This is an automatically translated article.
Leravir is indicated in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Leravir is not recommended for pregnant women, nursing mothers and children under 12 years of age. The following article provides you with information about the uses and precautions when using Leravir.
1. What does Leravir do?
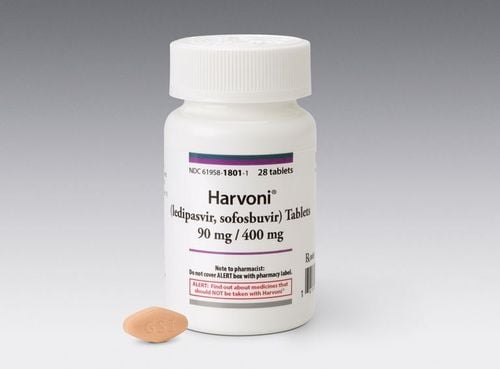
Leravir contains two main ingredients, Ledipasvir 90mg and Sofosbuvir 400mg. Leravir is available in the form of a film-coated tablet.Ledipasvir has an HCV inhibitory effect that targets the HCV NS5A protein - which is required for both RNA replication and HCV virion assembly.
Sofosbuvir genotype inhibits HCV NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, which is required for viral replication.
Some of the main uses of Leravir, including:
Leravir is effective in the treatment of killing the virus that causes chronic hepatitis C type 1, 3, 4, 5 and 6 with or without cirrhosis. Patients with type 1 and advanced cirrhosis, or patients with type 1 and 4 with or without cirrhosis, have received a liver transplant. Leravir is used together with Ribavirin. Leravir is contraindicated for use in the following cases:
Allergy or hypersensitivity to Sofosbuvir, Ledipasvir or any other ingredient in Leravir. Do not use Leravir and other drugs containing Sofosbuvir 400mg at the same time to avoid drug overdose. Children under 12 years of age, because the effects of Leravir in children have not been studied. Pregnant and lactating women: If treatment is required for a nursing woman, breast-feeding must be stopped while taking Leravir. The duration of treatment should recommend to women means of contraception to prevent pregnancy. Leravir should be used with caution in patients with hepatic and renal impairment.
2. How to take Leravir
Leravir is taken orally, the time of taking the drug is not related to the meal and should be taken at the same time of the day. Patients should take the tablet whole, do not chew or study the Leravir tablet due to its bitter taste. Treatment with Leravir for hepatitis C patients must be prescribed by a specialist.
Hepatitis C without cirrhosis: 1 tablet/day for 12 weeks. Hepatitis C with cirrhosis: 1 tablet/day for 24 weeks with Ribavirin. Using Leravir in combination with Ribavirin: Patients without decompensated cirrhosis, need to use Leravir in combination with Ribavirin in the treatment regimen, the daily dose of Ribavirin is calculated according to weight (< 75 kg using 1000 mg of Ribavirin and ≥ 75 kg of using Ribavirin). 1200mg Ribavirin), the dose is divided into 2 doses and taken with a meal. In patients with decompensated cirrhosis, the starting dose of Ribavirin: 600 mg/day, divided into small doses. If the initial dose is well tolerated, the dose can be adjusted to a maximum of 1000 mg -1200 mg/day (1000 mg for patients < 75 kg and 1200 mg for patients ≥ 75 kg). Where the starting dose is not well tolerated, reduce the dose as clinically indicated based on the patient's hemoglobin concentration. The highest recorded dose of Ledipasvir was 120 mg twice daily for 10 days and of Sofosbuvir as a single dose of 1200 mg, however no symptoms were reported. In case of Leravir overdose, immediately go to the nearest medical facility for timely treatment.
If you forget to take a dose of Leravir, take it as soon as possible. If it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and take the next dose as scheduled. Also, do not double the dose of Leravir.
3. Undesirable effects when using Leravir
Some undesirable effects when using Leravir have been reported:
Very common: fatigue, headache. Common: rash. Frequency not known: angioedema. In case of serious side effects, patients need to stop using Leravir and take them to the nearest medical facility for timely treatment.
4. Notes when taking Leravir
Do not take Leravir at the same time as Sofosbuvir 400mg to avoid drug overdose. Use with caution in patients who have failed Ledipasvir or Sofosbuvir therapy. Use caution when taking Leravir with other drugs.
5. Drug interactions
Antacids such as calcium carbonate, proton pump inhibitors, H2 receptor blockers may decrease Ledipasvir levels. Amiodarone: Concomitant administration of Leravir may cause severe symptomatic bradycardia. Digoxin: may increase Digoxin concentration when used concurrently. Vitamin K antagonists: Taking with Leravir increases the risk of bleeding. Rosuvastatin, Pravastatin: Leravir can significantly increase the concentration of these drugs. Leravir drug with two ingredients, Sofosbuvir and Ledipasvir, used in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C, can be used with Ribavirin. Before taking medication, it is best to consult your doctor for instructions on safe and effective use of the drug.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.