This is an automatically translated article.
Neurohadine is an antiepileptic drug, commonly indicated for the relief of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Because this is a prescription drug, patients should not use it on their own, but need to consult a doctor before using it to ensure safety for health.1. What are the uses of Neurohadine?
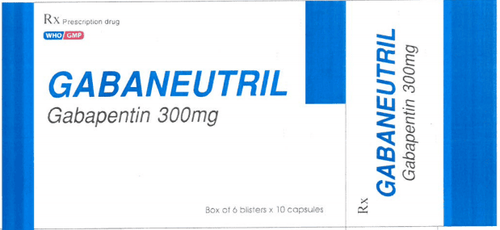
Neurohadine has the main ingredient is Gabapentin 300mg, the drug is in the form of hard capsules. This is an antiepileptic drug.
Gabapentin belongs to the group of antiepileptic drugs, for which the mechanism of antiepileptic activity of this drug is not really clear. The chemical structure of Gabapentin is similar to that of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), but Gabapentin has no direct effect on GABA receptors, neither inhibiting nor stimulating the receptor. this.
After oral administration, Gabapentin is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. When absorbed, Gabapentin is distributed throughout the body, enters breast milk and is almost not metabolized in the body. Thereafter, the drug is eliminated mainly by the kidneys as unchanged drug. The mean half-life of Gabapentin is approximately 5–7 hours in subjects with normal renal function. In elderly patients with impaired renal function, the elimination capacity of Gabapentin is reduced.
2. Indications and contraindications of the drug Neurohadine
Neurohadine is indicated for use in the following cases:
Treatment and support for partial seizures. Treatment of pain caused by nerve causes such as inflammation of the peripheral nerves, sciatica, postherpetic shingles. Contraindications:
Neurohadine should not be used in cases of hypersensitivity to Gabapentin or any of the excipients of the drug.
3. Dosage and usage of Neurohadine
How to use:
Gabapentin is in the form of capsules and should be taken orally with or without food. Dosage reduction, discontinuation, or replacement of gabapentin with another antiepileptic drug should be done gradually over a period of at least 1 week or longer as indicated by the physician. Dosage:
In case of epilepsy:
Adults and children over 12 years old: The first day should take 300mg x 1 time. On the second day, take 300mg/time x 2 times. Day 3 should take 300mg / time x 3 times. The dose may then be increased in increments of 300 mg/day, based on the patient's response and tolerability until an effective therapeutic dose is reached, the usual maintenance dose is 900–1800 mg/day, divided 3 times. Note that the maximum dose should not exceed 2400mg/day. If the drug is used more than once, the interval should not exceed 12 hours. When used in high doses, the drug can be divided into 4 times / day. For patients with renal impairment : An appropriate dose adjustment is required based on creatinine clearance, the recommended dosage is as follows:
Creatinine clearance from 50-70mL/min used with a maximum dose of 600-1200mg/ day, divided into 3 times. Creatinine clearance from 30-49mL/min administered with a maximum dose of 300-600mg/day in 3 divided doses. Creatinine clearance between 15-29mL/min administered with a maximum dose of 300mg/day in 3 divided doses. Creatinine clearance less than 15mL/min should be administered at a dose of 300mg every other day in 3 divided doses. Hemodialysis: Initial dose is 300-400mg, then 200-300mg every 4 hours on hemodialysis Children 6-12 years old or children weighing 30-36kg: First day 300mg/time and 1 time/day. day. The second day use 300mg / time and 2 times / day. The third day 300mg / time and 3 times / day. The usual dose for children is 300mg / time and 3 times / day. Some children who cannot tolerate daily increments may need to extend the increments by approximately every week.
Treatment of pain due to nerve causes for people over 18 years old:
Adults: Take the drug with a dose not exceeding 1800mg/day and divided into 3 times. Or another way can be used is to gradually increase the dose as follows: First day use 300mg; the second day use 300mg / time x 2 times / day; On the third day, use 300mg/time x 3 times/day. Next, it is necessary to increase the dose of the drug according to the response and tolerability, up to a maximum dose of 1800mg/day and should be divided into 3 times. Elderly: When used, it is necessary to adjust the dose due to decreased renal function and the risk of side effects.
4. Neurohadine side effects
When using Neurohadine medicine in addition to the main treatment effects, you may also experience unwanted effects including:
Loss of coordination in movement, feeling tired, nystagmus, dizziness, edema, drowsiness, memory loss. Children under 12 years of age may also experience neurological problems such as anxiety, irritability, feelings of euphoria or depression, overstimulation, oppositional attitudes...; Indigestion, dry mouth, constipation, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and peripheral angioedema may also occur. Rhinitis, pharyngitis, possibly pneumonia, double vision, decreased vision. Muscle pain, joint pain, rash, skin rash. Other side effects: Leukopenia, impotence may also occur. When you experience the side effects of the above drugs or other side effects, you need to stop using and should inform your doctor or you need to go to the facility immediately. nearest medical facility for prompt treatment.
5. Things to keep in mind when taking Neurohadine thuốc
Before using the medicine you need to tell your doctor about your medical and allergy history. For those with a history of mental disorders, impaired renal function and hemodialysis, the drug should be used with extreme caution. For those who drive and operate machinery: Due to the use of Gabapentin has effects on the central nervous system and causes symptoms of drowsiness, dizziness. These symptoms can affect the driver, so use with caution. Pregnancy and lactation: Gabapentin has been shown to be teratogenic in rodents. But there are currently no adequate studies in pregnant women. Therefore, Neurohadine should only be used during pregnancy when absolutely necessary. Gabapentin can pass into breast milk when taken orally. But the effect of the drug on the newborn is not really clear, so Gabapentin should only be used in lactating women when absolutely necessary and when used, breast-feeding should be discontinued to ensure safety. Gabapentin may cause a false positive in proteinuria. Overdose can occur when taken in very high doses, when used in high doses this medicine can cause symptoms including dizziness, double vision, slurred speech, difficulty speaking, drowsiness, excessive sleep, and diarrhea light flow. Supportive treatment should be instituted and the patient can usually make a full recovery. Neurohadine should not be stopped abruptly, as this may increase the frequency of seizures. Before discontinuing this drug or switching to another antiepileptic drug, a reduced dose should be prescribed for at least 7 days. Drug Interactions: Antacids can reduce the bioavailability of Gabapentin by about 20%. Therefore, gabapentin should be administered at least 2 hours after the antacid. In short, Neurohadin drug is used under the prescription of a doctor and you do not self-medicate. If anything unusual happens while taking the medicine, talk to your doctor for advice.