This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Phuong - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Troblastoma is a malignancy of the troblast, including invasive ovum and trophoblast cancer. The disease is common in older women, especially women with a low standard of living.
1. What is trophoblastic neoplasm?
Troblastomas are tumors of placental origin. There are many types of trophoblastic neoplasms, including malignancies such as invasive trophoblastic neoplasia, malignancies such as trophoblastic carcinoma, epithelial trophoblastic neoplasia, and trophoblastic trophoblastic neoplasms.2. Classification of trophoblastic neoplasms
According to the World Health Organization WHO, glioblastoma is classified into the following types:Invasive mole: A pregnancy with a tendency to malignancy and glioblastoma; Placental site trophoblastic tumor; Epithelioid trophoblastic tumour. Prognostic classification of glioblastoma cancer according to 2 types:
trophoblast cancer without metastases; Pancreatic cancer with metastases. Patients have a good prognosis (low risk) if:
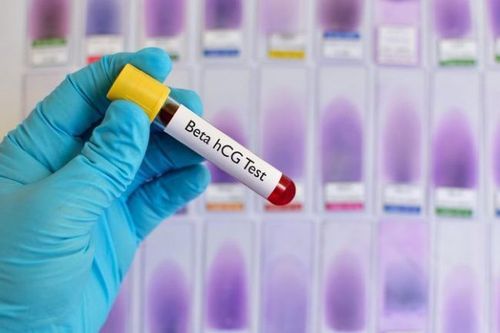
urinary hCG < 100,000 IU/24 h; Serum hCG < 400,000 mIU/ml; Symptoms appear less than 4 months; No brain and liver metastases; No previous chemotherapy treatment; Not after giving birth normally. Patients have a poor prognosis (high risk) if:
urinary hCG > 100,000 IU/24 h; Serum hCG > 400,000 mIU/ml; Symptoms appear less than 4 months; There are brain and liver metastases; Have had previous chemotherapy; Normal postpartum.

3. Treatment methods for trophoblastic neoplasms
3.1. Surgery Total hysterectomy to treat glioblastoma applies to the following cases:Elderly women or those who do not want to become pregnant anymore; Chemotherapy is not effective, 3.2. Chemotherapy Indicated in the following cases:
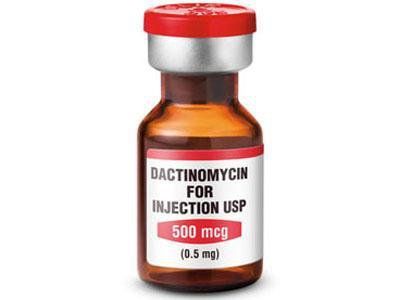
Young patient; The patient still wishes to give birth; The patient is unable to perform surgery. Monotherapy : Methotrexate or Actinomycin D is used when :
Trophoblast without metastatic nucleus ; Pancreatic cancer has metastatic nuclei but has a low risk. Multitherapy: Combination of many types of chemotherapy is applied when:
Pancreatic cancer with metastases in high-risk groups; Failure of monotherapy. Treatment monitoring: During the course of treatment, the patient should be closely monitored by performing the following tests:
Blood count, white blood cell count (daily test); Blood sugar; Liver and kidney function; Quantification of hCG. 3.3. Radiotherapy Indications for radiological treatment when choriocarcinoma has spread in the pelvic fossa beyond surgery.
Radiotherapy usually uses x-rays or cobalt to shine into the vagina or lower abdomen to prevent cancer cells from growing and spreading.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.