This is an automatically translated article.
A biopsy is a test that helps doctors check for and detect health problems that a person has, such as infection, tumor or cancer. Currently, there are many different types of biopsies, each method will be applied depending on the health status of the patient.
1. What is a biopsy?
A biopsy is a test to check for signs of a disease. Your doctor will take a small cell or tissue sample from a certain area of your body if you suspect an infection, cancer, or some other health problem. Then, the sample will be sent to a laboratory for the doctor to check for any cells that are harmful to the patient's health.
2. What preparation is needed before performing a biopsy?
Before performing a biopsy, your doctor will tell you what to do and what not to do. For example, you may have to stop taking aspirin, an anticoagulant, or not eat or drink for a few hours before the test. If your doctor requires anesthesia, you should ask someone to accompany you to return home afterwards.
3. What happens after the biopsy test?
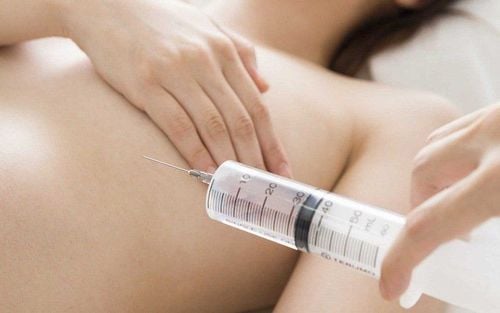
Does taking a biopsy sample hurt? The area where the biopsy sample was taken may be sore or uncomfortable for a few days, but your doctor may give you pain medication if needed. In addition, after the test, you should stay in a good mood and follow your doctor's instructions about when to wear the bandage and how to care for the wound.
Depending on the type of biopsy, such as a cell biopsy or a cancer biopsy, your doctor may test the sample right away for quick results. Other results can be sent to the patient in a day or two, even on the same day.
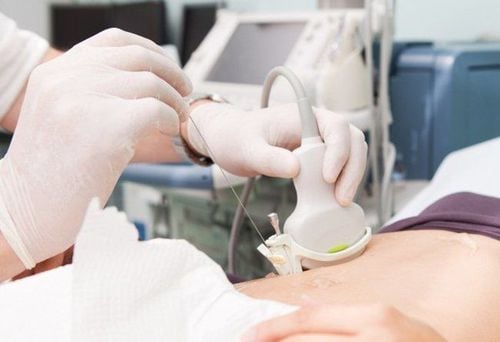
Người bệnh có thể bị đau tại vị trí sau xét nghiệm sinh thiết
4. Needle biopsy method
Needle biopsy is a procedure that uses a needle to take a tissue sample from a problem site on the patient's body. Doctors often recommend this test to examine tissue from the lymph nodes, breasts, testicles, or thyroid.
When performing this type of biopsy, the doctor will clean and numb the area where the sample is taken, and then use ultrasound or other imaging equipment to guide the needle to the place where the tissue needs to be aspirated. The doctor will then cover the area where the biopsy was performed. The process usually takes less than an hour. You may feel some pain or bruising at the sampling area.
5. Skin biopsy method
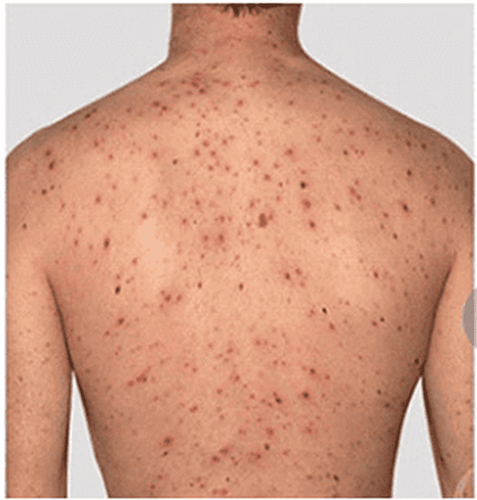
Skin biopsy is a method to help check the growth of moles, rashes or any other lesions on your skin. This type of biopsy is mainly used to detect skin cancers, such as skin melanoma. If the cancerous area is above the surface of the skin, the doctor will use a razor to remove a small sample. If the lesion grows deeper, your doctor will recommend a biopsy of the hole.
The biopsy sampling area will be cleaned and anesthetized with medication. When the sample is taken, you will not feel any pain, but the biopsy site will be red. Your doctor may have you put a little ointment on the area to keep the skin moist and prevent scarring or infection. The biopsy site may heal within 3 weeks.
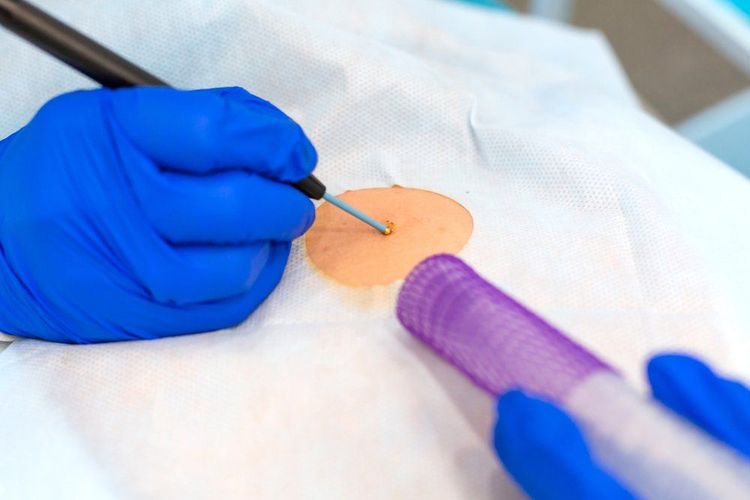
Phương pháp sinh thiết da giúp phát hiện tình trạng u ác tính tại da người bệnh
6. Open biopsy or incisional biopsy
These two biopsy methods are mainly used to help examine areas involving the skin, lymph nodes, breasts, or muscles. An open biopsy removes a large area of skin or polyp, while an incision biopsy removes a deeper but smaller area of skin. For example, if a doctor thinks a person has melanoma, they may remove the entire skin tumor with an open biopsy, while an incisional biopsy only removes a portion of the tumor.
Depending on the location and size of the biopsy area, the doctor will administer anesthesia or give the patient a sleeping pill. The doctor will then use a surgical knife to take the sample. These biopsies require stitches after the sample is taken. When the drug wears off, you will feel some pain or a little bleeding at the biopsy site. If you feel severe pain or bleed a lot, you should tell your doctor right away.
7. Endoscopic biopsy method
With this method, the doctor will use a long and thin endoscope, with a light and camera attached. This type of biopsy is recommended for taking tissue samples from areas deep inside the body, such as the colon, lungs, and bladder.
During an endoscopic biopsy, your doctor will give you a sleeping pill to carry the endoscope through the mouth, urinary tract, rectum, or small cuts through the skin. The camera guides the tube to the tissue to be examined. Overall, this is a safe test, but there is a small risk of tissue tearing, bleeding, or infection.
8. Bone marrow biopsy method
For blood diseases, marrow or lymph node cancer, bone marrow biopsy can be used to detect disease. The doctor will use a long needle to take a small sample of bone or bone marrow, which is then examined under a microscope. Before the biopsy, the doctor will apply a little numbing medicine to the area where the sample is taken, to help the patient feel more comfortable.
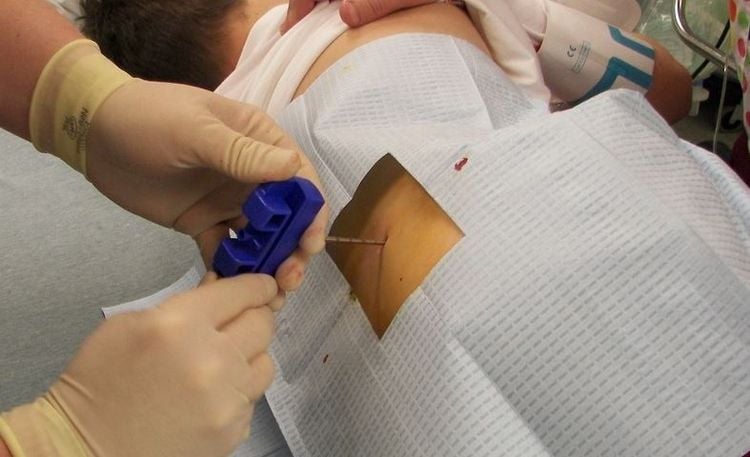
Sinh thiết tủy xương giúp bác sĩ kiểm tra tình trạng bệnh máu của người bệnh
9. Surgical biopsy method
Surgical biopsy is usually indicated for cases where a large amount of tumor, tissue or lymph node is removed for testing. In certain situations, the doctor may just make a small cut in the skin and then use a tube with a camera to guide it to the correct area. Sometimes, a surgical biopsy is also called an endoscopic biopsy because they are quite similar.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious and high-quality healthcare center with a system of modern medical equipment. Therefore, when there is a problem, customers can contact the hospital for advice and appropriate indications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.