. Adjust the direction of the needle so that it is at right angles to the skin or 10o up to the tip. After feeling the needle has passed through the bladder wall, push the needle 2cm in. Withdraw the catheter, drain urine into the catheter, or inject several ml of contrast agent to determine if the catheter has entered the bladder. Insert the catheter into the bladder and then push the catheter in the path of the guide. Empty bladder
Have the patient urinate to empty the bladder. Collect urine in a graduated pot to measure urine output.
Inject the contrast agent into the bladder
Check to see how much urine has been pumped to inject the equivalent or nearly equivalent amount of contrast. Contrast can be infused into the bladder. Film position during bladder filling: straight, oblique, sometimes taken when tilted. Film taken at full bladder (300-400ml of contrast and physiological saline). When the patient has a feeling of wanting to urinate, the shooting positions are taken: straight, sideways and inclined. Take a urine scan
Keep the catheter fixed and locked, absolutely do not remove the catheter when the bladder is full or under high pressure to avoid the risk of urine leakage. The shooting position is right back or left behind, for male patients, it can be taken lying down. Perform imaging during spontaneous urination and at urethral obstruction by clamping the posterior part of the penis, clamping with sufficient force to obstruct the urethra. Shoot poses: straight, sideways, sometimes tilted. Take the picture after urinating
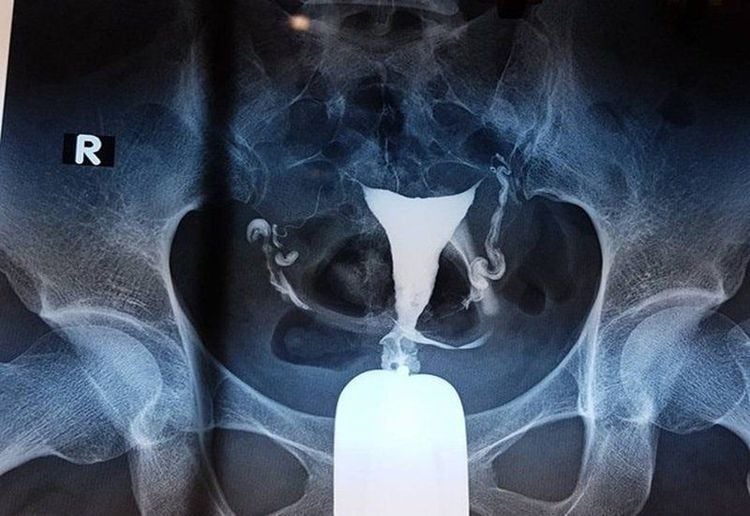
First remove the catheter after the scan is complete, then urinate. Have the patient empty their bladder in the toilet. After the patient finished urinating, a straight scan was taken.
Sau khi bệnh nhân đi tiểu sẽ tiến hành chụp thẳng
5. Evaluation of results after suprapubic cystography
The bladder border is regular, the bladder base is normal, close to the upper border of the pubic joint. Examining the diameter and border of the urethra, in the male urethra, there are 4 segments: the prostatic segment, the membranous segment, the bulbous segment and the cavernous segment. The female urethra is a straight tube that runs from top to bottom and from back to front. There was no passive or active vesicoureteral reflux. If the bladder neck does not prolapse, urinate. There is no residual urine.
6. Dealing with complications during cystography on the pubic bone
Complications are rare and not serious if the bladder is full. The doctor was unable to insert the catheter into the bladder. Rectal perforation: very rare Infection: very rare, due to not inserting a catheter directly into the urethra. Master Doctor Lam Thi Kim Chi graduated with a Master's degree in Radiology - Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy and has over 6 years of experience as a radiologist. Doctor Chi used to work at Da Nang Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital before becoming a radiologist at Vinmec Danang International General Hospital as now
To register for examination and treatment at Da Nang General Hospital Vinmec International Department, please come directly to Vinmec medical system or register online HERE.
MORE:
Possible problems with bladder catheterization Is acute cystitis dangerous? Having cystitis should avoid "love"?














