This is an automatically translated article.
This article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Khong Tien Dat - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital. The doctor has more than 14 years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging.Acute abdominal pain can be a symptom of many different diseases, from mild to dangerous. Therefore, the diagnosis of acute abdominal pain becomes a challenge for the clinician when differentiating from benign to urgent. Associated symptoms also lack specificity and are atypical. At this time, ultrasound will play an important role to support early diagnosis, determine the stage of the disease and have effective treatment.
1. Orientation in the diagnosis of acute abdominal pain
The abdomen is an organ with many internal organs, so it is difficult to diagnose a specific disease based on the clinical presentation of acute abdominal pain. However, functional studies can identify some typical diseases as follows:Perforation of hollow viscera : Uncommon, vomiting and no bowel obstruction in the first hours n Acute pancreatitis : Sudden inflammation In the short term, it can lead to bleeding in the gland, infection and the formation of pancreatic cysts. Intestinal obstruction: intermittent visceral abdominal pain, abdominal distension, bowel obstruction. Cholestasis: Acute abdominal pain can be very severe in acute biliary obstruction due to gallstones moving or trapped in the lower part of the common bile duct Renal colic: Occurs suddenly after mild pain in the hip, lasting from a few minutes to A few hours are often intense and there is no pain relief. Appendicitis in the early stage sometimes only pain in the epigastrium, low fever, later stages can be localized pain in the right iliac fossa, with obvious response to pressure.
2. Ultrasonography of acute abdominal pain in what diseases?
Acute abdominal pain is a symptom that can be encountered in many different diseases. Therefore, ultrasound will help doctors screen and localize common diseases for timely treatment of patients. Some common pathologies when detected on ultrasound for images are as follows:Acute cholecystitis with stones: Image of gallstones stuck in the gallbladder neck or common bile duct, gallbladder distended over 5cm and signs Murphy sign on positive ultrasound. Acute cholecystitis without stones: There is no image of gallstones, but the gallbladder is distended, Murphy's sign is positive on ultrasound, and the prognosis is worse than cholecystitis with stones. Acute hepatitis: Hepatomegaly, diffuse poor echogenicity, diffuse thickening of gallbladder wall, but gallbladder lumen is collapsed, Murphy's sign on ultrasound is negative. Dengue: Diffuse gallbladder wall thickening, non-collapsed gallbladder lumen, negative echogenic Murphy's sign, pleural or peritoneal effusion Cholelithiasis: Thick echogenicity with or without dorsal shadow, MRCP ( Biliary magnetic resonance imaging) is very sensitive for the diagnosis of gallstones.
3. Ultrasound of acute abdominal pain in women
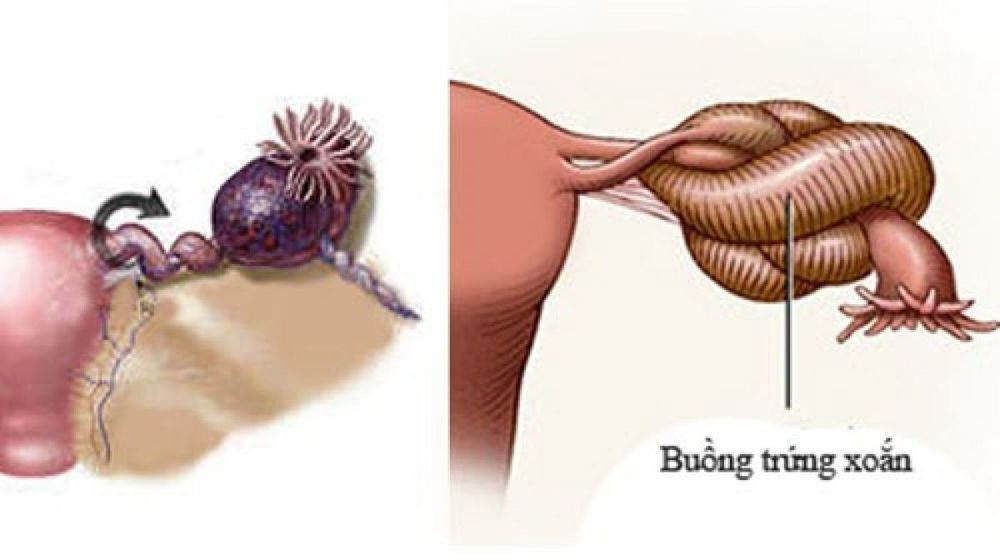
Pelvic inflammatory disease: The wall of the fallopian tube is thicker than 5mm, there are signs in the cross section of the fallopian tube. gear teeth and possibly tubal fluid retention, endometritis, enlarged ovaries, many small cysts (easily confused with polycystic ovaries), sacral fluid has poor echogenicity. Ovarian torsion: The ovary is enlarged many times (more than 4mm long) compared to the contralateral ovary, signs of thick echogenic border around the follicle, the ovary may be located in an abnormal position (anterior or fundus of the uterus). , on the bladder) Fetus ectopic in the fallopian tube: ultrasound finds a gestational sac or embryo with a fetal heart in the fallopian tube. Acute abdominal pain can be a symptom of many dangerous diseases, which can range from simple to dangerous and fatal. Therefore, when there is severe abdominal pain and no cause can be found, you should go to a medical center for examination and clinical diagnosis to determine the disease, from which an effective treatment plan can be established.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied ultrasound technology in examination and diagnosis of many diseases. Ultrasound technology at Vinmec is carried out methodically and in accordance with standard procedures by a team of highly qualified medical professionals, modern machinery system, thus giving accurate results, making a significant contribution to the identification. diagnosis and stage of the disease.
If you have a need for medical examination by modern and highly effective methods at Vinmec, please register for an online examination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.