This is an automatically translated article.
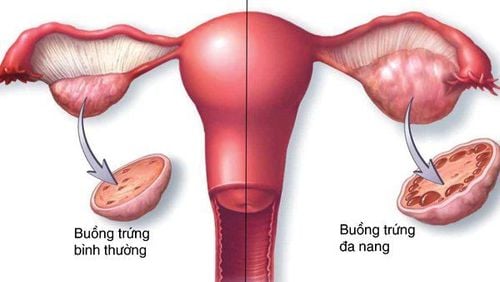
Ovarian cyst according to IOTA is a part of the ovary or tumor arising from an adnexa whose features on ultrasound are inconsistent with the functional picture of a normal ovary. Classification of ovarian cysts according to IOTA, using the benign - malignant assessment model of ovarian cysts according to IOTA helps to detect ovarian cysts early.
IOTA stands for International Ovarian Tumor Analysis Group, this is an organization specialized in ovarian cancer diagnosis, belonging to the International Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ISUOG), established in 1999. Up to now. , IOTA is a reputable organization that has published many valuable studies on ultrasound assessment of ovarian tumors.
1. Why is it necessary to evaluate ovarian cysts according to IOTA?
Ovarian cyst is one of the common gynecological diseases in women, the disease has poor clinical symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose and detect the disease early.Currently, there are many diagnostic techniques (ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, ...) to help detect and treat ovarian cysts at the earliest possible stage, with the expectation of specificity. High chemoradiation reduces costly diagnostic tools and complications, sensitivity and specificity, and screening techniques minimize false-positive and false-negative results that falsify tumor diagnosis.
Ultrasound assessment of ovarian cysts according to IOTA plays a pioneering and important role in predicting the risk of benign - malignant tumors. Ultrasound, if only stopping at detecting ovarian cancer, is not enough and should be directed to the diagnosis of benign or malignant tumors. Distinguishing benign from malignant tumors optimizes treatment and improves prognosis.
However, ultrasound requires a systematic and standardized diagnostic approach to help diagnose early and accurately, contributing to improved prognosis. In addition, it is necessary to unify descriptive terms and diagnostic criteria on ultrasound.
Pelvic ultrasound assessment of ovarian cysts according to IOTA aims to identify and classify benign and malignant tumors. In particular, vaginal ultrasound is the first choice because of its high sensitivity. This is a dynamic technique that interacts with the tumor with surrounding structures. A transabdominal ultrasound is indicated when the pelvic structure is altered because the tumor extends beyond the pelvis, or a transvaginal ultrasound cannot be performed.
During pelvic examination, IOTA-based vaginal ultrasonography for ovarian cysts is promoted in high-risk women for further early detection of ovarian cysts.
Vaginal ultrasound identifies early imaging changes and detects abnormalities, while physical examination is inconclusive. Ultrasound is the first step in finding ovarian cysts or as the second step after screening in high-risk women.
Imaging index and contrast-enhanced ultrasound help detect sonographic changes, neoplasms and predict metastasis - tumor stage.
Ultrasound and IOTA classification of ovarian cysts increase the sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of ovarian cysts. Assessment of the malignancy risk of ovarian cysts according to IOTA is a solution in cases where the tumor is difficult to classify, thereby helping to reduce the number of difficult-to-classify cases requiring magnetic resonance imaging.
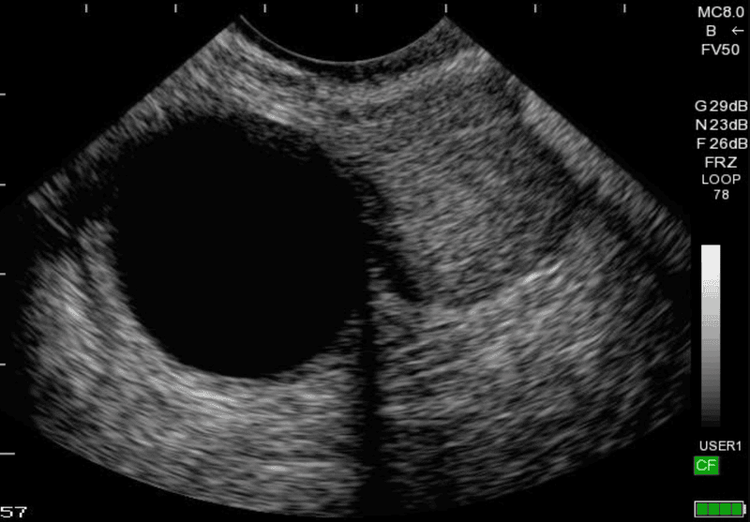
Siêu âm đánh giá u nang buồng trứng theo IOTA
2. Definition of ovarian cyst according to IOTA and descriptive terms on ultrasound
Definition of ovarian cyst according to IOTA, tumor is a part of the ovary or arising from an adnexa whose features on ultrasound are not consistent with the functional picture of the normal ovary.
In the ultrasound diagnosis of ovarian cysts according to IOTA, it is necessary to agree on the terms describing ovarian tumors as follows:
Components in the cyst: echoes empty, hemorrhagic, poor, opaque, mixed. Solid, dermoid, bud: The solid is a dense echogenic structure, suggesting the presence of parenchyma. The dermoid tumor has a benign character and is not counted as a solid part. The bud is a solid tissue from the wall of the cyst that protrudes into the lumen of the cyst, with a height of > 3mm. In the ultrasound diagnosis of ovarian cysts according to IOTA it is necessary to distinguish between buds and clots using the transducer push technique to view internal displacement. Color Doppler ultrasonography shows solid vascular solids within. If it cannot be distinguished, it is considered as solid tissue. In addition, it is also necessary to differentiate shoots from endometriomas, which are deposits of endometriosis that are not shoots. Tumor wall: Tumor inner wall with buds or solid parts <3mm; The image beyond the border is irregular. Complete and incomplete septum: In the IOTA diagnostic ultrasound, the complete septum is a thin band of tissue that runs across the lumen of the cyst, from one medial margin to the opposite medial margin. The incomplete septum is a thin band of tissue that runs across the lumen of the cyst, from one inner wall to the opposite, and is incomplete in several sections. Back shadow: Ultrasonic rays are lost after passing through a structure. Tumor size: Tumor size was measured in 3 vertical directions: top and bottom, front and back and horizontally.
3. Classification of ovarian cysts according to IOTA
Classification of ovarian cysts according to IOTA is divided into the following:
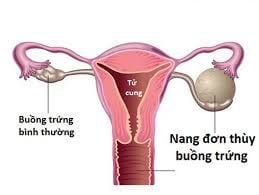
Single-lobed cyst: Cyst has a single lobe shape, no septum, no solid tissue or no buds. Single-lobed cyst - solid: Cyst has the form of a lobe, with a solid part or at least one bud. Polyloblastic cyst: Cyst with at least one wall, no solid component, and no buds. The septum is a poorly echogenic line that originates from the inner wall of the cyst and travels to the opposite wall. Polylobed - solid cyst: Cyst is multilobed, has at least one wall, has a solid part or at least one bud. Solid tumor: Solid tumor or solid component >80%. The classification of ovarian cysts according to IOTA and the rate of malignancy is as follows:
One-lobed cyst: the rate of malignancy is 0.6%. Multilobed cyst: the rate of malignancy is 10%. Single-lobed cyst - solid: the rate of malignancy is 37%. Multilobed - solid cyst: the rate of malignancy is 43%. Solid tumor: malignancy rate is 65%.
U nang buồng trứng theo IOTA, khối u là một phần thuộc buồng trứng
4. Ultrasound assessment of benign - malignant ovarian cysts according to IOTA
4.1 Using simple rules to diagnose benign and malignant ovarian cysts according to IOTA
Simple Rules for diagnosing and classifying benign - malignant ovarian cysts according to IOTA as follows:
Benign tumors:
Single-lobed cysts with solid diameter < 7mm With dorsal shadow Multi-lobed tumors smooth wall <100mm Low perfusion (grade 1) Malignant neoplasm:
Solid tumor with irregular margins Abdominal fluid More than 4 shoots Multilobe solid tumor irregular border >100mm Heavy perfusion (grade 4) Benign classification The malignancy of ovarian cysts according to IOTA using a simple rule has a high sensitivity of >96% and a high specificity of 88%. However, in some cases, simple rules do not help distinguish malignant and benign characteristics.
4.2 IOTA . malignancy risk assessment models
IOTA's main prediction models (including model LR1 and LR2) all show good and superior diagnostic performance, compared with previous algorithms.
The LR1 model for evaluating ovarian cysts according to IOTA includes the following criteria:
Abdominal fluid Flowing shoots Largest diameter of solid component Irregular inner wall of cyst Dorsal shadow Largest diameter of tumor Degree perfusion Solid tumor In addition, the patient's age, personal history of ovarian cancer, abdominal pain.
LR2 model for evaluating ovarian cysts according to IOTA includes the following criteria:
Abdominal fluid Flowing shoots Largest diameter of solid component Irregular inner wall of cyst With dorsal shadow Patient age LR2 model is used used to evaluate the risk of tumor malignancy when a simple rule cannot be used with a sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 69%.
In addition, the assessment of the risk of ovarian cyst malignancy according to IOTA also has the ADNEX (Assessment of Different NEoplasias in the adneXa) model. This is a more accurate model that helps distinguish between different subtypes of ovarian cysts. ADNEX is the first model to help distinguish between benign ovarian cysts and 4 types of malignant ovarian cysts, including:
Benign cyst Borderline tumor Early stage primary ovarian cyst (I) Ovarian cyst primary ovarian late stage (II-IV) Metastatic secondary ovarian cyst The risk assessment of ovarian cyst malignancy according to IOTA according to the ADNEX model using 3 clinical criteria: age, CA-125 ( U/ml), examination unit (oncology center or general hospital) and 6 ultrasound criteria including:
Largest diameter of tumor Size of solid More than 10 lobes Number of buds With shadow Back Abdominal fluid The risk assessment of ovarian cysts according to IOTA according to the ADNEX model has the advantage of being applicable to all tumors: gastric cancer metastasis to the ovary, malignant borderline tumor, fibroma Ovarian cyst, ovarian metastatic breast cancer...
Ultrasound assessment of ovarian cysts according to IOTA not only helps in early detection of tumors but also determines the risk of benign - malignant tumors, thereby supporting for treatment and disease prognosis.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been and continues to be fully equipped with modern diagnostic facilities such as: PET/CT, SPECT/CT, MRI, ultrasound..., blood marrow test , histopathology, immunohistochemistry, genetic testing, molecular biology tests to diagnose diseases.
After having an accurate diagnosis of the disease and stage, the patient will be consulted to choose the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. The treatment process is always closely coordinated with many specialties: Diagnostic Imaging, Biochemistry, Immunology, Cardiology, Stem Cell and Gene Technology; Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Endocrinology, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Psychology, Department of Nutrition... to bring the highest efficiency and comfort to the patient. After undergoing the treatment phase, the patient will also be monitored and re-examined to determine whether the treatment is effective or not. Especially, now to improve service quality, Vinmec also deploys an ovarian cancer screening package that can help customers detect cancer early before there are no symptoms, bringing a better prognosis. treatment and high chances of recovery.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.