This is an automatically translated article.
Varicose veins are a common cause of male infertility. Depending on the degree of dilatation, the disease does not show symptoms until the symptoms are rampant such as: enlarged scrotum, palpable zigzag veins under the scrotum, testicular atrophy and infertility. Varicose vein ligation is the most effective method in the treatment of this disease.1. What is vasectomy?
Varicocele is a problem in 8-16% of men and accounts for about 20-40% of infertile men. This condition occurs when blood from the veins flows backward (instead of toward the heart) because the seminal veins are compressed by other agents or because the valves in the veins are damaged.Patients with varicocele often have no obvious symptoms, mainly have mild pain or a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, more pain in the evening, after sitting a lot, standing for a long time or doing heavy work. If the varicocele is large, the patient may notice a bulge in the upper corner of the scrotum. This phenomenon occurs due to enlarged veins floating under the skin.
The cause is due to abnormal dilation of the testicular veins and the plexus of the testicles. 90% of varicoceles occur on one side and usually on the left side. The main reason for patients to go to the doctor is pain in the groin area or infertility.
The purpose of vasectomy is to prevent venous return to the testicle, while preserving arterial and lymphatic blood flow.
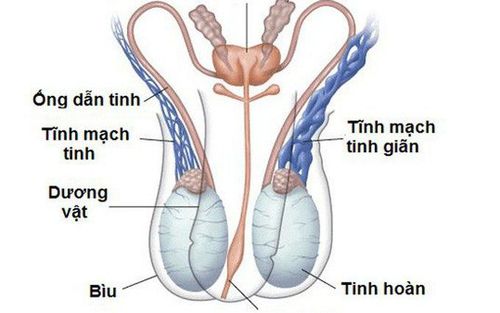
Hình ảnh giãn tĩnh mạch thừng tinh
2. Methods to cure varicose veins
Currently, there are many surgical techniques for varicocele being applied such as:The classic treatment for varicocele is laparoscopic or open surgery. Not everyone with a varicocele needs a vasectomy. Usually only surgery for typical cases (Grade III) accompanied by pain, prolonged scrotum Laparoscopic surgery for testicular ligation in the possibility of recurrence of surgery, similar to retroperitoneal surgery Obstruction Interventional vessels are usually more expensive and have a 4-11% chance of recurrence. Intraperitoneal ligation surgery with open surgery has a recurrence rate of 7-33%, and in children it is 15 -45% Traditional inguinal and scrotal surgery is less complicated but has the highest recurrence rate Microsurgery inguinal requires surgeons trained in microsurgery techniques, with modern equipment and time. Surgery lasts 2-3 hours. However, the surgical results are high, the recurrence rate is low. In addition to surgery to treat varicocele, your doctor may give you some more drugs to improve sperm count and quality, such as some endocrine-supporting drugs, minerals such as zinc (Zn ), antioxidants such as carnitine, those with vitamins E, A, C..
3. Indications for vasectomy
Palpable varicocele (grade 2-3) Infertile couple Wife with normal or otherwise potentially curable fertility Men with more than one whether abnormal semen analysis or sperm function test results In adult men with palpable varicocele and abnormal semen analysis but not currently trying to conceive In men In adults, there is evidence of a decrease in testicle size on the same side as varicocele Varicose veins cause prolonged pain and discomfort in the scrotum, affecting daily activities and work.
Chỉ định thắt tĩnh mạch tinh với cặp vợ chồng vô sinh
4. Contraindications to vasectomy
Patients with contraindications to surgery in general5. Steps to perform testicular ligation
5.1. Inguinal incision Schoysman's surgical techniqueStep 1: The skin incision is the same as that of the inguinal hernia. The lower end of the incision is at the point between the pubic spine and the pubic joint at the level of the external inguinal ring. The skin incision is oblique upward and outward, following the bisector of the angle between the femoral cord and the lateral border of the rectus muscle of the abdomen. The average length of the incision is from 8-10cm, the longer the more fat the patient is. Step 2: This surgical technique is contraindicated for patients with a history of inguinal hernia surgery because it is easy to violate the components of the spermatic cord when re-operating. Moreover, the seminal vein at this site has branched, so there are many branches that are easily missed when ligation. In addition, at this location the fine artery has branched, so it is difficult to distinguish with the naked eye. 5.2. Retroperitoneal iliacectomy Ivanissevich's technique
Skin incision above the deep inguinal ring and below the anterior superior iliac spine. The incision is about 8-10 cm long.
Palomo's technique
Step 1: Make a horizontal incision about 5cm above the deep inguinal ring, slightly higher than Ivanissevich's technique. Step 2: Incision of the great oblique muscle, separating the muscle fibers. Dissection enters the retroperitoneal space. Step 3: Dissect to reveal the seminal veins. Separation of the remaining components: arteries, lymphatics... Step 4: Cut and ligation of the seminal veins at the posterior peritoneal position outside the lumbosacral musculature and preserve the seminal arteries and lymphatics. Step 5: Stop the bleeding. Sewing wound recovery.
Có thể thắt tĩnh mạch tinh bằng cách mổ đường bẹn hoặc mổ đường chậu sau phúc mạc
6. Self-healing varicose veins
Things you should do to limit the progression of varicocele :Wear athletic underwear if you have a lot of varicocele Take a common pain reliever like acetaminophen if the pain persists Go see your doctor if the above symptoms become more severe Call your doctor if you have fertility problems You should not ignore pain or swelling in the scrotum to prevent it from getting worse and effective treatment. Varicocele is a common cause of reduced sperm count and quality in infertile men. Varicose vein ligation is given when the patient has infertility or an enlarged scrotum that affects activities and quality of life. After surgery, sperm count and quality improve in most cases.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.