This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Master, Doctor Tran Mai Phuong - Pediatrician - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Childhood obesity is an abnormal accumulation of excess fat that affects the health of both boys and girls. This is a burning problem that challenges global public health. Currently, the rate of childhood obesity in Vietnam has been increasing rapidly over the past decade, especially in urban areas, leading to potential risks of related dangerous diseases.
1. How to identify childhood obesity?
In order to evaluate overweight and obese children, in addition to observing the body, for objective assessment, we need to rely on the following measurements of height and weight:For children aged 0-5 years: Overweight children was defined as overweight when the weight-for-length or height index ranged from 2 standard deviations (SD) to less than 3 SD. Children are obese if their weight-for-height is greater than or equal to 3 SD. For children aged 5-19 years: Obesity is determined by body mass index (BMI). If the child's BMI is at or above the 95% percentile for children of the same age and sex, it is classified as obese. If BMI is just above the 85% percentile but lower than the 95% percentile, then you are classified as overweight.

Trẻ thừa cân béo phì được đánh giá thông qua chỉ số BMI
2. Causes of obesity in children
The cause of childhood obesity is not caused by just one person, but is a combination of many factors about the self, family and society. These causes include:The most common cause is improper nutrition and lack of physical activity. Diets rich in energy in excess of the needs will lead to excess energy converted into fat, accumulating in the tissues causing obesity. Living habits in families with overweight or obese people affect both the child's diet and exercise. Children are lazy due to excessive use of electronic devices. The school diet is rich in protein but lacks in fiber. Families let their children drink a lot of soft drinks and carbonated water. If they consume more than 5% of the total energy during the day, it can cause metabolic disorders and obesity. Newborns have too much weight. Children like to snack, eat sweets, drink soft drinks, fast food, especially in the evening before going to bed. Genetic factors: Children carrying genes that promote appetite, genes related to energy expenditure, regulation of metabolism, and related to differentiation and development of fat cells often inherit from overweight parents. fat. There are also cases of obesity due to hypothyroidism, adrenal hyperplasia, hypogonadism, brain disease or drug use (long-term corticosteroids).

Chế độ ăn thừa protein khiến trẻ bị béo phì
3. What diseases do obese children easily cause?
Obesity is a risk factor for many dangerous diseases of the body's organs, typically:Endocrine and metabolic disorders: Children are prone to poor glucose tolerance and insulin resistance. leading to diabetes, dyslipidemia or gout due to increased uric acid. Digestive disorders: Stone disease in the liver, fatty liver caused by using large amounts of fructose from sweeteners in carbonated drinks and canned foods. Cardiovascular diseases: Obesity is a high risk factor for high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, narrowing of the arteries of the extremities,... Respiratory diseases: Sleep apnea is very dangerous for children. Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis, low back pain due to the large body weight pressing on the skeletal system, especially the back, hip, knee, and ankle joints, causing pain and difficulty in movement and daily activities children's day. Affects children's psychology: Children are prone to low self-esteem, depression due to ridicule by friends, making children passive and inflexible. Being overweight and obese in childhood increases the risk of these diseases in adulthood.
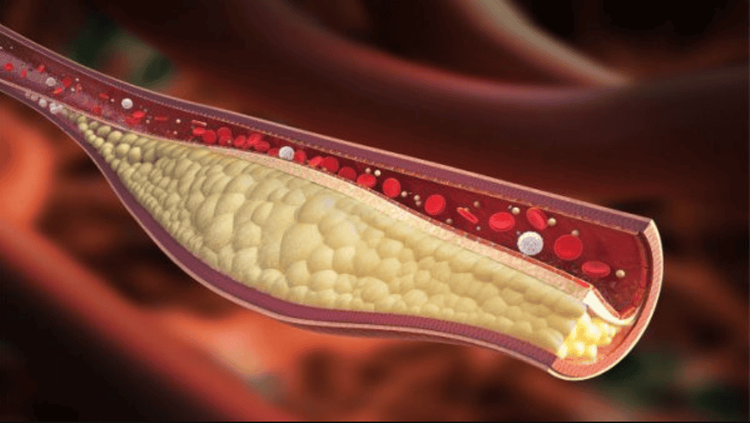
Xơ vữa động mạch do béo phì gây ra
4. How to prevent overweight and obesity in children?
To prevent overweight and obesity in children, it is necessary to take measures on both diet, exercise regime as well as monitor the weight - height of the child.Exercise mode: Do not allow children to sit for a long time to read stories, play games, watch TV for more than 2 hours a day, but encourage children to participate in movement games and help with simple housework. It is best to encourage and facilitate the participation of children in a sport (in older children).
Diet:
Feed children on time, don't skip meals and limit eating at night after 20 o'clock Limit sweet foods (maximum 1-2 times a week) Limit fatty foods, animal viscera Encourage Encourage children to eat vegetables and fruits Monitoring: Parents need to measure their children's weight periodically and consult a nutritionist if their children gain weight more than 0.5 kg/month (children over 2 years old) and more than 1 kg /month (puberty children).
For children who are currently overweight and obese, the treatment needs to adhere to the following principles:
Treatment of overweight and obesity is a long-term process, not just through 1-2 visits, so it needs careful attention. Patience and cooperation from parents. The most important part of weight loss treatment is education so that children can form a conscious awareness of eating and exercising. Weight loss is really only considered in children who are older and begin to have complications, severe obesity. Obesity under 2 years old does not need to lose weight, but only monitored and controlled under the advice of a doctor.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.