This is an automatically translated article.
Carbachol is available in the form of eye drops. So what is Carbachol drug, what are the uses of Carbachol and how to use it, let's find out through the article below.1. What is Carbachol?
Carbachol is an ophthalmic drug, used in the following cases:
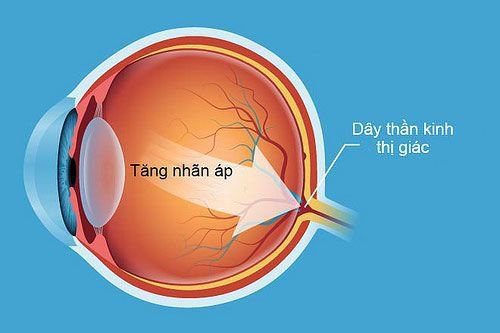
Open-angle glaucoma: Carbachol is effective in reducing elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with primary glaucoma. , open angle (simple chronic, non-congestive). Carbachol is used primarily in patients with discomfort or hypersensitivity to pilocarpine. Carbachol may be used concomitantly with sympathomimetic agents, β-adrenergic blockers, or carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Eye Surgery: Carbachol is used to produce blepharoplasty during surgery of the anterior chamber of the eye (eg, cataracts, keratoplasty, peripheral iridotomy). The drug reduces the intensity of IOP in the first 24 hours after cataract surgery. Angle-closure glaucoma: Carbachol is effective in reducing IOP in the emergency treatment of acute angle-closure (congestive) glaucoma before surgery. Ophthalmological examination: Carbachol has a blepharoplasty effect to counteract the mydriasis effects of sympathomimetic agents (eg, hydroxyamphetamine, phenylephrine) after ophthalmoscopy in patients with glaucoma. Carbachol is contraindicated in the following cases:
People with hypersensitivity to carbachol or any of its ingredients. Undesirable pupillary constriction conditions (eg, acute iritis, pupillary block).
2. Dosage and how to use Carbachol
Carbachol is used by eye drops into the conjunctival sac, not by injection. Some notes when using Carbachol:
Remove contact lenses (if any) before instilling Carbachol solution. To minimize side effects, start with a low concentration of Carbachol and increase it gradually as needed. After topical application of Carbachol, apply pressure to the lacrimal sac with your finger for 1-2 minutes to minimize nasal and pharyngeal drainage and reduce the risk of absorption and systemic reactions. Remove excess Carbachol solution around the eyes with a tissue and wash off the medication from your hands immediately. The dosage of Carbachol drug should be according to the prescription of a specialist. Adjust the concentration and frequency of Carbachol instillation according to patient requirements and response, as determined by intraocular pressure measurements before and during treatment.
Carbachol drug dosage in some specific cases as follows:
Open-angle glaucoma: Instill 1-2 drops of 1.5-3% drug solution up to 3 times per day.
3. Carbachol side effects
While using Carbachol, you may experience some side effects of the drug, including:
Eye irritation (burning or discomfort). Weep . Headaches at the temples or around the eye sockets. Muscle spasm pain. Blurred vision . Short-sighted . Conjunctival hemorrhage. Poor vision in dim light. If you see any unusual symptoms while using Carbachol, you should immediately notify your doctor for timely measures.
4. Carbachol drug interactions with other drugs
Carbachol may interact with the following drugs:
Accutane (isotretinoin). Activated carbon. Acuvail (ketorolac eye drops). Adderall (amphetamine/dextroamphetamine). Adrenaline (epinephrine). Alaway (ketotifen eye drops). Alcaine (proparacaine eye drops). Azasite (azithromycin eye drops). Co-trimoxazole (sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim). Coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone). Copper (copper gluconate). Glycerol (glycerin). Metoprolol Tartrate (metoprolol). Nevanac (nepafenac eye drops). Paracetamol (acetaminophen). Quercetin (bioflavonoids). TobraDex (dexamethasone/tobramycin ophthalmic). Xanax (alprazolam). Zaditor (ketotifen eye drops). Zymaxid (gatifloxacin eye drops).