This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Le Thi Thanh Thuy - Infection Control Doctor - Vinmec Times City International General HospitalSurgical site infection is the most common type of infection after surgery. One of the measures to prevent UTIs is surgical hand hygiene. Bacteria on the surgeon's hand can enter the surgical site if the glove is accidentally punctured without the surgeon noticing.
1. Purpose of surgical hand washing
Surgical hand hygiene can reduce the amount of bacteria on the hands of surgical personnel. Surgical hand sanitizers must limit the spread and significantly reduce the bacteria colonization of the hands from the start of the operation and keep the release of bacteria from the hands below baseline until the time of surgery. End of surgery.
There are 2 methods of surgical hand hygiene including:
Wash hands with antibacterial soap Rub hands with alcohol-based solution
Vi khuẩn trên tay phẫu thuật viên có thể xâm nhập và làm nhiễm trùng vết mổ của bệnh nhân
2. Surgical hand washing method with antibacterial soap
Surgical hand washing with antibacterial soap and water is considered the traditional method of hand washing. In the 19th century, surgeons washed their hands before surgery with antibacterial soap, warm water, and the use of a hand brush.
In the first half of the 20th century, surgeons, after washing their surgical hands with antibacterial soap and water, were recommended to dip their hands in a disinfectant solution such as iodine solution. For many years, surgeons washing their surgical hands for 10 minutes often resulted in skin damage. In the late 20th century, research by O'Farrell et al. comparing the number of microorganisms on the hands after washing with 4% chlorhexidine soap after 10 minutes and 5 minutes showed that: At the time immediately after Washing hands for 10 minutes reduces the number of microorganisms on hands compared to washing hands for 5 minutes. After surgery, the number of microorganisms on the hands of the surgeons who washed 5 minutes increased slightly compared with the surgeons performed 10 minutes, but there was no statistical significance. Therefore, the study recommends only 5 minutes of surgical hand washing for hip arthroplasty.
In other studies, washing hands for 2-3 minutes also reduced the number of bacteria to an acceptable level. The study by O'Shaughnessy and colleagues used 4% chlorhexidine gluconate to wash surgical hands for 2, 4, and 6 minutes. Results showed that surgical hand washing for more than 2 minutes was also not more effective. This study recommended that surgeons wash their surgical hands for 4 minutes for the first surgery and 2 minutes for the following surgeries.
Most studies discourage the use of a brush for surgical hand brushing. In the 1980s, Mitchell et al suggested limiting brush use. Hand brushing with a sponge or brush-sponge has the same effect as using a brush. Recent, randomized, clinical studies have also failed to show an antibacterial effect of the toothbrush. It is conceivable that a brush can be effective for stains between fingernails.
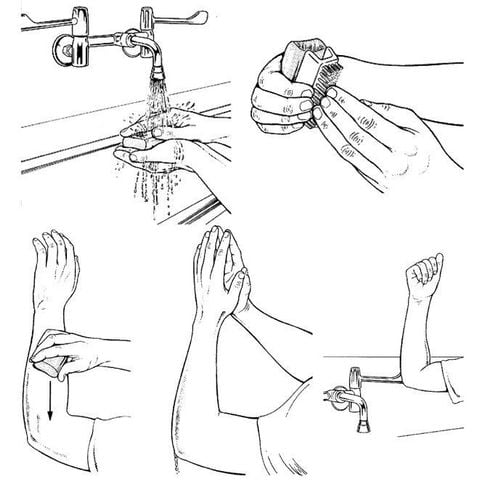
Hướng dẫn các bước rửa tay ngoại khoa bằng xà phòng khử khuẩn
3. Method of surgical hand hygiene with alcohol-based solution
The antibacterial effect of alcohol-based formulations is better than that of current surgical hand sanitizers. Many studies have demonstrated that formulas containing 60-95% alcohol or at a concentration of 50-95% when combined with other disinfectant chemicals such as QAC, hexachlorophene or chlorhexidine gluconate, reduce the number of bacteria on the skin immediately after hand hygiene better than other chemicals.
The World Health Organization recommends that it is not necessary to wash your hands with water before rubbing your hands with an alcohol-based solution unless the hands are visibly dirty. Surgeons should wash their hands thoroughly with neutral soap before entering the operating room area. Washing hands with water can limit the risk of bacterial sporulation, but does not help reduce the number of bacteria on the hands. An alcohol-based hand rub can even be affected if hands are not completely dry before rubbing alcohol or are affected by the water handwashing phase itself.
Therefore, for consecutive surgeries, medical staff only need to repeat the steps of disinfecting hands without washing their hands with water before moving on to the next surgery. Surgical hand rub technique is quite simple, hands are always scrubbed last to ensure the cleanest hands.
>>> Antiseptic hand sanitizer: After how many minutes is it safe?
Surgical hand hygiene with an alcohol-based solution is required for 3 minutes according to the reference method in the European standard EN 12791. According to the results of recent studies, even a 90-second surgical hand rub is as effective as a 3-minute hand rub with a mixed solution of iso- and n-propanol and mecetronium etilsulfate.
Alcohol-based gels should not be used for surgical hand hygiene unless the product meets the European standard EN 12791 for surgical hand hygiene or equivalent standards, e.g. FDA TFM 1994 of the US .

Các dung dịch chứa cồn mang lại hiệu quả khử khuẩn cao hơn nhiều lần sản phẩm rửa tay thông thường
Many gels available on the market today for hand hygiene do not meet the European EN 1500 standard for routine hand hygiene. Some chemicals recommend 3 minutes of surgical hand rub, others recommend a shorter surgical hand rub time, 1 minute or 1.5 minutes. Therefore, the duration of surgical hand hygiene with an alcohol-based solution is based on the manufacturer's recommendations. Manufacturer recommendations should be at least based on laboratory evidence.
In summary, both methods of surgical hand hygiene are appropriate for the prevention of UTIs. However, the antibacterial effectiveness of alcohol-based preparations far exceeds that of any current antibacterial soap. In addition, the rapid reduction in the number of microorganisms immediately after hand washing and the effectiveness of inhibiting bacterial regrowth to an acceptable level after 6 h of hand hygiene make surgical hand hygiene with a solution containing Alcohol is being prioritized in many medical facilities.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources:
Ministry of Health, 2012, Guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infections, issued together with Decision No. 3671/QD-BYT. WHO, 2009, Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care