This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Dr. Le Van Binh - Pediatric Intensive Care Physician - Intensive Care Unit - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Fever is a common symptom in many diseases. Fever in children is always a concern of parents, one of the main reasons why parents or carers take their children to the doctor and emergency room. Understanding and properly orienting the cause of fever can help us feel secure in taking care of and treating children at home or sending them to early medical facilities for timely treatment.
1. Characteristics of body temperature regulation in children
1.1. Physiology of body thermoregulation The human body has a constant body temperature thanks to a balance mechanism between two parallel processes: heat generation and heat loss. Heat is generated mainly due to the metabolism (catabolism) of substances in the body and the activity of the muscular system. The process of heat dissipation is mainly through radiation, evaporation, convection and heat transfer due to direct contact. Regulation of the balance of heat production and heat loss is achieved by the thermoregulatory center in the hypothalamus, which determines the threshold for body temperature. The thermoregulatory center regulates heat generation and elimination through the nervous and humoral systems, in which hormones play an important role (see diagram 1).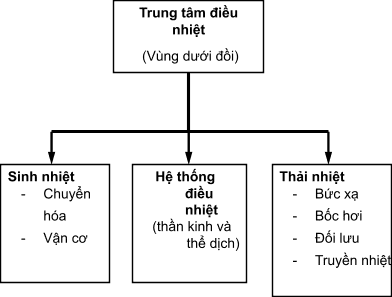
When the threshold of body temperature is high (febrile condition), the body responds to increase body temperature by both increasing the production of heat and retaining heat causing the body temperature to rise to reach the new threshold body temperature. Peripheral capillaries constrict to retain heat, making the child feel cold and want to dress warmly. The increased liver generates more heat. If it's still not enough to raise the blood temperature through the brain to a new threshold, the muscles also increase heat, causing the baby to shiver. When the fever is gone, the hypothalamic threshold temperature drops, the reverse process occurs (vasodilation, shivering, sweating and body temperature return to normal).
1.2. Characteristics of temperature regulation in children Thermoregulatory centers in children are not yet complete and are more prone to disorders than adults. The skin area compared to the body weight is large, so it is easier for children to lose heat as well as increase body temperature through contact and evaporation. Heat loss through evaporation (breathing fast, sweating a lot,...) in children is stronger. Children are always active, moving their muscles, so the ability to generate heat is more. Children are prone to endocrine-nervous disorders, especially during puberty. Children may experience some congenital diseases that cause temperature disturbances such as hypoplasia of sweat glands, ectoderm,...
2. Definition, classification and role of fever in children
2.1. Definition Fever is a condition in which the body's body temperature is raised due to disturbances in the thermoregulatory center, creating an abnormal threshold for body temperature. However, in practice, we often define fever when the body temperature rises without physiological reasons (such as after strenuous activity, changes in the menstrual cycle, ...)Adult body temperature is considered increased when over 37.5 degrees Celsius, but children's body temperature is defined as increased when the rectal temperature is 38 degrees Celsius or higher (equivalent to 37.6 degrees Celsius measured in the mouth and 37.4 degrees Celsius). C measured in the armpit).
Need to distinguish 3 states: Hyperthermia, hypothermia and fever.
Hyperthermia: The measured body temperature is above the normal range. This condition occurs when very hot ambient temperatures increase the body's temperature, the body reacts by increasing heat loss and decreasing heat production to maintain a normal body temperature threshold. Hypothermia: The measured body temperature is below the normal range. This condition occurs when very cold ambient temperatures lower the body's temperature, the body responds by reducing heat loss and increasing heat production to maintain a normal body temperature threshold. Fever: Threshold of body temperature is high (new threshold), normal body temperature becomes low body temperature. 2.2. Classification of fever According to degree (according to rectal temperature) as follows:
Mild fever: 38.1 degrees C to 39 degrees C. Moderate fever: 39 degrees C to 40 degrees C. High fever: 40.1 degrees C to 41.1 degrees C. Very high fever: Over 41.1 degrees C. Regardless of the cause, a fever of this degree is a priority emergency because it can cause brain and internal organ damage. , can cause disturbances in consciousness,... Over time:
Short-term fever, caused by benign viruses (usually self-healing after 2-3 days, no need for special treatment). Persistent fever: Daily fever for 2 weeks or more. Concurrent fever: Fever for many days but not continuously, there are days without fever. By nature of fever:
Continuous high fever (highland fever). Cyclical fever (such as malaria). High fever fluctuates: Alternating during the day, there are times when there is a high fever, there are times when there is no fever. Wave fever: Body temperature slowly rises, then after a while it slowly drops back to normal. After a short period of time, depending on the case, the fever recurs (such as spirochete). Regression of fever: After each fever for 3-7 days, there is a feverless episode, followed by a return of fever. 2.3. The role of fever Benefits: Usually fever is a supportive response that increases the immune response, increases the immune response (activation of immune cells and immune responses, fibrosis, collagen formation. ,...), increase bone marrow cell mobilization, destroy pathogens.
Bad effects: Usually occurs when the child has a high fever
Increased hypersensitivity reactions, shock. Increase the process of degradation, destruction, reduction of zinc and iron in the blood,... Dehydration, electrolyte disturbances. May cause febrile convulsions. Other neurological disorders: If the fever is very high, it can cause brain damage, delirium, excitement, hallucinations, ... can cause physical damage. Anorexia, exhaustion. Heart failure, respiratory failure, ... when high fever persists.

3. Methods of measuring body temperature
Body temperature can be measured directly when the probes are inserted into blood vessels or organs. Usually, only used when the patient has to perform interventional procedures. In fact, body temperature is mainly measured at the following 3 convenient locations:Rectal temperature measurement. Measure oral temperature. Measure armpit temperature. 3.1. Take the temperature in the armpit Dry the armpit area. Flick the thermometer so that the mercury level is below 35 degrees Celsius. Place the mercury bulb in the center of the armpit. Read the results after 10 minutes. A temperature equal to or above 37.4 degrees Celsius is considered a fever. 3.2. Oral temperature measurement Do not eat or drink for at least 10 minutes before taking the thermometer. Check the mercury level below the 35°C mark. Place the mercury bulb under the tongue – for young children, at the corner of the cheek, close the mouth gently (avoid biting the thermometer). Read the results after 5 minutes. A temperature equal to or above 37.6 degrees Celsius is considered a fever. 3.3. Take an rectal temperature (rectal temperature) A thermocouple is placed in the rectal tube (usually a separate thermometer). This is the temperature that most faithfully reflects body temperature. It should be done with care because roughness can damage the anus or rectal canal in young children. Read the results after 5 minutes. A temperature at or above 38 degrees Celsius is considered a fever.
4. Common causes of fever
There are some common causes of fever such as:Infections (most common)
Bacterial . Due to viruses and rickettsia. Due to parasites – especially malaria. Due to blood diseases, malignant diseases.
Due to colloid system diseases.
Due to other causes: Allergies, drugs, neurological causes,...
4.1. Common causes over time fever Acute fever:
Respiratory infections: Pharyngitis, pneumonia,... Urinary tract infections: Cystitis, pyelonephritis,... Gastrointestinal infections: Acute diarrhea, gastritis, enteritis,... Nervous infections: Encephalitis, meningitis,... Some viral diseases: Dengue fever, influenza, measles, chickenpox,... Fever Prolonged:
Infections: Infectious endocarditis, tuberculosis, typhoid, CMV infection, EBV,... Autoimmune diseases: Systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis,... Malignancy : Acute leukemia, lymphoma,... Congenital, endocrine, genetic diseases: Sweat gland hypoplasia,... Other diseases: Arteriovenous thrombosis, allergies,...

5. Handling and taking care of children with fever
5.1. General principles For children to wear light, airy clothes, let them lie in a cool place. Warm compress: Place a warm, damp towel on the child's forehead, armpit and groin, change the towel continuously. Give the child liquid food (porridge, soup) and drink plenty of water. Antipyretics are not the first solution. However, it is also necessary to reduce the child's fever when the child's fever is above 38.5oC. Start taking fever-reducing medicine for children when the temperature measured in the armpit is above 38.5 degrees Celsius. Note the following things not to do: Put the child in front of a fan or air-conditioner. Let the child shiver, as this can cause the temperature to rise even higher. Wake the child up to take the temperature (unless the child has been sleeping for an unusually long time). 5.2. Antipyretic drugs Use antipyretic drugs when the child has a high fever of 38.5 degrees Celsius or higher (measured in the armpit), it should be combined with the above care measures.Using the right antipyretic helps the child avoid serious complications caused by fever such as convulsions, vasomotor disorders and makes the child more comfortable. In particular, it is necessary to pay attention to reducing fever in high-risk children such as children with cardiovascular, neurological, and metabolic disorders. Fever > 41°C indicates that the child is at high risk of severe infection, hypothalamic disorders, and cerebral hemorrhage, requiring special attention in the use of antipyretic therapy.
5.2.1. Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) How to use: Oral, rectal. Dosage: 10-15mg/kg/time, every 4-6 hours, maximum 60mg/kg/24 hours. Need to prevent poisoning: Paracetamol can cause poisoning for children, destroy liver cells, cause increased liver enzymes, liver coma. Children are at risk of paracetamol poisoning when: Using Paracetamol ≥ 30mg/kg/time, or ≥ 60mg/kg/24 hours, or taking long-term high doses
5.2.2. Other antipyretic drugs Acetaminophen, Ibuprofen, Aspirin all inhibit hypothalamic cyclooxygenase, thereby inhibiting PGE2 synthesis and have the same antipyretic effect. However, because aspirin causes Reye's syndrome in children and reduces platelet aggregation, it is rarely used. Ibuprofen: May cause dyspepsia, gastric bleeding, renal hypoperfusion, noninfectious meningitis, hepatotoxicity. However, serious complications from ibuprofen overdose are uncommon. Dosage 5-10mg/kg/time every 6-8 hours. Alternating paracetamol and ibuprofen every 4-6 hours is also effective. 5.3. Examination to determine the cause Pay attention to epidemiological factors and history when the child has a fever:
This helps to identify the causes of fever in the child. If the child lives in a malarial area or has been to a malarial area within the past 6 months, a malaria risk assessment should be instituted in the child. Children who live in a dengue area or have been in a dengue area within the last 2 weeks are important information in determining the risk of dengue infection in children. If your child has had measles in the past 3 months and now has a fever, it is important to be alert for complications of measles,... Paying attention to whether your child is receiving medication before the fever appears will help with the prevention of measles. more information to determine the cause of the fever.
Identify the symptoms accompanying the fever that can guide the diagnosis of the cause of the fever:
Inflammation of the respiratory tract. Tired, dry lips, dirty tongue. Pimples or burns on the skin. Redness or bleeding. Swollen lymph nodes. Headache, joint pain. Diarrhea. Urinary disorders. If possible, the child should have a blood count test, CRP,... to determine the infection status before giving specific treatment.

5.6. Education, counseling and care in the home Teach caregivers how to detect and initially treat a child with a fever. Instructions on how to measure the standard temperature. For children with a history of febrile convulsions or a chronic illness, separate guidance and monitoring and prevention are required. Education and communication on scheduled vaccinations. The pediatric department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to such as: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in With a system of facilities, modern medical equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread, Vinmec will bring satisfaction to customers. Products and is highly appreciated by experts in the industry with:
Gathering a team of leading doctors and nurses in Pediatrics: Including leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctors). , masters), rich experience, worked in big hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108,... The doctors are well-trained, professional, have a heart - reach, understand young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. Advanced techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in pediatrics more effective: Neurosurgery - skull, stem cell transplant blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to play comfortably and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.