This is an automatically translated article.
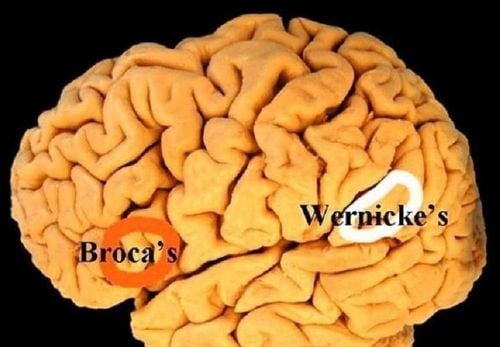
The article was written by Master, Doctor Mai Xuan Thien - Emergency Doctor - Emergency Department of Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Wernicke encephalopathy is an acute neurological condition characterized by triad of ophthalmoplegia (eye paralysis), ataxia (ataxia), and confusion. This disease is caused by a deficiency of thiamine (vitamin B1), which affects the functioning of the central and peripheral nervous systems.
1. Causes of Wernicke's encephalopathy
Wernicke encephalopathy is common in alcoholic patients. Many cases are also seen in malnourished patients, profuse vomiting due to severe morning sickness during pregnancy, prolonged parenteral nutrition, malignancies, immunodeficiency syndromes, liver disease, hyperthyroidism, and severe anorexia. Thiamine is a B vitamin, commonly known as Vitamin B1, is a coenzyme that is essential for complex organic pathways and plays a central role in brain metabolism. The vitamin acts as a catalyst for several enzymes in the Krebs cycle and the pentose phosphate pathway, including alpha-keto-glutamic acid oxidation and pyruvate decarboxylation.Thiamine-dependent enzyme function as a bridge between the glycolytic and citric cycles. Therefore, thiamine deficiency results in decreased alpha-keto-glutarate, acetate, citrate, acetylcholine levels and accumulation of lactate and pyruvate. This deficiency can cause metabolic imbalances that lead to neuronal cell death. Neuroblastoma in the mammary and thalamic bodies has been described in many cases of Wernicke encephalopathy.
Study of computed tomography and cranial magnetic resonance imaging showed damage to the thalamus with ventricular dilatation and hypovolemia in the mammary body. Lesions are usually symmetrical in the midbrain, hypothalamus, and cerebellum.
2. Clinical diagnosis
Wernicke encephalopathy is suspected in all cases of alcoholism, malnutrition, and any of the following: Sudden changes in mental status, vision paralysis, gait ataxia, delirium and hypotension.A prominent sign of Wernicke's encephalopathy is an abnormality of the eyeball, especially signs of nystagmus. Other symptoms of oculomotor syndrome are related to the cranial nerves that control oculomotor ophthalmia, the vestibular nucleus causing paralysis to produce associative vision. Slow pupil movement, drooping eyelids, and misaligned pupils may occur.
Ataxia gait is also described in Wernicke encephalopathy, even in many cases the patient is unable to walk. Disorientation and altered sensation are also characteristic of the disease.
In addition, Wernicke encephalopathy is clinically diagnosed in patients who are chronically malnourished and have confusion or altered consciousness. A few decades ago, gastric bypass surgery was associated with Wernicke encephalopathy and malnutrition; The main reason is that after surgery, eating is restricted and thiamine stores are quickly depleted.
The diagnosis of Wernicke's encephalopathy needs to be exploited from the history, careful examination combined with laboratory tests, appropriate X-ray indications and diagnosis mainly based on suggestive clinical signs. Notes such as:
Eye signs Thiamine deficient diet Changes in consciousness Cerebellar dysfunction.

3. Treatment of Wernicke's encephalopathy
The aim of the treatment of Wernicke encephalopathy is to rapidly correct the thiamine deficiency in the brain.Intravenous thiamine is the most effective and fastest treatment; however, in some cases the nerve damage is irreversible, and the acute condition can progress to chronic Korsakoff syndrome. The dose of thiamine can be 500mg one to three times daily. All cases of thiamine deficiency due to malnutrition require higher doses. Oral thiamine is not recommended.
Thiamine is usually given along with glucose when parenteral nutrition is given because the oxidation of glucose can reduce thiamine levels thereby causing the manifestation of acute Wernicke encephalopathy. Patients with magnesium deficiency should be treated as this may result in reversible reduction of Wernicke's encephalopathy particularly in alcoholic patients.
Most patients require hospitalization and intravenous Thiamine and Magnesium therapy.
3.1 Differential diagnosis Diseases that need to be differentiated include:
Hepatic encephalopathy Stroke Withdrawal syndrome Acute alcohol delirium Chronic hypoxia Chronic ventriculomegaly. Clinical signs of Wernicke encephalopathy should be considered in alcoholics who, if dietary deprivation, have signs of cerebellar dysfunction, ocular signs, and altered consciousness. Serum total thiamine should be measured prior to treatment.
MRI can support the diagnosis of Thiamine should be used intravenously After gastric bypass surgery, Thiamine levels should be monitored for at least 6 months. 3.2 Prognosis Wernicke encephalopathy is a life-threatening disorder with multiple sequelae. While thiamine may be partially ameliorated, neurological deficits may persist in many cases. Confusion can be improved with intravenous thiamine, learning and memory can only be partially improved. A small number of patients who do not improve and may progress to Korsakoff psychosis often require psychiatric hospitalization. Very few cases can recover at this stage.
4. Complications of Wernicke's encephalopathy
Wernicke encephalopathy can cause complicationsNerve damage Ataxia Korsakoff syndrome Eye paralysis Heart failure Lactic acidosis. Because Wernicke encephalopathy is preventable, you can prevent the syndrome by avoiding excessive alcohol intake and eating a balanced, vitamin B1 diet. In addition, when there are symptoms of the disease, it is best not to be subjective and go to reputable medical facilities for examination, so that the disease can be detected and treated promptly.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.