This is an automatically translated article.
Venofer® (iron sucrose injection, USP) is indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in adult and pediatric patients (2 years of age and older) with chronic kidney disease (CKD). The drug should only be used under the supervision of medical professionals.
Venofer (iron sucrose) injection is an intravenous form of iron - the key ingredient for making new red blood cells.
1. Uses of Venofer
Venofer (iron sucrose) injection is used to treat "iron deficiency" blood (anemia) in people with long-standing kidney disease. You may need extra iron due to blood loss during dialysis. Your body may also need extra iron if you use the medicine erythropoietin to help make new red blood cells. Iron is essential for bone marrow to build new red blood cells and deliver oxygen to organs and tissues through hemoglobin. Many patients with kidney disease cannot get enough iron from food and require injections.
Venofer is indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in adult and pediatric patients (2 years and older) with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
2. How to take Venofer
Venofer is injected into a vein as directed by your doctor. The medication is usually given slowly over 2 to 5 minutes or as directed by your doctor. Iron sucrose can also be mixed in saline and given intravenously for a longer time.
Your doctor will be able to check how Venofer is working by looking at your blood tests. There are 2 tests your doctor will likely monitor along with your hemoglobin and red blood cell count:
Ferritin : This is a protein that contains stored iron. Transferrin saturation (TSAT): Transferrin is a protein that takes iron from the storage protein (ferritin) or iron you're being treated for and delivers it to the bone marrow, where it's used to make healthy red blood cells strong.
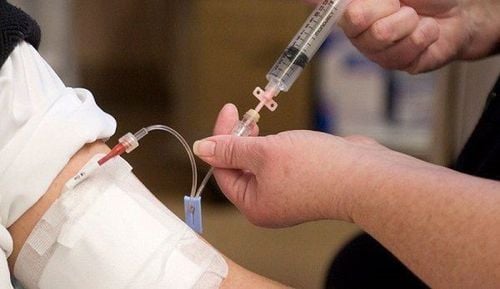
Thuốc Venofer được đưa vào cơ thể người bệnh qua đường tiêm
3. Venofer side effects
Adult patients: The most common adverse reactions (≥2%) included diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, hypotension, pruritus, extremity pain, arthralgia, back pain , muscle spasticity, injection site reactions, chest pain and peripheral edema.
Pediatric patients: The most common adverse reactions (≥2%) were headache, respiratory viral infection, peritonitis, vomiting, fever, dizziness, cough, nausea, arteriovenous fistula thrombosis, hypotension and hypertension.
Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: stomach pain, chest pain, irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), pressure in your chest, severe headache and blurred vision (hypertension), problems with access to dialysis.
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic-type reactions (itching, rash, swelling, wheezing, difficulty breathing, fainting or other allergic symptoms), some of which are life-threatening. life-threatening and fatal, may occur in patients receiving Venofer. Physicians should monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity during and after administration of Venofer for at least 30 minutes. Use Venofer only when medical personnel are available immediately to handle serious hypersensitivity reactions. Most reactions involving intravenous iron preparations occur within 30 minutes of completion of the infusion. Call your doctor or get medical help right away if you have symptoms of an allergic reaction, including: rash, chest pain, cough, dizziness, fainting, trouble breathing, sweating or throat tightness.
Using too much Venofer can lead to iron overload. All patients receiving Venofer injections require periodic blood tests to monitor iron levels in the blood. Venofer may decrease the absorption of iron preparations taken by mouth.
4. Be careful when using Venofer
Venofer can cause clinically significant hypotension. Monitor for signs of hypotension after each administration of Venofer. Hypotension following administration of Venofer may be related to the rate of administration or the total dose delivered.
Inform your doctor if you are pregnant, or plan to become pregnant or are breastfeeding. There may be risks to the mother and fetus related to untreated iron-deficiency anemia during pregnancy. Untreated iron-deficiency anemia during pregnancy is associated with adverse maternal outcomes such as postpartum anemia.

Người bệnh nên hỏi ý kiến bác sĩ trước khi dùng thuốc Venofer
Serious adverse reactions including circulatory failure (severe hypotension, shock including anaphylaxis) may occur in pregnant women with parenteral iron products (such as Venofer). , can cause fetal bradycardia, especially in the second and third trimesters.
Venofer Vial is only used when prescribed by a qualified doctor, so patients should not use the drug on their own, because it will affect health and the treatment process.
Vinmec International General Hospital always has a team of experienced doctors and pharmacists. When there are health problems, patients can contact the hospital for examination and instructions from a specialist doctor.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com