This is an automatically translated article.
In the US, cord blood is a biological product regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration. It is found in the blood vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord, and cord blood is collected after the baby is born and after the cord is cut. Because cord blood is usually collected after the baby is born and the cord is cut, the procedure is generally safe for both mother and baby.
1. In what cases is cord blood used?
Cord blood is easy to collect and has 10 times more stem cells than liquid collected from bone marrow. Stem cells from cord blood rarely carry any infectious diseases and are half as likely to be rejected as adult stem cells.
Cord blood is only approved for use in “hematopoietic stem cell transplantation” procedures, performed in patients with disorders affecting the hematopoietic (hematopoietic) system. Umbilical cord blood containing hematopoietic stem cells can be used in the treatment of patients with blood cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma, as well as certain blood and immune system disorders, such as sickle cell disease and Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.
Cord blood is useful because it is the source of stem cells that form blood cells. It can be used for transplantation in people who need the regeneration of these hematopoietic cells.
For example, in many cancer patients, the disease is found in the blood cells. Chemotherapy for these patients destroys both cancer cells and healthy blood-forming stem cells. Stem cells transplanted from umbilical cord blood can help regenerate healthy blood cells after chemotherapy.
However, cord blood is not a cure for all diseases. Because cord blood contains stem cells, there have been inappropriate use cases for stem cells involving cord blood. Consumers may think that stem cells can cure any disease, but science doesn't show this to be the case. Patients should be suspicious if cord blood is advertised for uses other than stem cell regeneration.
2. How is cord blood drawn?
If you want to store cord blood, after birth, your doctor will clamp the umbilical cord in two places, about 10 inches apart, and cut the cord, separating the baby from the mother. They then insert a needle and collect at least 40ml of blood from that umbilical cord. The blood is sealed in a bag and sent to a lab or cord blood bank for testing and storage. This process takes only a few minutes and is painless for mother and baby.
Cord blood banks can also send tubes so that the mother's blood can also be collected. If so, the bank kit will have instructions along with the blood collection tubes.
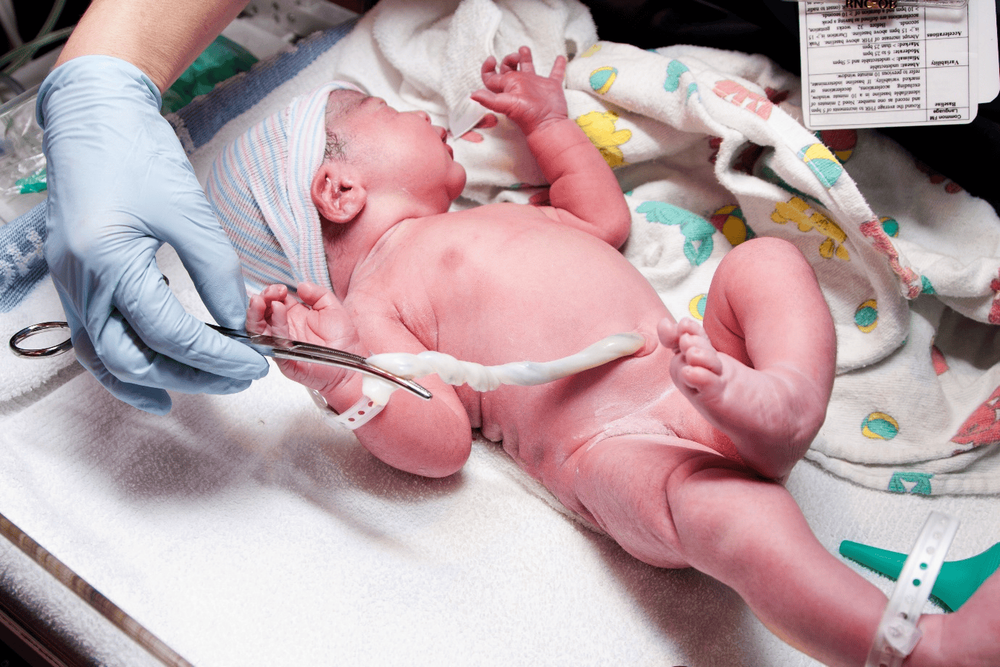
Quá trình lấy máu dây rốn chỉ diễn ra trong vài phút và không gây đau đớn cho mẹ và bé
3. Where is cord blood stored?
After cord blood is collected, it is frozen and can be safely stored for many years. The freezing method, known as cryopreservation, is important for maintaining the integrity of cells. Umbilical cord blood should be stored with such care.
There are three options for storing cord blood, including:
Public banks do not charge for storage. Cord blood stored here can be given to anyone who needs it. Banks may also use donated cord blood for research. A private (commercial) umbilical cord bank will store donated blood for use only by the donor and family members. These banks charge annual processing and storage fees, which can be expensive. Direct financing is a combination of public and private banking. They store cord blood for public use. But they also accept family-specific donations. No charge. The FDA regulates cord blood in a variety of ways, depending on the source, degree of handling, and intended use. Umbilical cord blood is stored for personal use, first- or second-degree use, and also meets other criteria in the FDA regulation, without agency approval prior to use. use.
Private umbilical cord banks in the US are still subject to other FDA requirements, including registration and listing of incorporation, applicable tissue practice regulations, and infectious disease screening and testing of donor (except where cord blood is used for the original donor). These FDA requirements ensure the safety of these products by minimizing the risk of contamination and transmission of infectious diseases.
Cord blood stored for use by an unrelated patient who meets the legal definitions of both “drug” and “biological product”. In this case cord blood must meet additional requirements and be licensed under a biologics licensing application or be the subject of an investigational new prescription prior to use. FDA requirements help ensure that these products are safe and effective for their intended use.
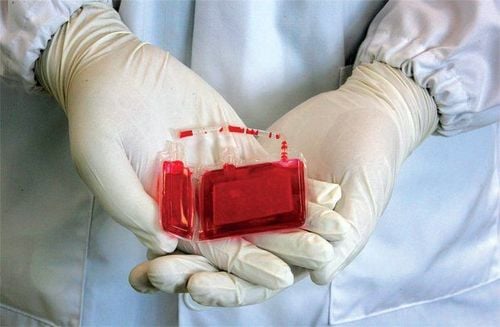
Máu dây rốn sẽ được bảo quản bằng phương pháp đông lạnh
4. Should you store your baby's cord blood?
Although commercial cord blood banks often bill their services as "bioinsurance" against future diseases, blood is not routinely used. One study said the chance for a child to use cord blood throughout their life is between 1 in 200,000 and 1 in 400.
The stored blood is not always used, even if the person develops the disease later, because if the disease is caused by a genetic mutation, that blood will also be in the stem cells. Current research says stored blood may only be useful for 15 years.
The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the American Academy of Pediatrics do not recommend routine cord blood storage. The groups say that private banks should only be used when there is a sibling with the disease who could benefit from stem cells. Families are encouraged to donate stem cells to a public bank to help others.
If you are considering donating to a cord blood bank, you should consider your options during your pregnancy to allow enough time to decide before having your baby. For public banks, ask if your birth hospital participates in the cord blood banking program.
If you have questions about collection procedures and risks, or about the donation process, ask your healthcare provider. The FDA also provides a searchable database that stores information on registered cord blood banks.
Be skeptical of claims that cord blood is a miracle cure, because it is not. Some parents may see private banking as a form of “insurance” against future illness. But remember, currently, the only approved use of cord blood is to treat blood-related diseases.
You should also be aware that in some cases, your stored cord blood may not be suitable for use in children who have donated blood. For example, you cannot cure certain diseases or genetic defects with cord blood that has the same disease or defect.
Parents of ethnic minority groups may especially want to consider donating to public banks, because more donations from these populations will help more minority patients in need of a transplant. more stem cells. Because doctors are more likely to find a good match among donors from the recipient's ethnic group.
When it comes to public banking, the need for cord blood is proven. And especially ethnic minorities need a stem cell transplant. Umbilical cord blood is an excellent source for stem cell transplants. And these transplants can change a patient's life.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, cord blood collection and treatment package is available at Vinmec Hi-Tech Center - the first cord blood bank in Vietnam operating under a closed and professional process. and modern. At Vinmec Cord Blood Bank, cord blood samples are:
Stored by the world's most modern BioArchive automated system being used by advanced countries around the world. Processing is performed by a sterile closed system in a clean laboratory operating in accordance with international GMP standards. storage and preservation is equivalent to the world's leading cord blood banks today. Currently, Vinmec is the first health system in Vietnam to successfully research and apply stem cells in the treatment of many incurable diseases such as stem cell transplantation to treat cerebral palsy, paralysis due to spinal injuries, cirrhosis of the liver, etc. Congenital biliary atresia... Therefore, when needed, cord blood samples will be treated with advanced methods in modern facilities, bringing high treatment efficiency.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference: fda.gov