This is an automatically translated article.
Because congenital CNS malformations are the most common group of malformations in the fetus, second only to cardiac malformations, fetal head ultrasound in the 2nd trimester is still an important screening tool. important for early detection of fetal abnormalities. Then, appoint fetal head survey in the 3rd trimester ultrasound to assess the degree of malformation as well as plan preparation for safe birth, treatment options right after.1. What is fetal head ultrasound?
Evaluation of the fetal central nervous system is an important aspect of fetal ultrasound during pregnancy to easily identify some major malformations and thereby provide sufficient information to advise the father. mothers about pregnancy monitoring, fetal treatment options and also postpartum treatment and prognosis. Therefore, assessment of the fetal central nervous system in the prenatal period is extremely important with the main tool being fetal nervous system ultrasound.Therefore, all professionals involved in the morphological evaluation of the fetal nervous system need to be familiar with the embryology and anatomy of the fetal CNS, as well as its sonographic features in these areas. different gestational ages, to avoid diagnostic errors.
On the other hand, besides the need to screen and monitor congenital central nervous system malformations, which are common malformations in the fetus, the indications for ultrasound examination of the fetal head are also aimed at monitoring head circumference during pregnancy. This is one of the basic biometric parameters used to assess fetal size. Head circumference, along with biparietal diameter, abdominal circumference, and femoral length were necessary parameters to be calculated to provide an estimate of fetal weight. During the second trimester, this parameter can be extrapolated to estimate gestational age and estimated due date as well as to assess fetal development. Then, on the 3rd trimester ultrasound, near the due date, head circumference was also a reference for the pattern of labor.

Việc đánh giá hệ thống thần kinh trung ương của thai nhi là một khía cạnh quan trọng của siêu âm thai trong suốt thời gian thai kỳ
2. Anatomical features on ultrasound to examine fetal head
Basic fetal brain assessments are performed routinely during the second trimester with transabdominal transducers. This technique is used to screen for CNS malformations during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy in low-risk patients, with a sensitivity of 80% for detecting CNS malformations and CNS malformations. involves the study of the structure of the fetal brain and spine.Structures evaluated in fetal nervous system ultrasound include:
Skull: about shape and biometric indicators Brain parenchyma: about structure Lateral ventricles Choroid plexus Intersemical fissure bridge The tentacles Cerebellum Posterior fossa For a complete baseline ultrasound assessment of the fetal brain morphology above, it is necessary to perform three-sectional scans of the skull: trans-lateral, trans- posterior fossa and transversely. through the bivertex.
3. Ultrasound examination of the fetal head in the cross-section of the lateral ventricles
This plane represents the projection of the fetal head in the transverse axis with the lateral ventricles. Landmarks that need to be investigated by ultrasound to determine the correct anatomical plane include the lateral ventricles, transparent septum, and crescent of the brain. On this view, the width of the lateral ventricles will be measured. If the size is greater than 10mm, it will be identified as ventricular dilatation, which is the most common intracranial anomaly diagnosed preoperatively. This malformation is associated with many other intracranial anomalies and fetal aneuploidies.Therefore, when ventricular dilatation is detected, a detailed anatomical ultrasound of the fetus will need to be repeated, as well as counseling for genetic testing of the fetus.
Fracture encephalopathy, which results from a failure to divide brain branches during early brain development and embryogenesis into two lateral ventricles, can also be detected in this plane. In addition, some other malformations are also found in this section, such as anencephaly or anencephaly.
4. Ultrasound examination of the fetal head on the cross section of the posterior fossa
The plane at the level of the posterior fossa, also known as the transcerebellar plane, is an axis (or slightly oblique) at the level of the posterior fossa. In this plane, the physician can see the cerebellum, the posterior fossa, and the 3rd and 4th ventricles. This view is easily obtained by tilting the ultrasound transducer backward about 45 degrees from the plane. pass through the biparietal while avoiding the shadow from the skull.The most common abnormalities detected in this plane are Dandy-Walker malformation, Chiari II malformation (typical of spina bifida) and cerebellar necrotizing dysplasia. Occasionally, small posterior occipital brain sections may also become more prominent on this plane.

Những bất thường phổ biến nhất được phát hiện trong mặt phẳng mặt phẳng xuyên tiểu não là dị tật Dandy-Walker, dị tật Chiari II và loạn sinh hoại tử tiểu não
5. Ultrasound examination of the fetal head in cross-section through the biparietal line
Ultrasonographic landmarks that define the correct biparietal cross-section include the midline crescent, the septum, and the thalamus. Abnormalities detected in this view include dilated ventricles, cerebral fissures, corpus callosum and 23) and septal aplasia.In addition, other rare intracranial abnormalities, such as brain tumors, brain cysts, can also be detected in this plane. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment of the fetal central nervous system requires a thorough understanding of the anatomical structures as well as the development and physiological changes of the condition during pregnancy.
6. Common CNS malformations on fetal head ultrasound
6.1 Ventricular dilation This is the most common CNS abnormality diagnosed by fetal nervous system ultrasound based on the width of the lateral ventricles. Mild ventricular dilatation is when the ventricular width is 10 to 12 mm, moderate 12 to 15 mm, and severe if greater than 15 mm.>>> Does fetal ventricular dilatation have any effect?
Neural tube defects belong to a group of serious malformations of the central nervous system in the fetus. The most common conditions are anencephaly, spina bifida, and brain herniation. The pathogenesis is due to malfunction in the process of primary neural tube closure from day 17 to day 30 after insemination suspected due to maternal folic acid deficiency.
6.2 Abnormalities of cortical formation The development of the cortex is through three steps: proliferation and differentiation of neuronal precursors; migration of immature neurons and cortical maturation. Disruption of any of these steps in cerebellar development, either inherited or acquired, can lead to a variety of abnormalities, including:
Cerebral palsy : persists cleft extends across the hemispheres from the ventricles to the surface of the brain
Flat cerebral malformation : absence of cortical surface grooves, leading to microcephaly
Midline abnormality Anterior cephalic malformation : due to abnormality Incomplete segmentation of the neural tube
Nonsegmental malformation : is the most severe type, there is no complete separation of cerebral hemispheres, resulting in a single brain.
Posterior fossa abnormalities Posterior fossa abnormalities include:
Dandy-Walker malformation : complete or partial formation of the cerebellum, fourth ventricle dilatation and posterior fossa enlargement
Posterior fossa dilatation : when enlarged more than 10 mm in size
Blake's cyst cyst
Vascular abnormalities Possible causes of cerebral hemorrhage during fetal period detected on fetal nervous system ultrasound are mainly the result of vascular abnormalities, including benign or malignant arterial malformations, intracranial tumors, fetal infections, drug toxicity, and coagulopathy.
Brain Parenchyma Destructive Damage Types of brain parenchymal destructive lesions can include a wide range of conditions including encephalitis, brain tumors, brain compression due to brain tumors, cysts, brain infections, dysplasia , intracranial hemorrhage and other lesions. The early identification of these abnormalities on fetal nervous system ultrasound can be helpful in informing the family about the prognosis at birth and subsequent management options.
In summary, fetal head ultrasound is used to assess the fetal nervous system, find birth defects in high-risk subjects, or obtain head circumference, as a biometric index according to monitor fetal development. However, a reliable result depends on the cross-sectional quality, knowledge and experience of the fetal sonographer across the trimester and requires high resolution on ultrasound equipment.
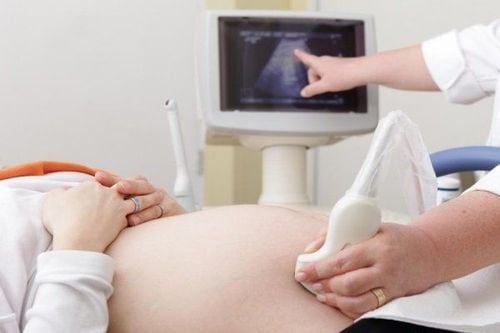
Siêu âm khảo sát đầu thai nhi nhằm đánh giá hệ thần kinh thai nhi, tìm các dị tật bẩm sinh trên những đối tượng có nguy cơ cao
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article references source: NCBI, glowm.com