This is an automatically translated article.
This article is advised by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Nhat - Infectious Diseases - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Humans are not always infected by viruses despite being exposed to viruses on a daily basis, in the environment they live in. The reason is because the body's immune system takes care of most of this condition. When the body is exposed to a new virus for the first time or because of exposure to a large amount of the virus, the body becomes infected with the virus.
1. What is a virus?
Viruses are thought to be the first organisms to appear and are the ancient ancestors of all species, including humans, because they help us build our genomes. Viruses have existed for a very long time. According to scientists, more than 50% of the DNA in the human genome comes from retroviruses. In addition, viruses are also considered to be the basis of many DNA replication enzymes, which play a role in cell division and growth.However, viruses are capable of causing diseases that are infectious to both humans and animals. Some viruses are less harmful, such as cold viruses, making people feel tired, sick but without long-term consequences. However, some other viruses are very dangerous, they have the risk of causing pandemics and deaths, such as the flu pandemic that occurs every year with a rapid spread. According to statistics, the world has about 201,200 people died from acute respiratory infections and more than 83,300 other related deaths during the 2009 H1N1 flu pandemic alone.
We are not always infected by viruses, although Although humans are exposed to viruses on a daily basis, in the environment they live in. The reason is because the body's immune system takes care of most of this condition. When first exposed to a new virus or from exposure to a large amount of the virus, the body becomes sick
The body's immunity to the flu virus may no longer protect us from common strains of the flu virus also change from year to year. In particular, besides the ability to mutate, the virus also has a rapid speed of spreading and reproducing. They become weapons of mass destruction and fearsome pathogens.
Vaccines are the best way to prevent diseases caused by viruses, with the mechanism of activating the body's immune response, so that the body can respond more effectively when infected with viruses. Many viruses, such as measles, rubella, influenza, or smallpox, are less dangerous if fully vaccinated.

2. Source of infectious diseases caused by viruses
The source of viral infections is the environment in which pathogens live, grow, and multiply. Sources of infectious diseases include humans, animals and the environment.Human-to-human infectious diseases caused by viruses: Many infectious diseases caused by viruses are transmitted directly from person to person. Diseases that are not transmitted from person to person include sexually transmitted diseases, measles, mumps, streptococcal infections, and many respiratory pathogens. Because humans were the sole reservoir of the smallpox virus, natural smallpox was eliminated after the last case was identified and isolated.
Carriers often transmit disease because they do not realize they are infected and therefore do not take special precautions to prevent transmission. On the other hand, some think their disease is less contagious because they don't go out, take precautions to reduce transmission or limit treatment.
Sources of infectious diseases in animals caused by viruses: Humans are also subject to diseases that are transmitted from animals. Many of these diseases are transmitted from animal to animal, with humans as the random host. Many newly recognized human infectious diseases, including Ebola and SARS infections, are thought to have emerged from hosts, although these hosts have not been identified.
Sources of infectious diseases in the environment caused by viruses: Plants, soil, and water in the environment are also reservoirs for some infectious agents. Many agents, such as those that cause histoplasmosis, live and multiply in the soil. Outbreaks of Legionnaires' disease usually originate from water supplies in cooling towers and evaporative condensers, which are a source of the organism that causes Legionella pneumophila.
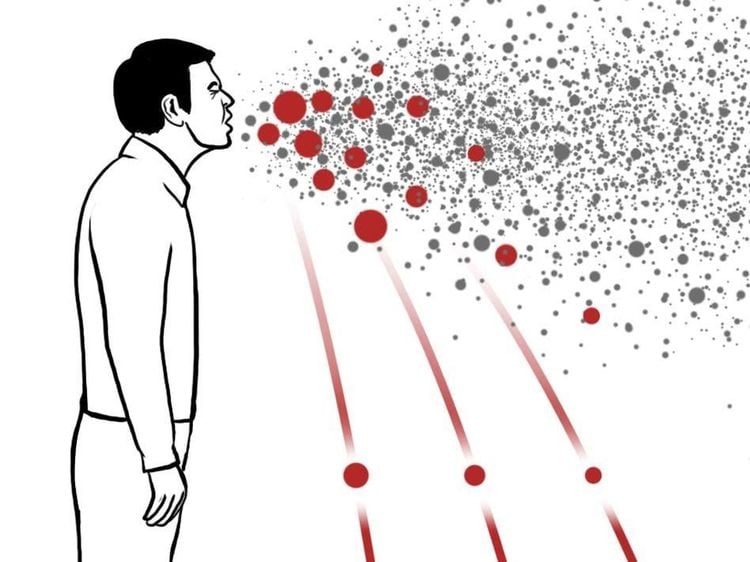
3. Viruses usually spread by what method?
Viruses are usually spread through the following methods:3.1 Respiratory tract
Through bodily fluids, such as when an infected person coughs or sneezes. When these fluids are released, the virus can stay suspended in the air for a period of time or attach to all kinds of surfaces. This is the method by which infectious diseases are most easily spread due to their high dispersal capacity and difficulty to control. The larger the community, the more unpredictable it becomes.Infectious diseases caused by viruses, transmitted through the respiratory tract are very common, such as
Tuberculosis Influenza Meningococcal infection Chickenpox Measles. Viral pneumonia (SARS, COVID19) Diphtheria.
3.2 Digestive tract
This is also considered a common form of viral infection, especially gastrointestinal diseases. These pathogens will spread through eating, food and water sources. In addition, without good sanitation management, especially the source of feces, the risk of infection through this route increases many times, human feces or animal feces are at high risk.Some infectious diseases caused by viruses spread through the gastrointestinal tract, such as:
Cholera, this disease can cause large epidemics if not well controlled. Dysentery: can be caused by bacillus or amoebic dysentery. Welding . Hepatitis A, Hepatitis E.
3.3 Spread through direct contact with pathogens
Some infectious diseases are caused by virusesSpread through blood, such as: Hepatitis B virus, HIV infection, Hepatitis D, malaria,... Spread through contact with secretions, through contact sexual system: Genital warts, gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV, Herpes infection... Skin: Scabies, skin fungus,... See more: Some dangerous sexually transmitted diseases

3.4. Transmitted by animal vectors
In this way, the vector that transmits the disease plays an extremely important role in the route of transmission. This is a constitutive factor and blocking this source of animal exposure can reduce the likelihood of disease. Some animals are vectors of the disease, such as:Dengue fever through mosquito larvae Japanese encephalitis through culex nose Malaria transmitted by Anophen mosquito Mosquito-borne tick fever Rabies through dogs Plague through rats Shrimp, clams, oysters, snails,... intermediates of many flukes, larvae, parasites such as cholera, dysentery, typhoid, amoeba, .... In addition, the virus also Indirect transmission of disease, i.e. transfer of infectious agent from source of infection to host through airborne fluids, other objects (doorknobs, etc.).
Airborne transmission occurs when infectious agents are carried with dust or fluids suspended in the air. Airborne dust includes material that has settled on surfaces and returned by air currents as well as infectious particles blown from the soil by wind. Drip fluid is a dry residue less than 5 microns in size. In contrast to water droplets that fall to the ground within a few feet, dripping fluids can remain suspended in the air for long periods of time and can be blown away over great distances. For example, measles has occurred in children who went to the doctor's office after the child with measles left, because the measles virus remained airborne.
Items that can indirectly transmit an infectious agent include food, water, biological products (blood) and fomites (inanimate objects such as handkerchiefs, linens or scalpels). Objects can passively carry disease - as food or water can contain hepatitis A virus.
4. Some diseases caused by viruses
Rotavirus This is a virus that causes very large diarrhea in children and adults. Through eating and drinking, the virus enters the body. Viruses reduce the absorptive function of the intestine by multiplying mainly in the small intestinal columnar cells, stagnation of carbohydrates outside the intestinal wall, thus pulling water, causing signs of diarrhea, watery stools, rarely with blood. Patients often have diarrhea several times a day, accompanied by low-grade fever, with little vomiting. The disease usually occurs in autumn - winter with children under 2 years old, most often children under 12 months.Poliovirus The polio virus, like other enteric viruses, is transmitted through food or water by infection with the virus in the urine or feces of an infected person. Incubation period is 5 to 10 days after infection. when ingesting infectious substances.
Hepatitis A Virus Hepatitis A virus belongs to the family of enteric viruses with similar biological characteristics as intestinal viruses and quite stable resistance.
Hepatitis A virus is common in children and adolescents, spread through the digestive tract. After entering the body, the virus will multiply in the epithelial cells of the digestive tract. Part of the virus is excreted in the feces, the rest is mostly spilled into the blood, causing viremia when there is a large amount of virus. When spilled into the blood, the virus darkens the liver, kidneys, and spleen, damaging cells, especially liver cells.
Hepatitis B virus Hepatitis B virus is usually spread through blood (blood transfusion, injection, mother-to-child transmission through the placenta...), sexual contact, rarely gastrointestinal transmission. The incubation period after infection with the virus is quite long, about 60 to 180 days with very few symptoms.
Virus that causes dengue Virus is only spread from animals to humans or from sick people to healthy people through mosquitoes that suck blood and then transmit the disease. The virus that causes the disease is called dengue virus. The aedes mosquito is the mosquito that transmits the dengue virus.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: aaha.org, who.int, cdc.gov