This is an automatically translated article.
HPV is the most common sexually transmitted virus. In most cases, the disease can pose no health risk. Otherwise, the virus can also cause genital warts or certain types of cancer.1. HPV virus
Viruses that cause genital warts or cancer: Cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, oropharynx. There is no treatment for this virus yet. However, it is still possible to treat health problems caused by this virus.When having genital acne, the patient should go to a gynecologist to be diagnosed and treated by a doctor. In some cases, these genital warts go away on their own.
Viruses can cause some cancers. Women should have regular Pap tests and follow-up cancer screening. Prevention is better than cure, if diagnosed early, the disease can be treated more easily.
2. What diseases can HPV cause?
HPV is the main cause of cervical cancer and many other cancers such as anal, vulvar, vaginal, and penile cancers. HPV can also cause cancer in the back of the throat, including under the tongue and tonsils.Cancer usually occurs years, even decades, after HPV infection. The types of HPV that can cause genital warts are not the same as the types of HPV that can cause cancer.
2.1. Genital warts
A sexually transmitted disease, caused by the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), with an association between genital warts and HPV. The incubation period is from 1 to 3 months, can also be longer from a few months to 1 year. The age group most affected is between 20-45 years old. The prevalence of the disease is higher in women than in men.The causative agent is a virus belonging to the group PAPOVA types 6, 11 most commonly. HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35 often combine to cause dysplasia or cervical cancer.
Transmission is mainly through sexual contact, secretions or skin contact. In neonates, transmission can occur during birth. Risk factors are poor hygiene, often wet genitals, long foreskin, vulvovaginitis, immunodeficiency, mostly with other venereal diseases.
Proactive prevention is the use of HPV vaccine. Currently, the quadrivalent vaccine Gardasil against HPV types 6, 11, 16, 18 used in women from 9 to 26 years old can prevent genital warts caused by 2 strains of HPV 6 and 11.
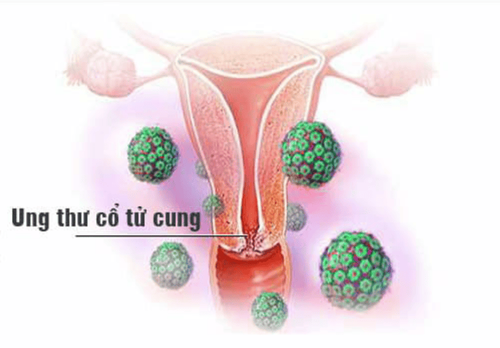
2.2. Cervical cancer

Virus HPV có thể gây ung thư cổ tử cung
To prevent the disease, women aged 9-26, whether sexually active or not, can get vaccinated against high-risk strains of HPV. After this age, it is advisable to have a safe sex life; periodic gynecological examination; In particular, cervical cancer often develops latently for a long time, so women are often subjective in the treatment of the disease. On average, the process from being infected with HPV to developing cervical cancer will take 10 to 15 years.
2.3. Anal cancer Anal cancer is a malignancy arising from the anus. Anal cancer is different from colorectal cancer in that its etiology, risk factors, clinical progression, and treatment are all different.
Types of anal cancer are squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, lymphoma, melanoma, or basaloid carcinoma.
2.4. HPV vulvar cancer is one of the factors that are closely related to this disease, second only to age. The mean age of the disease is 65 years old. Vulvar cancer is a type of cancer that occurs on the outer surface of the female reproductive organs. The vulva is the skin surrounding the urethra and vagina, including the clitoris and labia. The most commonly reported forms of vulvar cancer are: vulvar tumor or ulcer causing pain and/or itching. The incidence is lower than other gynecological cancers. There are two types of vulvar cancer: vulvar squamous cell carcinoma and vulvar melanoma.
Patients often come to the doctor with signs and symptoms such as itching, pain, bleeding, vulvar abnormalities, vulvar skin discoloration or thickening, cancerous lesions or warts.
2.5. Oropharyngeal cancer
Ung thư hầu họng có thể do virus HPV
2.6. Penile cancer Penile cancer is a relatively uncommon disease. Not being circumcised and exposure to HPV are major risk factors. Another risk factor is a history of genital warts, which is often the result of infection with HPV, the most common cancer-causing virus that causes warts. and is often the source of squamous cell carcinoma of the penis as well as cervical cancer in women. HPV can be detected in 30 to 50% of penile carcinoma cases.
Anyone who has sex can get HPV, even if it's just one person. It is also difficult to know when a person becomes infected, because symptoms of the disease often appear many years after infection.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.