This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vo Thien Ngon - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital
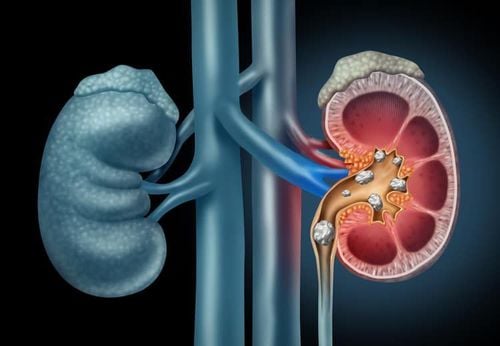
Kidney stones are crystals that are deposited in the urinary system, sometimes causing patients to be hospitalized for severe renal colic. The nature of kidney stones is very diverse, according to which the treatment and prevention also differ. Learning about the types of kidney stones will help us know the right kidney stone prevention.
1. What is kidney stone disease?
Kidney stone disease is the most common disease of the urinary tract. This disease is more common in men than in women. The age of onset is usually between 30 and 55 years, but can also occur in children. The worldwide prevalence of urolithiasis is approximately 3% of the population and varies from country to country.
Unreasonable diet with too much protein, urinary tract infections, drinking little water, living in hot areas, tropical areas,... are favorable factors for urinary stones to arise. When the concentration of crystals in the blood is too high, after filtering through the kidneys, they are deposited to form stones right inside the renal parenchyma or renal pelvis, called nephrolithiasis.
2. What are the types of kidney stones?
Based on the composition of the stone, kidney stones are classified into 6 common types: calcium, oxalate, phosphate, uric acid, struvite, and cystin stones. Each type has different causes and treatments.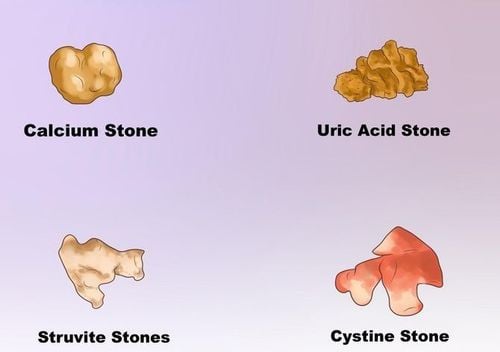
2.1. Calcium stones
Calcium stones are the most common of all stones.
The main cause is urine oversaturation with calcium salts due to increased intestinal calcium absorption or increased renal tubular calcium reabsorption. The causes of increased calcium levels in the urine are:
Hyperparathyroidism. Large fractures and prolonged immobilization. Take a lot of Vitamin D and Corticosteroids. Metastasis of cancer through the bone, causing bone destruction. In addition, there are many cases of increased calcium concentration in the urine without finding a cause (accounting for about 40-60% of the total cases).
2.2. Oxalate stones
This type of gravel accounts for a high percentage in tropical countries like ours.
When the urine is saturated with oxalate, due to eating food containing oxalate, these molecules will pass through the digestive tract and be excreted as a waste product. When passing through the intestines, oxalate can combine with calcium to form the compound calcium oxalate and be excreted in the waste. Too much oxalate in the kidneys can lead to kidney stones. Oxalate often combines with calcium to form calcium oxalate stones.
2.3. Phosphate stones
The most common type of phosphate stone is ammonium-magnesium-phosphate. This type of gravel has a large size, coral shape, and contrast. Stones form as a result of infection of the urinary system, especially by proteus bacteria.
2.4. Uric acid stones
The increase of uric concentration in the blood, in addition to deposition in cartilage, mucous sacs, muscle skin, ... the uric concentration in the kidney also increases. Uric acid deposition in the kidneys is the main cause of uric acid stones, common in gout patients (results of nucleic acid metabolism disorders). The causes can increase purine metabolism:
Using a lot of foods containing purine substances such as pork intestines, beef intestines, dried fish meat, mushrooms. Gout . Decomposition of cancerous tumors with chemotherapy drugs. Note that uric acid easily dissolves in alkaline environment and easily crystallizes in acidic environment, when the urine pH is below 6. Accordingly, acidified urine is a favorable environment for stone formation.
2.5. struvite gravel
Struvite stones form due to long-term bacterial infection of the urinary tract. Bacteria release urease enzyme, this enzyme breaks down urea into ammonia, making the urine alkaline, leading to reduced solubility of struvite, facilitating stone formation.
2.6. Cystine stones
Stones formed because cystin is excreted by the kidneys a lot, but it is less soluble, so it is easy to accumulate. These stones are usually caused by congenital disorders of cystin transport and reabsorption in the renal tubules and intestinal mucosa. This type of kidney stone is relatively uncommon in our country.
3. Progression of urinary kidney stones
After the stone is formed, if it is small, the stone will pass through the urine and be expelled. But if the size is large, the stone is stuck in a certain position in the urinary tract, manifesting kidney stone pain such as renal colic, back pain, blood in urine, sharp urination, ... When kidney stones are not resolved early, long-term obstruction and infection will damage the kidney parenchyma, causing kidney failure.
4. Diagnosis and treatment of kidney stones
With some types of stones that do not cause complications, the doctor may prescribe some drugs that dissolve the stones with urate or cystine ingredients to treat kidney stones.
If the stone is large in size, the patient needs to be treated with the following surgical measures:
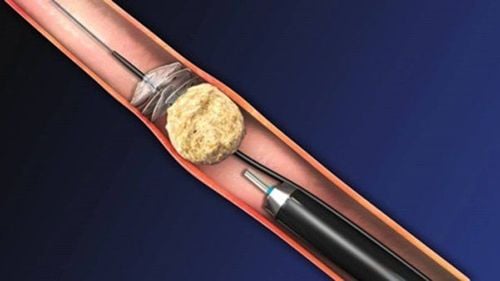
Standard endoscopic percutaneous lithotripsy (Standard PCNL): This method is highly effective, limiting invasion encroachment. The patient was under general anesthesia, less damage to the kidney, less pain, surgery scar < 1 cm, short hospital stay. This method can completely replace open surgery with stones > 25mm, especially "coral" stones. Minimally percutaneous endoscopic lithotripsy (Mini PCNL): This method helps patients limit bleeding, less bleeding, less damage to the kidneys, hospital stay only 1-2 days. In particular, Mini PCNL is very effective in cases of stones 15-25 mm in size, ureteroscopy or lithotripsy has failed. Ureteroscopy: This method does not cause scarring, reduces pain and will shorten the hospital stay. The doctor uses a very small ureteroscope to pass through the urinary opening, up the ureter to access the stone. Then, using a laser to break up the kidney stone and then suck the stone out with a ureteroscope. Extracorporeal lithotripsy (ESWL): This method of kidney stone treatment is considered the most gentle, usually applied to cases of stones <15mm. The doctor uses shock waves to break the stone, the fragments of the stone will be taken out with the urine. The hospital stay is only 1⁄2 days. At the same time, it is necessary to build a balanced diet, drink enough water, adhere to the treatment of urinary tract infections when acquired... is the most effective way to prevent kidney stones.
Each person needs to actively check their health periodically to detect kidney stones early and treat them thoroughly before stones cause symptoms. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is developing general health checkup packages including abdominal ultrasound, urine test, you will be consulted by urologists and have complete peace of mind about your urinary system. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.