This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
The umbilical cord plays the role of providing nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. The phenomenon of umbilical cord prolapse is a dangerous obstetric condition, easily causing fetal distress and should be handled promptly to avoid unfortunate consequences.
1. Overview of umbilical cord prolapse
Umbilical cord prolapse is a condition in which the umbilical cord prolapses into the cervix, enters the birth canal before the fetus, causing the umbilical cord to be compressed between the pelvic wall or prolapse out of the vagina. The blood supply of the umbilical cord to the fetus is interrupted, so if not immediately cesarean section will lead to fetal death within 30 minutes.
The phenomenon of umbilical cord prolapse is common in the last months of pregnancy, with an incidence of 1/10 births. Usually the umbilical cord will prolapse when the water has broken, but there are also cases where the umbilical cord prolapses while the amniotic sac is intact.
2. Classification of umbilical cord prolapse
There are two types of umbilical cord prolapse: lateral prolapse and anterior prolapse. Here are the characteristics of each case of umbilical cord prolapse:
2.1. In lateral prolapse, the umbilical cord is compressed by the shoulder or head of the fetus, which can lead to hypoxia, slow fetal heart rate. Pregnant women with umbilical cord prolapse can actively adjust their sitting position and activities to reduce pressure on the umbilical cord. However, if fetal cardiac examination still shows abnormalities, immediate cesarean section should still be considered.
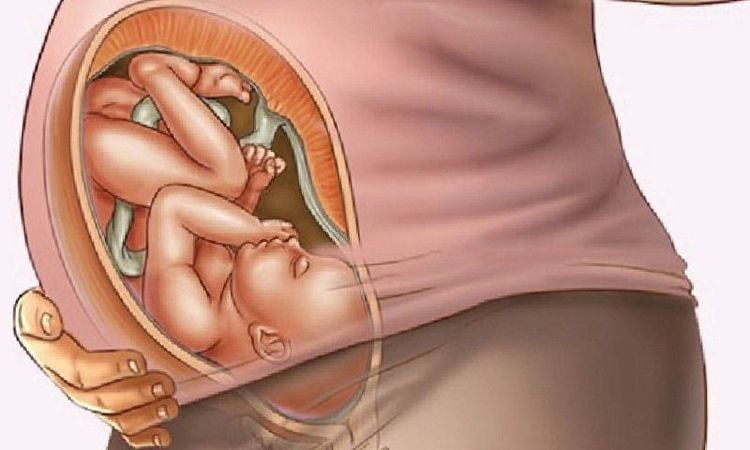
2.2. Anterior prolapse: the umbilical cord protrudes from the vagina Women with anterior umbilical cord prolapse often have amniotic membranes and rupture of membranes spontaneously or are affected before the head is inserted (common with the breech or transverse position).
Treatment of prolapse of the anterior umbilical cord protruding from the vagina begins with slightly elevating the fetal position and continuously holding it off the umbilical cord to gradually restore fetal blood flow during a cesarean section. Place the pregnant woman in a position where her knees are bent to her chest and give terbutaline 0.25 mg intravenously to relieve contractions.
3. Causes of umbilical cord prolapse
Umbilical cord prolapse can be caused by many causes, including maternal, fetal and fetal causes:
Maternal causes: Most are in women who have experienced it many times. childbirth, the adjustment of the fetal position is not good, causing abnormalities: distorted pelvis, narrowing, tumor in the prostate... Causes from the fetal side: the fetal position cannot rest on the cervix, leading to a condition Abnormal position (horizontal, inverted...), the umbilical cord may prolapse in front of the throne, prolapse of a limb, causing the umbilical cord to sag. Causes from the appendages of the fetus: Polyhydramnios makes the amniotic fluid too tight, with the risk of sudden rupture pulling the umbilical cord with it; abnormal vegetables, abnormally long umbilical cord... Diagnosis of umbilical cord prolapse is not difficult because during labor, the umbilical cord can be seen protruding out of the vulva or vaginal examination shows that the umbilical cord is coiled in the vagina or in the lateral cervix through the unbroken amniotic sac (prolapse of the umbilical cord in the amniotic sac), or the umbilical cord in front of the throne in the unbroken amniotic sac (prolapse of the umbilical cord before the throne in the amniotic sac). In most cases, the cervix is not fully dilated.
Almost any pregnant woman can have a prolapsed umbilical cord. However, there are certain factors that increase the risk of cord prolapse, including:
Women with narrow or distorted pelvis. Pregnancy with multiples or twins.
There is an abnormal pregnancy position: the buttocks, the horizontal position. Umbilical cord abnormalities: the umbilical cord is too long, the umbilical cord clings to the lower edge. Placenta attached low. Give birth many times. Sudden rupture of membranes.
4. Complications of umbilical cord prolapse
Umbilical cord prolapse is an obstetric emergency that needs to be detected and treated urgently to save the life of the fetus. Umbilical cord prolapse is most common in late pregnancy (when the fetus is more than 38 weeks old).
Prolapse of the umbilical cord easily causes acute fetal distress during labor, so if the baby is taken out late, the baby is prone to respiratory failure, brain damage due to lack of oxygen or even death. Therefore, if a pregnant woman is found to have prolapsed umbilical cord, she should be given emergency treatment within 30 minutes to promptly save the baby.
Note for pregnant women with umbilical cord prolapse:
When you feel abnormal signs: the umbilical cord is in the private area, the fetus kicks a little or a lot... you need to call an ambulance as quickly as possible. Do not try to push the umbilical cord back into the uterus. While waiting for the car to arrive, avoid compressing the umbilical cord by maintaining a kneeling position, face down, elbows and hands on the floor. Avoid eating and drinking before giving birth to prepare for the cesarean section.

Currently, there are no specific measures to prevent umbilical cord prolapse. However, if women are in the high-risk group for umbilical cord prolapse, after the 38th week of pregnancy, they should regularly go to the hospital for examination and stay in order to promptly deal with labor. Especially, in the last 3 months of pregnancy, the health of both mother and baby needs to be closely monitored and checked. Pregnant women need:
Know the real signs of labor to get to the hospital in time, affecting the health of the fetus. Differentiate between amniotic fluid and vaginal discharge for timely handling to avoid premature birth, fetal distress, and stillbirth. Be especially careful when bleeding in the last 3 months of pregnancy needs urgent emergency care to ensure the life of both mother and baby. Monitor the amount of amniotic fluid regularly and continuously. Monitor fetal weight in the last 3 months to assess baby's development and predict possible risks at birth. The special monitoring group is the same as the striker, and the fetal growth retardation needs to be closely monitored by the doctor and given appropriate indications. Distinguish between physiological contractions, labor contractions and mechanical pregnancy to get to the hospital in time. Maternity services at Vinmec make the pregnancy process easier and safer for pregnant women. During pregnancy, pregnant women will be examined by top doctors in the Obstetrics and Gynecology Department with high professional qualifications and experience, giving the best advice and treatment for the health of both mother and child. little.
For detailed information about all-inclusive maternity service packages, please contact the hospitals and clinics of Vinmec Health system nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.