This is an automatically translated article.
Fusamix medicine is made in the form of suppositories placed rectally, the main ingredient is Piroxicam. The drug is used to treat inflammation and pain relief for rheumatoid arthritis, gout, ankylosing spondylitis, dysmenorrhea,...
1. What is Fusamix?
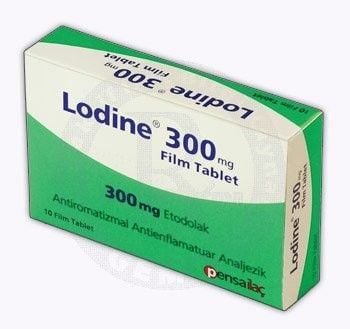
Fusamix medicine has the main ingredient Piroxicam 20mg and other excipients. Piroxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the oxicam group. The drug has antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. The general mechanism of the drug is due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase, which prevents the formation of prostaglandins, thromboxane and other products of the enzyme cyclo-oxygenase.
In addition, Piroxicam inhibits the activation of neutrophils even in the presence of cyclo-oxygenase products. Therefore, the anti-inflammatory effect of the drug also includes inhibition of proteoglycanase and collagenase in cartilage. At the same time, Piroxicam also inhibits platelet aggregation. And because Piroxicam inhibits prostaglandin synthesis in the kidneys, it reduces blood flow to the kidneys.
Indications to use Fusamix: Used in diseases that need anti-inflammatory and pain relief such as:
Osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis; Acute musculoskeletal diseases, ankylosing spondylitis, sports injuries; Acute gout; Dysmenorrhea, toothache, pain after surgery. Contraindications to the use of Fusamix:
Patients with hypersensitivity to Piroxicam or other components of the drug; Patients with gastric ulcer, acute duodenal ulcer; People with a history of bronchospasm, nasal polyps, asthma, Quincke's edema or urticaria caused by aspirin or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; Patients with cirrhosis of the liver ; Patients with severe heart failure; People at high risk of bleeding; Patients with renal failure (glomerular filtration rate <30ml/min).
2. How to use and dose of Fusamix
How to use: Administer the drug by placing it rectally. When administering medication, the patient should bend/bend to make it easier to administer. The medicine should be kept in the refrigerator (temperature 2 - 8°C) for 10 - 30 minutes before placing the medicine.
Dosage:
Adults: 1 tablet/time/day. In case of acute gout, take 2 tablets/day (morning and evening) for 5-7 days; Children 45kg name: Take 1 tablet/time/day. Overdose: When taking an overdose of Fusamix, symptomatic and supportive treatment is required.
3. Fusamix side effects
Over 15% of all Piroxicam users experience side effects. The majority of reactions are gastrointestinal dependent but are unlikely to preclude treatment. Only about 5% need to stop treatment.
Some side effects patients may experience when taking Fusamix include:
Common: Anorexia, stomatitis, nausea, epigastric pain, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, anemia, decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit, eosinophilia, leukopenia, skin pruritus, rash, drowsiness, dizziness, dizziness, uremia, increased blood creatinine, headache, malaise, buzzing ear, edema; Uncommon: Jaundice, hepatitis, abnormal liver function, gastrointestinal perforation and ulceration, gastrointestinal bleeding, dry mouth, petechiae, thrombocytopenia, marrow depression, skin bruising, sweating , erythema, Stevens - Johnson syndrome, depression, restlessness, irritability, insomnia, hematuria, proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome, interstitial nephritis, fever, flu-like symptoms, blurred vision, eye swelling, irritated eyes, increased blood pressure, worsening congestive heart failure; Rare: Pancreatitis, hair loss, nail loss, restlessness, hallucinations, restlessness, confusion, paresthesia, mood changes, dysuria, weakness, temporary loss of hearing, hemolytic anemia; Laboratory: Risk of cardiovascular thrombosis. Patients should inform their doctor about the side effects encountered when using Fusamix so that appropriate intervention measures can be taken.
4. Be careful when using Fusamix
Some precautions patients need to remember before and while taking Fusamix:
Fusamix may increase the risk of cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can lead to increased risk of cardiovascular events. chance of death. This risk may appear as early as the first few weeks of taking the drug, increasing with duration of use. The risk of cardiovascular thrombosis is mainly observed at high doses; Physicians should periodically assess the risk of cardiovascular events in patients receiving Fusamix even if the patient has no prior symptoms of cardiovascular disease. Patients should be warned about the risk of serious cardiovascular events, and should see a doctor as soon as they have unusual symptoms; To minimize the risk of adverse events, patients should take Fusamix at the lowest effective daily dose and for the shortest possible time; Patients with mild and moderate renal impairment do not need to adjust the dose of Fusamix; Patients with severe renal failure and hemodialysis should not use Fusamix because there are no studies on the effectiveness and safety of the drug in this subject; Use Fusamix with caution in the elderly, people with bleeding disorders, liver failure, cardiovascular disease, a history of peptic ulcer, people taking diuretics; Piroxicam causes an increase in residual pulmonary pressure in the neonate due to antenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus, if used during the third trimester of pregnancy. In addition, Piroxicam also inhibits labor, prolongs pregnancy, and causes gastrointestinal toxicity in pregnant women. Therefore, do not use Fusamix in the last 3 months of pregnancy or near labor; Piroxicam is excreted in breast milk, so it should not be used in nursing women; Because Fusamix can cause dizziness, lightheadedness and drowsiness, it should be used with caution when driving or operating machinery.
5. Fusamix drug interactions
Some drug interactions of Fusamix include:
When using Piroxicam concurrently with coumarin-type anticoagulants and drugs with high protein binding, the doctor needs to closely monitor the patient so that the dose can be adjusted. Use the right medications. Because of its high protein binding, Piroxicam can displace other drugs from plasma proteins; Fusamix should not be used concomitantly with aspirin, because it will lower the plasma concentration of Piroxicam and increase side effects; When taking Fusamix with lithium, it will increase the toxicity of lithium, due to the effect of increasing the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma. Therefore, patients should be closely monitored for lithium plasma concentrations; Piroxicam has no pharmacodynamic interactions with cimetidine, antacid and hypoglycemic drugs (Glibornuride, Glibenclamide) but the effectiveness of anticoagulants and hypoglycemic agents should be monitored when starting Piroxicam. Concomitant use of Probenecid will increase the rate of elimination of Piroxicam. In general, Fusamix is well tolerated, side effects are usually not too serious and in most cases do not interfere with the course of treatment. However, in the process of taking the drug, the patient still needs to strictly follow all the instructions of the doctor to ensure the best treatment effect and limit the risk of unpredictable events and side effects.
Follow Vinmec International General Hospital website to get more health, nutrition and beauty information to protect the health of yourself and your loved ones in your family.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.