This is an automatically translated article.
Fungal infection is a common clinical condition. People with fungal infections need to use the right antifungal medications to control the disease and reduce discomfort. One of the commonly used antifungal drugs today is the product Trifungi 100mg. So what is Trifungi, how does it work?
1. What is Trifungi?
TriFungi is a product of Pymepharco Joint Stock Company, the main ingredient of Trifungi is Itraconazole 100mg. Trifungi is available in the form of hard capsules.
Itraconazole contained in Trifungi is a synthetic anti-fungal triazol that has better effect than the active ingredient in the same group, Ketoconazole, against some fungi, especially Aspergillus spp.. Trifungi also works against other fungi. fungal strains such as: Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, Candida, Histoplasma, Blastomyces, Sporotrichosis spp. Active ingredient Itraconazole acts by inhibiting cytochrome P450-dependent enzymes of fungi, inhibiting ergosterol biosynthesis, causing dysfunction of cell membranes and membrane-bound enzymes, thereby affecting survival and growth of fungal cells.
Itraconazole is well absorbed when taken immediately after a meal or with food. The relative bioavailability of the capsule compared with the oral solution is over 70%, especially the solubility of Trifungi is higher in acidic medium. Peak serum concentrations reached 4 to 5 hours after oral administration of Trifungi 100 mg in the fasted state are 20 mcg/L and can be increased to 180 mcg/L when taken with food.
More than 99% of Trifungi after absorption is bound to plasma proteins (mostly albumin) and very little is in the free form (0.2%). The solubility of Trifungi in lipids is relatively good, concentrations in tissues are much higher than in serum. Active ingredient Itraconazole is metabolized in the liver to a variety of substances and then excreted in the bile or urine, among them Hydroxy Itraconazole, a metabolite with antifungal activity and concentrations in serum twice that of Itraconazole when in the state. steady state.
Regarding excretion, approximately 3-18% of the dose will be unchanged and 40% excreted in the urine as inactive metabolites. The elimination half-life following a single oral dose of Trifungi 100mg is 20 hours and is longer with high daily doses.
2. What is the effect of Trifungi?
Indications to use Trifungi drug for the following cases:
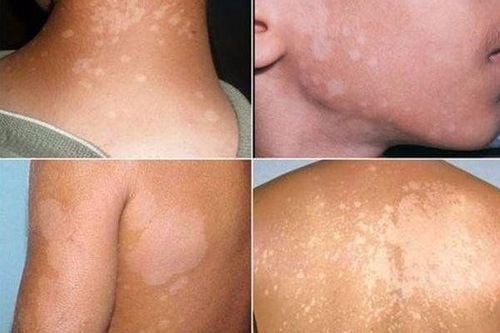
Candida infections in the mouth, throat, vulva, vagina; Ringworm, fungal infections of the skin in places such as legs, groin, trunk or between fingers; Fungal infections of fingernails and toenails; Visceral fungal infections caused by Aspergillus or Candida; Some cases of fungal infections Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Sporothrix, Paracoccidioides, Blastomyces; Maintenance treatment for new HIV/AIDS cases for the purpose of preventing recurrent latent fungal infections; Prophylaxis of fungal infections due to prolonged neutropenia.
3. Dosage of the drug Trifungi 100Mg
Trifungi is used orally, right after eating with specific doses depending on each case.
Candida infections in the vulva, vagina: 2 tablets / time, 2 times a day and used in a single day or 2 tablets taken once a day and taken for 3 days; Ringworm: 2 tablets taken once a day for 7 days; Ringworm infection: 2 tablets of Trifungi 100mg, orally once a day for 7 days or 1 tablet a day for 15 days; Fungal infections in highly keratinized areas on the soles of the feet and palms: 2 Trifungi 100mg tablets/time, 2 times/day for 7 days or 1 tablet, 1 time/day for 30 days; Candida infections in the mouth and throat: 1 tablet per day for 15 days; Patients with AIDS, organ transplant or neutropenia: take 2 tablets of Trifungi 100mg, once daily for 15 days; Toenail and nail fungus: Divide into 2-3 treatment sessions, each session lasts 7 days with a dose of 4 Trifungi 100mg tablets, divided into 2 oral doses, 2 tablets each time. Treatment sessions are spaced 3 weeks apart without using Trifungi. Or the patient can take it continuously for 3 months, 2 tablets of Trifungi 100mg per day, taken only once; Visceral fungal infections caused by Aspergillus: Take 2 tablets, 1 time a day for 2 - 5 months, cases of disseminated fungal infection can increase 2 tablets / time, 2 times / day; Visceral candidiasis: Take 1-2 tablets of Trifungi 100mg, 1 time per day for 3 weeks to 7 months; Epidural Cryptococcus infection: Use 2 Trifungi 100mg tablets, 1 time / day for a period of 2 months to 1 year; Cryptococcal meningitis: Take 2 tablets/time, 2 times/day, then maintain: 2 tablets orally once a day; Histoplasma and Blastomyces infections: Take 2 tablets per day, divided into 1-2 times, the average treatment time is about 8 months; Maintenance treatment in HIV/AIDS: Take 2 Trifungi 100mg tablets once a day; Prophylaxis of fungal infections during neutropenia: Take 2 tablets, once a day.
4. Side effects of the drug Trifungi 100mg
During treatment with Trifungi, it is entirely possible for patients to experience unwanted side effects (ADRs).
Diseases requiring short-term treatment with Trifungi, patients may experience nausea, abdominal pain, headache or indigestion. In the case of long-term treatment in the background of people with many other diseases and the use of many drugs at the same time, the risk of unwanted effects will be higher.
Some common side effects of Trifungi:
Dizziness, headache; Nausea; Stomachache; Constipation or digestive disorders. Uncommon side effects:
Allergic reactions such as itching, rash, urticaria and angioedema; Stevens-Johnson syndrome; Menstrual disorders; Reversible elevation of liver enzymes or hepatitis, especially when taken for a long time; Hypokalemia; Edema; Hair loss, hair loss.
5. Contraindications of Trifungi
Trifungi should not be used in the following cases:
History of hypersensitivity to Itraconazole or other ingredients in Trifungi; Pregnancy or breast-feeding is relatively contraindicated, should only be used in life-threatening visceral infections or when the potential benefit outweighs the potential harm to the fetus/breastfed infant; Do not use Trifungi concurrently with other drugs such as Terfenadine, Astemizol, Cisaprid, Triazolam and Midazolam.
6. Be careful when using Trifungi
Impaired liver function: Although with a short-term treatment regimen, Trifungi drug does not affect liver function, but it is best for people with a history of liver disease or liver toxicity due to other drugs should not use. Cases requiring long-term treatment with Trifungi (over 30 days) need to periodically check liver function; Renal Impairment: The bioavailability of Trifungi is reduced in patients with renal impairment, so plasma Itraconazole concentrations should be checked to adjust the dose accordingly; Cases of systemic fungal infections suspected of being caused by fluconazole-resistant Candida may also be insensitive to the active ingredient Itraconazole in Trifungi. Therefore, it may be necessary in some cases to test the sensitivity to Itraconazole before starting treatment; Women in pregnancy are only treated with Trifungi when absolutely necessary; Breastfeeding women should not breast-feed while taking Trifungi.
7. Drug interactions of the drug Trifungi
The active ingredient Itraconazole inhibits the cytochrome P450 3A enzyme system, so the concomitant use of Trifungi with drugs metabolised by this enzyme system may be increased because of the potential to increase plasma concentrations, prolong the therapeutic effect and increase the risk of the chance of unwanted effects; Products such as Terfenadin, Astemizol, Cisaprid when used together with Trifungi can increase plasma concentrations and increase the possibility of cardiac arrhythmias, possibly even death; Oral Diazepam, Midazolam, Triazolam should not be combined with Trifungi; TriFungi combined with Warfarin increases the anticoagulant effect of Warfarin, so it is necessary to monitor the PT index to reduce the dose of warfarin accordingly; TriFungi combined with calcium channel blocker may cause edema, tinnitus and requires dose reduction; The interaction of Trifungi with drugs that control blood cholesterol of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor group such as Lovastatin, Atorvastatin, Simvastatin causes the concentration of these drugs to increase in the blood; Digoxin combined with the antifungal Trifungi leads to increased plasma concentrations of Digoxin, sometimes requiring drug discontinuation and dose adjustment; Severe hypoglycemia may occur when oral antidiabetic agents are combined with azole antifungals (including Trifungi); Active ingredient Itraconazole requires an acidic environment of gastric juice to increase absorption, so when used with antacids, H2 antagonists, PPIs or sucralfate, bioavailability will be significantly reduced and may be lost. resistance to fungus; Enzyme inducers reduce plasma concentrations of Trifungi, so consider using other antifungal agents if the use of enzyme inducers is more necessary.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.