This is an automatically translated article.
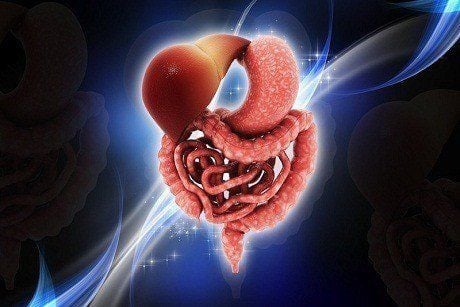
This article is expertly consulted by MSc Vu Tan Phuc - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.The intestine is a long, continuous tube that runs from the stomach to the anus. Most of the absorption of nutrients and water occurs in the intestines. The intestines include the small intestine, the large intestine, and the rectum. The small intestine is responsible for absorbing most of the nutrients from what we eat and drink. The smooth tissue of the small intestine, which is divided into the duodenum and ileum. The large intestine absorbs water from waste, creating stool. When stool enters the rectum, the nerves there create the urge to defecate.
1. Diseases related to the digestive system
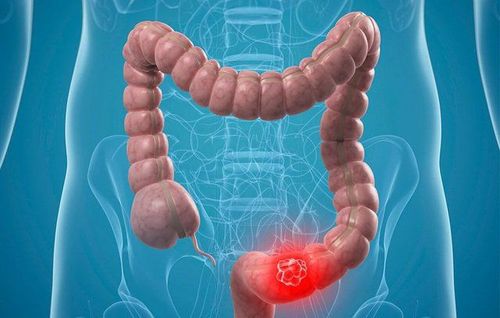
Stomach flu (Inflammation of the small intestine): is an infection caused by a virus, bacteria, or parasite. Small bowel cancer: Cancer that can affect the small intestine. There are many types of small bowel cancer, causing about 1,100 deaths each year. Celiac disease: An "allergy" to gluten (a protein found in most breads) causes the small intestine to not absorb nutrients properly. Abdominal pain and weight loss are common digestive system symptoms with this disease. Carcinoid tumor: Benign or malignant growth in the small intestine. Diarrhea and skin redness are the most common symptoms. Intestinal obstruction: A part of the small or large intestine may become blocked or twisted. Abdominal obesity, pain, constipation, and vomiting are symptoms of intestinal obstruction. Colitis: Inflammation of the intestines or infection is the most common cause. Diverticulitis: Small areas of weakness in the muscular wall of the colon allow the lining of the colon to protrude, forming small pouches called diverticula. Diverticulitis usually causes no problems, but can bleed or become inflamed. When a diverticulum becomes inflamed or infected, diverticulitis results. Abdominal pain and constipation are common symptoms.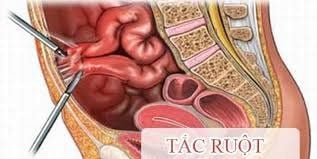
2. Human digestive system test
Capsule endoscopy: Swallow a capsule containing the camera. The camera takes pictures of possible problems in the small intestine, sending the images to a receiver worn on the waist. Upper endoscopy, EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy): A flexible tube that incorporates a camera on its end (esophagogastroduodenoscopy): endoscope) is inserted through the mouth. Endoscopy allows examination of the duodenum, stomach, and esophagus. Colonoscopy: An endoscope is inserted into the rectum and advanced through the colon. Virtual colonoscopy: A test in which an X-ray machine and computer create images of the inside of the colon. If problems are found, a traditional endoscopy is usually needed. Fecal occult blood test: If blood is found in the stool, a colonoscopy may be needed to find the source. Sigmoidoscopy: An endoscope is inserted into the rectum and passed through the left side of the colon. A sigmoidoscopy can be used to view the middle and right side of the colon. Colon biopsy: During a colonoscopy, a small piece of colon tissue may be removed for testing. A colon biopsy can help diagnose cancer, infection, or inflammation.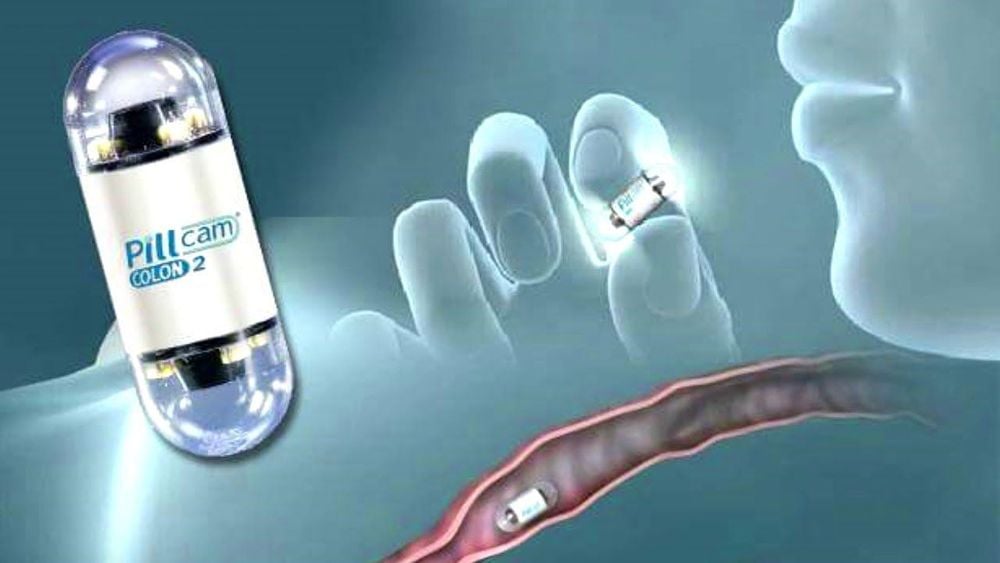
3. Treatment of intestinal diseases
Anti-diarrheal medications: Various medications can slow diarrhea and reduce discomfort. Reducing diarrhea does not slow recovery for most diarrheal illnesses. Stool softeners: Over-the-counter and prescription medications can soften stools and relieve constipation. Laxatives: Medications can relieve constipation by several methods including stimulating the bowel muscles, and bringing in more water. Enema: The term for pushing fluid into the colon through the anus. Advertisers may offer medications to treat constipation or other colon conditions. Colonoscopy: Using tools that are passed through the endoscope, your doctor can treat a number of colon conditions. Bleeding, polyps, or cancer can be treated with endoscopy. Polypectomy: During a colonoscopy, removal of a colon polyp is called a polypectomy. Colon surgery: Using open or laparoscopic surgery, part or all of the colon can be removed (colectomy). This may be done for severe bleeding, cancer or ulcerative colitis. Article reference source: webmd.comPlease dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.