This is an automatically translated article.
Gallbladder polyp is a disease with no specific symptoms, detected only during examination. Therefore, for diagnosis, ultrasound is necessary. The diagnosis of gallbladder polyps with ultrasound helps the doctor to see the location, size, and danger level as well as monitor the progression of polyps, thereby giving appropriate treatment.
1. What are gallbladder polyps?
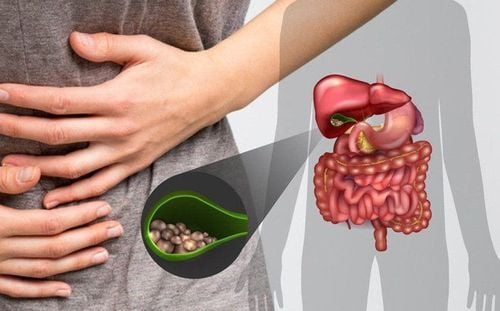
The gallbladder is a small, blue-colored sac with a capacity of 30-60 ml, attached to the lower right lobe of the liver, and connected to the bile duct through the cystic duct. The gallbladder will project onto the abdominal wall, located in the upper right abdomen. The role of the gallbladder is to concentrate and store bile. When we eat, the gallbladder will contract to push the bile contained in it into the bile duct and then down the duodenum to mix with food to help digest fats.
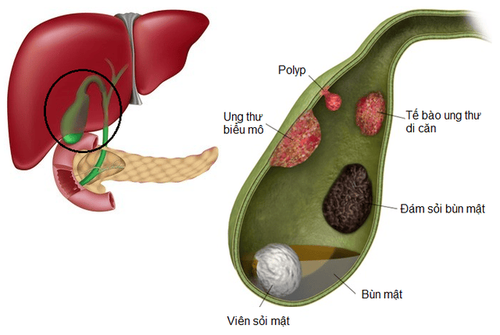
Gallbladder polyps, also known as biliary mucosal papillomas, are a type of tumor or pseudotumor that develops on the surface of the gallbladder lining. Gallbladder polyps are usually classified into 5 types as follows:
Cholesterol polyps: Cholesterol polyps are usually small polyp sizes, only from 2 -10 mm, with stalks. Gallbladder myoma: This type of polyp is cholesterol crystals, bile sludge, which can be localized or diffuse. Inflammatory polyps: This is usually a solitary polyp, polyp size from 5 to 10 mm, composed of granulation tissue, fibrous and inflammatory cells. Gland polyps: This is also a solitary, sessile gallbladder polyp. Other rare forms of polyps: granulomatous cells, fibroids, lipomas, malformed tissues,... There are many causes related to the formation of gallbladder polyps such as: Hepatobiliary dysfunction; blood fat levels increase; People who are obese, infected with hepatitis virus... Symptoms of gallbladder polyps may include:
When polyps cause secretion disorders, bile secretion in the gallbladder lumen or gallstones or accompanying cholecystitis. , the patient will feel mild pain in the right lower quadrant or epigastrium, pain appears after eating. In addition, abdominal bloating, indigestion, nausea and vomiting may occur. Mild pain when pressing the right lower quadrant, most of which do not detect abnormal signs.
2. Ultrasound detection of gallbladder polyps
Gallbladder polyp is a disease with no specific symptoms, detected only during examination. Therefore, for diagnosis, ultrasound detection of gallbladder polyps is necessary. Ultrasound is a simple method, the diagnosis of gallbladder polyps by ultrasound helps doctors:
Can see the images of gallbladder polyps on ultrasound, position, size as well as assess the level of danger. they. In addition, the image of gallbladder polyps on ultrasound also helps to monitor the progression of polyps, thereby giving appropriate treatment. When the gallbladder polyp is ultrasounded many times, the results are different because the course of the disease and the time of eating will be different from that of fasting, so there is a fluctuation in the size of the polyp. Therefore, before the ultrasound detects gallbladder polyp, the patient should not eat or drink so that the gallbladder polyp will be seen very clearly.
Ultrasound of gallbladder polyps has a high diagnostic accuracy rate, but it does not distinguish between benign and malignant polyps, so to be more accurate, the doctor may measure the size of the gallbladder polyps and rely on them. Use the following criteria to assess the potential risk of cancer:
Gallbladder polyps larger than 1cm have a 46-70% chance of developing into cancer. Polyps with rough shape, spreading legs and no stalk are at risk of malignant polyps. Gallbladder polyps increase rapidly in both number and size.

Siêu âm polyp túi mật cho tỷ lệ chẩn đoán chính xác cao
3. Gallbladder polyp treatment
Gallbladder polyps do not go away or go away on their own. For polyps to disappear, the treatment is cholecystectomy. However, this method is only performed when polyps have a high risk of cancer. In the remaining cases, the priority goal is still to prevent polyps from increasing in size to preserve the gallbladder. Treatment methods include:
Make a reasonable diet:
Diet affects the growth of polyps, so to make sure you should make yourself a reasonable diet. People with gallbladder polyps should eat plant-based fats instead of animal fats. Increase the intake of green vegetables and fruits for easy digestion. Avoid eating the skin of poultry such as chickens, swans, ducks and animal organs because these foods contain high cholesterol, creating an opportunity for polyps to increase. Periodic ultrasound of gallbladder polyps to help control the size as well as monitor the growth of polyps:
In case of polyps less than 6cm in size, we will periodically re-examine health every 6-9 months. If the polyp is larger than 6-9 cm, it will be periodically re-examined about every 3 months. Cholecystectomy to avoid risks, polyps develop into cancer when:
Gallbladder polyps are large, the size of gallbladder polyps increases rapidly with a large number. The polyp's foot is widespread, irregular in shape. Multiple gallbladder polyps. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has Hepatobiliary Screening packages, which help detect Hepatitis Virus at an early stage even when there are no symptoms. In addition, the comprehensive hepatobiliary screening package helps customers:
Assess the liver's ability to work through liver enzyme tests; Evaluation of bile function; vascular nutrition; Early screening for liver cancer; Perform tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C Assessment of hepatobiliary status through ultrasound images and diseases that have the potential to affect liver disease/cause liver disease. more severe liver disease In-depth analysis of parameters to evaluate hepatobiliary function through laboratory, subclinical; the risk of affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.