This is an automatically translated article.
The human nervous system is the most complex of the organs in the body. It plays an extremely important role, governs almost all living activities in the human body, from basic such as breathing, chewing to as complex as the way of thinking and thinking.
1. Human Nervous System
1.1. command center
The command center of the brain is made up of billions of neurons. It regulates everything from your breath, to your steps to your dreams. The command center has two main nervous systems:
Central nervous system including the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (all other nerves in the body). The human nervous system operates in two modes: automatic and voluntary (with human control). Voluntary activities that occur with conscious thought, such as walking or clapping, are innervated by somatic nerves. Autonomic activity is an activity that occurs not under human control such as heart rate, which is governed by the autonomic nervous system.
1.2. Sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system is in charge of the body's "fight or flight" response. When facing threats, the sympathetic nervous system will begin to be activated, quickly changing activities in the body such as breathing, heart rate to replenish energy, ready to face danger or run. hide.
Stress can cause the sympathetic nervous system to become overactive. Over time, it can cause you to lose your mental sharpness, react slowly, and be more prone to making mistakes.
High levels of stress can also affect physical health such as weakening the immune system and increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
1.3. Parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system works in the opposite way to the sympathetic nervous system. It acts as a brake pedal, creating a "rest and digest" response to return the body to normal after the danger has passed.
1.4. Neuron
Nerve cells are wires that help the brain and body "talk" to each other. They use special parts to communicate. The axon secretes a chemical called a neurotransmitter, which is then picked up by the dendrites of another neuron, where it is converted into an electrical signal.
Sensory neurons respond to things like sound, smell, and touch, delivering information to the brain. Meanwhile, motor neurons carry messages from the brain to the muscles.
1.5. Glial cells
Glial cells surround, support, and cushion nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. In addition, now researchers are learning its role in how the brain works, neurological diseases, and more.
For example, some glial cells serve to provide support, provide nutrients, and maintain the right chemical environment for neurons to signal well. It also plays a role in clearing debris, dead nerve cells, and repairing injuries related to the nervous system.
1.6. The brain
The mind is an extremely complex and important organ. It is made up of 100 billion nerve cells. It is the organ that controls every movement, speech, heartbeat, and breath, and is the root of all thoughts and emotions.
The brain is about the size of two clenched hands and weighs about 1.36kg, protected by the skull and cerebrospinal fluid.
Khối óc có kích thước bằng hai bàn tay nắm chặt
1.7. Great brain
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, divided into two halves called hemispheres. The left hemisphere controls the right side of the body, processes speech, controls logic, calculates math, retrieves data from memory. The right hemisphere of the brain controls the left side of the body, and also has musical abilities, facial recognition, and spatial awareness.1.8. Cortical
The cerebral cortex is the outermost layer of the brain and has many wrinkles and folds. This is where the brain's "gray matter" is located, where information is processed.1.9. Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia is a network of blood vessels located deep within the cerebral hemispheres. They help coordinate movement, behavior and emotions, making things happen in the right order, such as walking, dancing, pattern learning, forming habits, stopping activities and then starting activities. new motion. Damaged basal ganglia can cause Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease.
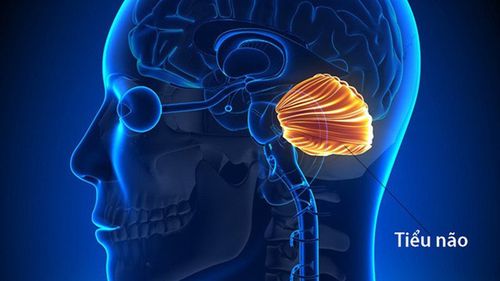
1.10. Cerebellum
The cerebellum is responsible for regulating complex movements, posture and balance. It coordinates different muscle groups, fine-tuning movements when practicing like golfing, playing hockey. Thanks to the cerebellum, walking becomes a smooth and continuous movement.
1.11. Almonds
The amygdala is responsible for emotions and some behaviors. It helps you do almost everything from forming memories to collecting cues from your environment. It emits an alarm signal that triggers a “fight or flight” response to protect the body against danger.1.12. hippocampus
The hippocampus is located near the center of the brain. It helps you learn and remember important details about who, what, where and turns short-term memories into long-term ones. This is one of the first areas damaged by Alzheimer's disease.
1.13. Town hill
The thalamus is the top part of the brain stem. It receives signals related to sight, smell, hearing, taste, and touch and transmits the information to other parts of the brain.
1.14. Pontine
The pons is the middle part of the brain stem and is the bridge between the cerebrum and the cerebellum. It is the source of the nerves that control facial expressions, eye movements and bladder control, and where dreams are formed.
1.15. Brain onion
The medulla oblongata controls things beyond your control like breathing, blood pressure and heart rate. It also plays an important role in chewing and swallowing.
The medulla is located at the bottom of the brain stem, where it also plays a role in transmitting signals between the brain and spinal cord.
1.16. Spinal cord
The spinal cord is about 43cm long and less than 1.27cm wide, thinner than an adult finger. It runs from the base of the brain down to the back, surrounded by vertebrae. Nerve fiber bundles are protected by tissue and fluid, which carry information back and forth between the brain and organs in the body.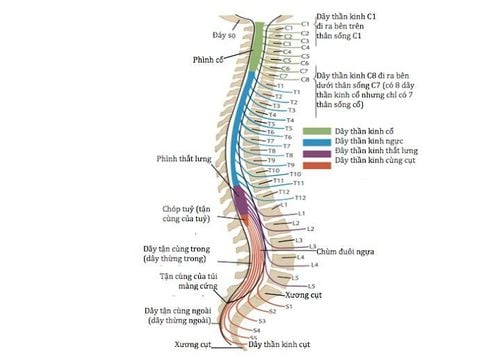
Tủy sống chạy từ đáy não xuống lưng
1.17. Peripheral nerves
If the central nervous system is the headquarters, the peripheral nervous system is the workers on the construction site. There are 12 cranial nerves that connect to the brain, including those that help you smell, see, laugh, and swallow.
There are 31 other pairs of nerve roots (sensory and motor) that branch from the spinal cord between the vertebrae. The sciatic nerve is the largest single nerve that runs from the pelvis down the back of the thigh.
1.18. Enteric nervous system
The enteric nervous system is the “second brain” in the body. It is a separate network of more than 100 million nerve cells that help support and control digestive activities such as moving food into the stomach and out, breaking down food, and absorbing nutrients. .2. Diseases of the nervous system
Factors like infection, trauma, toxins, even high blood sugar can damage the nervous system. It causes nervous system disorders such as stroke, meningitis, polio, migraines, carpal tunnel syndrome, epilepsy, MS and shingles.
3. How to protect the nervous system?
Learning to take better care of yourself will help maintain a healthy nervous system, for example:
Get enough sleep Don't smoke Relax Exercise Eat in moderation, lots of vegetables, fruits and omega-3s Cut cut carbs Avoid foods high in sugar, saturated fats and trans fats Spend time with friends and learn new skills to train your brain Your child's nervous system is so important, governs almost every life activity in the body. To protect the nervous system you can adopt a healthy lifestyle and maintain proper nutrition.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com