This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi Man - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Gestational trophoblastic disease is a term that refers to diseases associated with the abnormal proliferation of trophoblastic cells during pregnancy. Troblastoma is classified into two types, trophoblastoma and fetal ovum.
1. What is egg pregnancy? How is the treatment?
1.1 Classification of fetuses
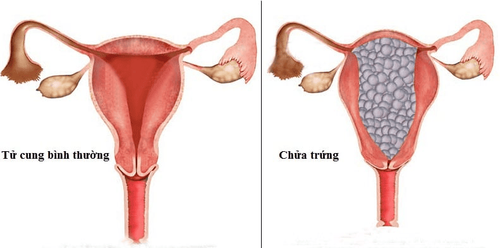
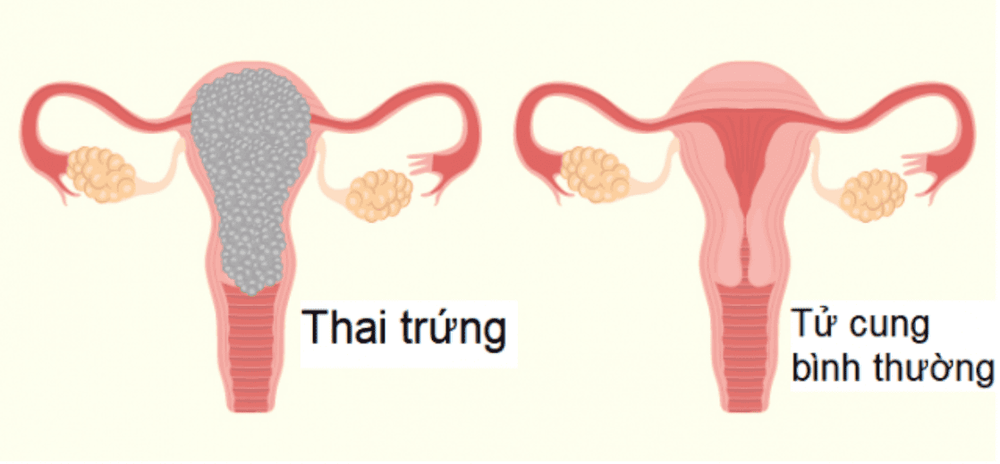
Ovulation is characterized by an abnormal proliferation of trophoblasts. This is a condition in which the placenta does not develop normally. In which, part or all of the placenta degenerates into fluid-filled sacs that stick to bunches like grapes, occupying the entire area of the uterus, overwhelming the development of the fetus.Fetal ovum is classified into 2 types as follows:
Complete oocyte : All placental spines are degenerated into egg sacs; Partial ovum: There are both egg sacs in the uterus and normal placental tissues or both embryos and fetuses (usually dead and atrophied). Women carrying eggs often experience severe morning sickness, abnormal uterine bleeding, and an enlarged uterus for gestational age. The rapid growth of the uterus is due to the large mass of trophoblastic cells and dehydration. Pregnant women can also have hyperthyroidism, gestational hypertension, but this is not a common sign. In addition, the patient may have a thyroid cyst, causing distension in the lower abdomen, accompanied by a large ovarian tumor.
1.2 Treatment of pregnancy
Immediately after being diagnosed, women who are pregnant with eggs will be treated to avoid endangering the pregnant woman. The treatment is as follows:Do necessary tests: Blood chart, blood group, Rh; electrolyte; liver, kidney, thyroid function; Straight chest X-ray and urinalysis; Patient preparation: Counseling the patient's condition and relatives on the type of disease and treatment methods; specialized examination of accompanying diseases; blood transfusion if severe anemia and pre-chemotherapy test before chemotherapy; Uterine aspiration curettage: Perform pre-anesthesia or anesthesia for the patient, then dilate the cervix if (the cervix is closed) and then perform aspiration of the ovum, suction of the uterus. Next, take the specimen for histological examination, give the patient antibiotics and follow up after curettage. 3 days after aspiration curettage, perform a re-examination, if the uterus is still large due to a lot of fluid retention or egg tissue, then perform curettage to check again; Treatment of hysterectomy in cases where the patient is over 40 years old, has had enough children and is diagnosed with a high-risk pregnancy or who has bleeding, uncontrolled heavy bleeding from the uterus; Prophylactic chemotherapy for high-risk pregnancies. The use of chemotherapy drugs with the dose will be done exactly as prescribed by the doctor. When chemotherapy, patients may experience some side effects such as hematologic and bone marrow toxicity (leukopenia, anemia), gastrointestinal toxicity (oral mucositis, gastritis, enteritis). necrosis ), skin toxicity (alopecia, allergies), hepatotoxicity (increased liver enzymes); Follow up after treatment at the hospital and be discharged if the health indicators are normal, no metastases appear; Apply contraceptive measures during post-pregnancy follow-up (using condoms, intrauterine devices, oral contraceptives). The minimum follow-up period for low-risk pregnancies is 6 months, and for high-risk pregnancies is 12 months. After the follow-up period, the patient can become pregnant again. When pregnant again, it is necessary to go to the antenatal clinic immediately to prevent repeat pregnancy.
2. Trophoblastoma
Troblastomas are classified into the following four common types:2.1 Invasive egg pregnancy
About 15% of oocytes progress to invasive oocytes. This is a condition in which the proliferating trophoblastic tissue invades the site, invades the uterine muscle, and can cause uterine perforation or heavy bleeding. Invasive ovum has the characteristics of cancer: The ability to invade locally, metastasize distantly and have the presence of placental hairs.Treatment of invasive ovum is mainly surgical: Peeling or clipping the invasive oocyte; perform a hysterectomy in combination with chemotherapy.
2.2 Thrombocytosis persists
A definitive diagnosis of trophoblastic disease exists if beta HCG remains above 20,000 mIU/ml 1 month after abortion or if beta HCG does not decrease for 3 consecutive weeks. The disease is classified as stage I of glioblastoma. Treatment for the disease can be chemotherapy or surgery.
2.3 trophoblastic neoplasms at the site of placental attachment
Placental trophoblastic neoplasm is a tumor arising from the placental attachment site caused by trophoblastic mediators. This condition usually occurs after the treatment of the ovum, after a normal delivery or after the fetus stops growing. Manifestations are prolonged bleeding, low beta HCG test (16-400mIU/ml).Regarding the treatment method, it is recommended to surgically remove the trophoblastic tumor at the site of placental attachment because this tumor is not sensitive to chemotherapy.

2.4 Trophoblastoma
Throblastoma usually occurs after the whole ovum, can appear after the partial ovum or after delivery - miscarriage. Manifestations are prolonged vaginal bleeding, when ultrasound detects vascular proliferative mass in the uterus or ectopic, beta HCG is usually high, plateau or slow decrease. If the trophoblastic cancer has metastasized, a vaginal nodule can be detected, and a bubble image on a chest X-ray can be seen. When dissecting the uterine tissue, it was found that the trophoblastic cells were malformed, and there was no image of the placenta.Treatments for glioblastoma include chemotherapy or surgery. Chemotherapy is given to most patients, except for some cases with liver and blood enzyme problems. Surgery includes: hysterectomy (for those who do not want to have more children, are over 40 years of age, have bleeding problems, rupture of the chorio nucleus, difficult to stop bleeding, do not respond to chemotherapy) or conservative surgery. Uterine in areas with threatened trophoblastic cancer (for people under 40 years of age, who want to have more children and respond to chemotherapy). In case of trophoblastic cancer with metastases to the brain, liver, and large and deep metastases in the pelvis, it is necessary to treat with radiation.
After treatment for glioblastoma, it is necessary to closely monitor the patient for signs of vaginal bleeding, size of uterus, testicular cysts and vaginal metastases, if any; HCG beta chart; perform blood tests, electrolytes, liver function to detect chemical toxicity.
During the follow-up period, it is necessary to apply contraceptive measures. After discharge, the patient needs to continue to be examined and monitored for blood beta HCG for 5 years with a gradually dilated frequency. After at least 2 years of treatment, the patient should be pregnant again. When pregnant again, it is necessary to go to the antenatal clinic immediately to prevent repeated pregnancy.
Trophoblast disease includes oocyte and troblastoma. These are diseases that are at risk of malignancy, threatening the patient's health and even life. Therefore, patients need to absolutely follow the doctor's instructions during the diagnosis and treatment of the disease to ensure the best therapeutic effect and reduce the risk of unpredictable disease progression.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.