This is an automatically translated article.
Hematuria (hematuria) is the presence of blood in the urine. Many cases can be cured on their own, but patients should not be subjective because up to 95% of cases of hematuria are signs of some dangerous diseases.
1. What is hematuria?
Urine is a liquid secreted by the kidneys and excreted from the body through the urethra. Depending on the diet of each person, the color and amount of urine secreted will be different. The change in color of urine also reflects the health status of the body (showing how healthy a person is). Hematuria is a condition in which a patient urinates blood, which means that there is an abnormal amount of red blood cells in the urine.
2. Distinguishing diseases when urinating blood
Hematuria is divided into 2 types: gross hematuria and microscopic hematuria.
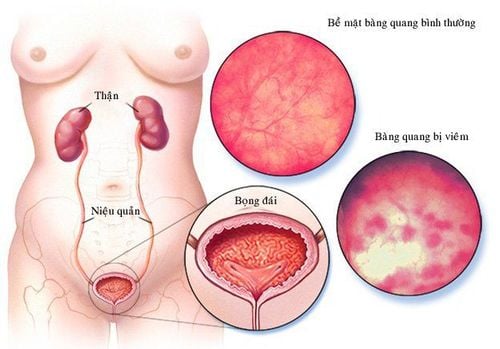
Gross hematuria: When the urine has a dark red color that is easily recognized by the naked eye, it is called gross hematuria. Gross hematuria at a small degree will have a light pink color, at a large level will be dark red with blood clots. In rare cases, the urine is dark brown with brown deposits. Microscopic hematuria: If the urine is normal in color, blood is not visible to the naked eye, but when cytological examination shows a red blood cell count > 10,000 red blood cells/ml, it is called microscopic hematuria. This disease is often discovered incidentally when the patient has a urine test during routine examination. In addition, there will be some cases where the urine is red but must be hematuria, which can include the following cases:
The tested person regularly eats some foods with dyes or natural foods causing red urine like beets, beets, blackberries, raspberries or sour vegetables... these are all agents that are considered harmless. Using some drugs that cause red urine such as antibiotics Rifampicin, Metronidazol...). Menstrual cycle: Women who are menstruating when urinating may have blood in them. Blood in the urine after sex or during sex can be caused by improper sex, causing damage and scratching the urethra, at this time blood appears in the female vaginal tract, and in men, there is bleeding when ejaculating. lead to urine later with a little blood, not blood in the urine.
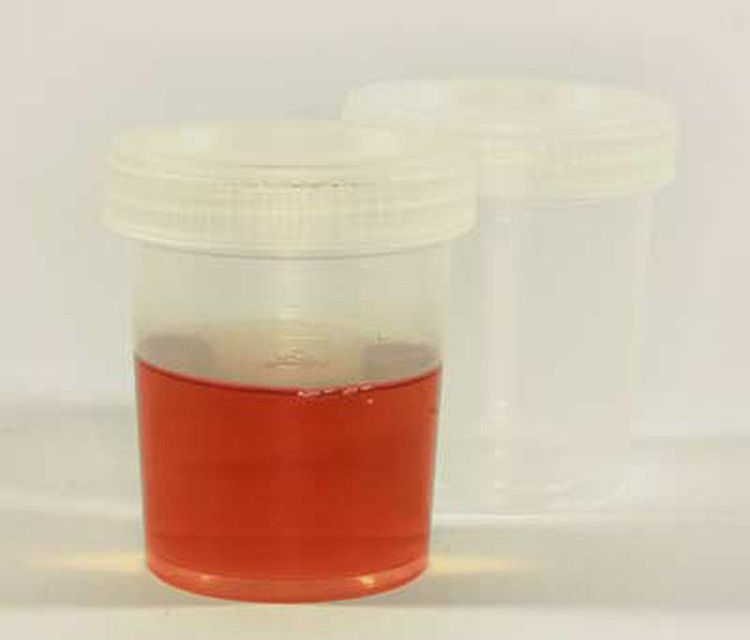

Đái máu đại thể khiến màu nước tiểu đỏ sẫm
3. Causes of hematuria and signs to recognize
There are 4 causes of hematuria:
Bladder disease: The most common pathology is bladder stones, diverticulum, viral cystitis, bladder tumor. Recognizing symptoms are dysuria, urinary frequency, hematuria, often detected by ultrasound. Due to pathology in the urethra - prostate: For men, hematuria is often caused by prostate enlargement or prostate cancer. It can be recognized when it is difficult to urinate, urinary frequency, urinary incontinence, when ultrasound shows an enlarged prostate. As for women, hematuria may be caused by urethral polyps, which can be detected and diagnosed based on urethroscopy.
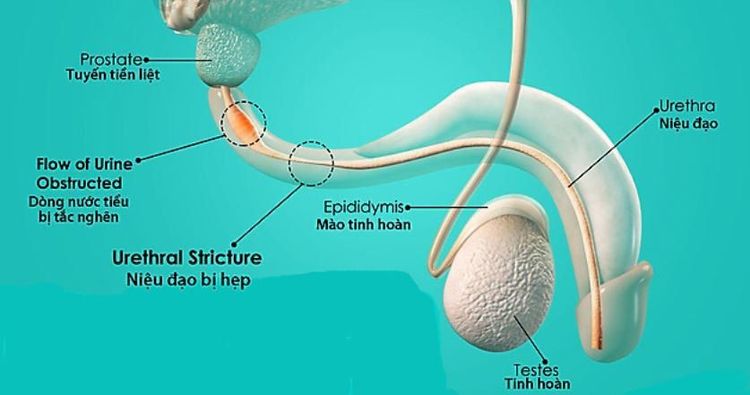
Bệnh lý niệu đạo ở nam giới
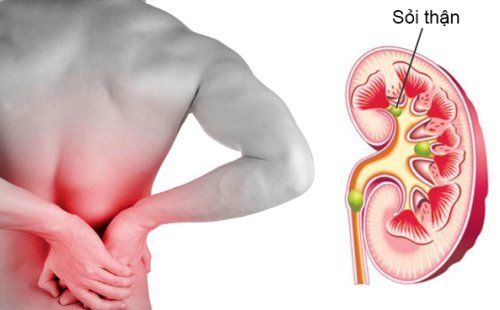
Sỏi thận có thể gây đái máu
Due to trauma (kidney injury, urinary trauma, bladder injury, pelvic or lumbar trauma). Blood in urine can also appear after vigorous exercise such as swimming, running, kicking soccer, boxing... causing injury. However, this condition does not last long and gradually recovers as usual in 24-48 hours.
4. How to diagnose hematuria?
To determine the cause of hematuria is usually not difficult, but there are cases where it is necessary to apply many combined test measures to diagnose and provide specific treatment. Commonly used methods are:
Urinalysis: Finding malignant cells, performing bacterial cultures and measuring 24-hour proteinuria. Imaging: Ultrasound methods, unprepared abdomen, contrast-enhanced retrograde nephrography (UPR), drug nephrography (UIV), multi-slice computed tomography (MSCT), Computed tomography (CT), nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) all have renal angiography to help look for stones, bladder tumors, signs of prostate cancer, acute and chronic cystitis , endometriosis , bowel - bladder fistula , determine hematuria from 1 kidney or 2 kidneys .
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.