This is an automatically translated article.
Ultrasound of face and neck malformations in the fetus is one of the safe and accurate diagnostic methods, helping doctors to detect abnormalities in the fetus's face and neck early and take timely intervention measures. .
1. Face and neck malformation in the fetus
Birth defects in the fetus occur with many different causes, can affect any child. Fetal head and neck abnormalities are often associated with chromosomal abnormalities and associated central nervous system anomalies. Early diagnosis and detection of abnormalities in the fetal face and neck is very important, because these can be important signs to help detect genetic disorders, or other complex syndromes. In addition, malformations have a great impact on the mental life of children later, so early diagnosis will help pregnant women as well as doctors to make accurate decisions.
Some malformations of the baby's face and neck include:
Hypoplasia or aplasia of the nasal bones Cleft lip and palate Cleft palate Large tongue defects Small jaw defects Two eyes apart Small eyes and no eyes Cranial fusion Thickness neck skin Angioedema

Siêu âm giúp chẩn đoán dị tật thai nhi vùng mặt cổ
2. Ultrasound of face and neck malformation in the fetus
2.1 Hypoplasia or aplasia of the nasal bone Fetal ultrasound detecting nasal bone aplasia is usually done at 11-14 weeks of pregnancy (at the end of the first trimester), which is a risk sign for Trisomy 2. By the second trimester , continue to look for aplasia or hypoplasia of the nasal bone. However, it should be noted that each different race will have different fetal nasal bone length. According to a study, for Caucasians, the average fetal nasal bone length is longer than that of Asian and Caribbean fetuses.
Based on the nasal bone assessment table “NORMAL RANGES FOR NASAL BONE LENGTHS”. Survey from 15th to 24th week of pregnancy, presence of nasal bone aplasia when the 5th percentile is small, and high risk of Trisomy 21,13 and 18.
2.2 Survey of maxillary frontal angle Initially, the survey of the maxillary forehead angle applied to the fetus from 11-14 weeks of pregnancy, now someone has applied it to the survey from the 15th to the 24th week of pregnancy. In a normal fetus, this angle decreases with gestational age, while with trisomy 21, this angle is still larger than normal. In addition, the fetus with Trisomy 21 will have abnormally thick skin on the nape of the neck and forehead. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct an additional survey of the forehead-maxillary angle with the forehead plane parallel to the skin, not with the frontal bone.
2.3 Examination of ear length In some chromosomal abnormalities, the fetal ear is shorter than normal. Measure by taking longitudinal or rim sections. The ear is measured from the top of the ear to the point below the earlobe. The ear length measurement is for reference only because the sensitivity is not high.
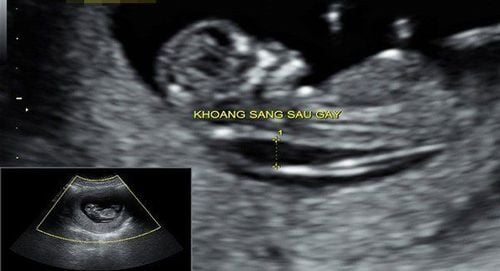
Siêu âm thai phát hiện các bất thường của thai nhi
2.4 Cleft lip and cleft palate Cleft lip, cleft palate is divided into 3 types including:
Cleft lip is a birth defect in the upper lip. Cleft lip and cleft palate is a defect that affects both the upper lip and the upper jaw bone. A simple cleft palate is a lesion of the posterior hard and soft parts of the cleft palate, whereas the upper lip and anterior jaw are normal. This is a malformation that occurs due to a failure to close the palate between the 5th and 8th days of pregnancy, causing the fetus to not be able to swallow amniotic fluid and resulting in polyhydramnios. Cleft lip, cleft palate can be unilateral or bilateral or can be a defect in the midline. Lesions in the midline of the lips are often associated with intracranial abnormalities, especially holoprosencephaly. Cleft lip, unilateral or bilateral cleft palate may be associated with a number of syndromes related to chromosomal abnormalities.
The ultrasound image shows 3 standard sections including:
Coronal section Cross section: Continuous alveolar ridge shows that the fetus does not have a cleft palate. This is the main section to examine cleft palate. Mid longitudinal view For cleft lip:
Coronal view: Unilateral or bilateral defect, or midline defect extending from the upper lip to the nostrils Longitudinal view: For bilateral cleft lip, the midline of the upper lip sometimes protrudes anteriorly For cleft palate:
Cross section: Defect on one or both sides or in the line between the upper lip and alveolar ridge Longitudinal view: When 2D ultrasound fetal tongue Abnormal elevation due to a defect in the palate. When doppler ultrasound follows fetal breathing movements, the flow of amniotic fluid into the nose and mouth merges through the cleft of the palate.
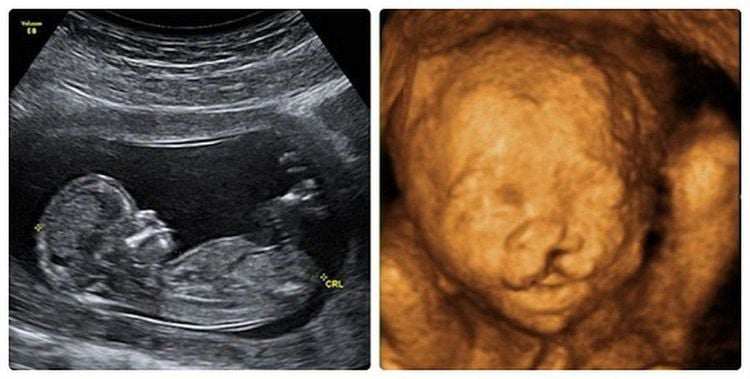
Siêu âm thai phát hiện các dị tật như hở hàm ếch
Diagnosis of cleft lip, unilateral or bilateral cleft palate or midline is usually easy because polyhydramnios makes it easier to examine the fetal face. However, prenatal diagnosis of cleft palate alone cannot be made because the craniofacial bones block all ultrasound.
2.5 Enlarged tongue Enlarged tongue occurs in fetuses whose mothers have diabetes, fetuses with hypothyroidism, fetuses with a syndrome characterized by enlarged organs, large tongue, umbilical hernia (Beckwith syndrome) -Wiedemann), fetus Trisomy 21. The fetus' tongue is abnormally large and protrudes from the mouth, which will prevent the swallowing of amniotic fluid, causing the fetus to have polyhydramnios.
On ultrasound images mainly based on longitudinal section. The tongue of the fetus is large and protrudes from the mouth. For doppler ultrasound, because the large tongue narrows the oral cavity, it is very difficult for the fetus to swallow, leading to a smaller flow of amniotic fluid through the mouth than the flow of amniotic fluid through the nose.
2.6 Micromaxillary Micromaxilloma due to hypoplasia of the mandible. The small lower jaw will lead to the fetus having difficulty swallowing amniotic fluid, causing polyhydramnios. This malformation is commonly seen in many chromosomal abnormalities, especially trisomy 18 and 13.
Diagnosis on ultrasound imaging is based on the mid longitudinal section showing a small and indented chin. Normally, when the tangent line to the frontal bone passes through the base of the nasal bone in the mid sagittal section, this line is located behind the fetal chin. With small jaw defects, this line is located in front of the fetal chin.
2.7 Binocular ptosis is defined when the distance between the eyes is closer than normal. Measure the distance between the two eye sockets and compare with the normal value according to gestational age. Binocular malformations are often associated with brain malformations, especially holoprosencephaly, MeckelGruber syndrome, Williams syndrome, trisomy 13.
2.8 Binocular diplopia When the eyes are located far apart. each other than usual. Measure the distance between the two eye sockets and then compare the normal value according to the gestational age. This malformation is often accompanied by facial malformations such as brain herniation, cleft lip,...
In short, facial and neck malformations often have a significant impact on a child's later life. Ultrasound of face and neck defects in the fetus is a safe diagnostic measure, helping to detect abnormalities in the fetus early and thereby have appropriate intervention methods. Therefore, pregnant women need to have regular antenatal check-ups and note the important milestones in order to conduct ultrasound and diagnose facial and neck malformations. During pregnancy, especially the second 3 months of pregnancy is a period of strong fetal development. Pregnant women need:
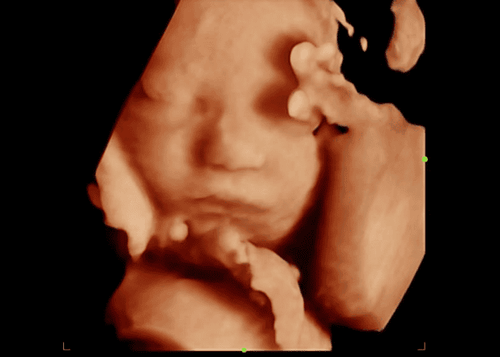
Comprehensive fetal malformation screening by superior 4D ultrasound technique. Screening for gestational diabetes, avoiding many dangerous complications for both mother and baby. Control the mother's weight reasonably to assess the health status of the pregnant woman and the development of the fetus. Understand the signs of threatened early delivery (especially in those carrying multiple pregnancies or having a history of miscarriage or premature birth) so that they can receive timely treatment to maintain pregnancy.
Bằng phương pháp siêu âm 4D có thể tầm soát dị tật thai nhi toàn diện.
To protect mother and baby during pregnancy, Vinmec provides a package Maternity service to help monitor the health status of mother and baby comprehensively, periodically check antenatal care with leading obstetricians, perform full range of tests, important screening for pregnant women, timely advice and intervention when detecting abnormalities in the health of mother and baby.
For detailed information about all-inclusive maternity packages, please contact the hospitals and clinics of the Vinmec health system nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.